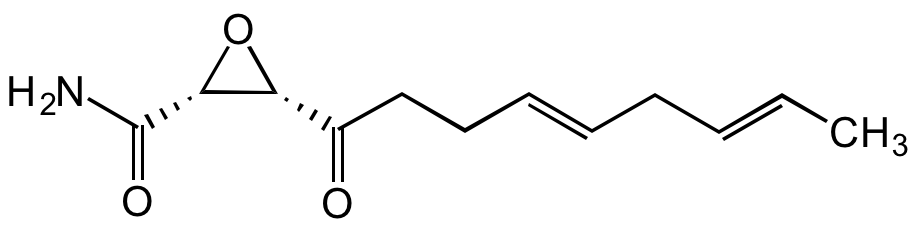
Chemical Structure
Cerulenin [17397-89-6]

AG-CN2-0513
Overview
- SupplierAdipoGen Life Sciences
- Product NameCerulenin [17397-89-6]
- Delivery Days Customer10
- CAS Number17397-89-6
- CertificationResearch Use Only
- Estimated Purity>98%
- Hazard InformationWarning
- Molecular FormulaC12H17NO3
- Molecular Weight223.3
- Scientific DescriptionAntibiotic and antifungal compound. Inhibitor of bacterial fatty acid synthesis (inhibits FabH, FabB and FabF condensation enzymes). Irreversible fatty acid synthase (FASN) inhibitor. Inhibits sterol and fatty acid biosynthesis. In fatty acid synthesis, reported to bind in equimolar ratio to beta-keto-acyl-ACP synthase, thus inhibiting protein acylation. In sterol synthesis, inhibits HMG-CoA synthetase activity. Palmitoylation (a post-translational lipidation) inhibitor. Anticancer agent. Apoptosis inducer in tumor cell lines, with upregulated expression and activity of fatty acid synthase (FAS). Shown to induce apoptosis via disruption of the interaction between AIF and Hexokinase II (HKII). Necroptosis inhibitor by blocking very long-chain fatty acids (VLCFA) synthesis and accumulation, which is important in the process of necroptosis (RIP1-dependent cell death). Also leads to profound weight loss and feeding inhibition in both high-fat diet wild type obese and leptin-deficient ob/ob mice. - Chemical. CAS: 17397-89-6. Formula: C12H17NO3. MW: 223.3. Isolated from Cephalosporium caerulens. Antibiotic and antifungal compound. Inhibitor of bacterial fatty acid synthesis (inhibits FabH, FabB and FabF condensation enzymes). Irreversible fatty acid synthase (FAS) inhibitor. Inhibits sterol and fatty acid biosynthesis. In fatty acid synthesis, reported to bind in equimolar ratio to beta-keto-acyl-ACP synthase, thus inhibiting protein acylation. In sterol synthesis, inhibits HMG-CoA synthetase activity. Palmitoylation (a post-translational lipidation) inhibitor. Anticancer agent. Apoptosis inducer in tumor cell lines, with upregulated expression and activity of fatty acid synthase (FAS). Shown to induce apoptosis via disruption of the interaction between AIF and Hexokinase II (HKII). Necroptosis inhibitor by blocking very long-chain fatty acids (VLCFA) synthesis and accumulation, which is important in the process of necroptosis (RIP1-dependent cell death). Also leads to profound weight loss and feeding inhibition in both high-fat diet wild type obese and leptin-deficient ob/ob mice.
- SMILESO=C(CC/C=C/C/C=C/C)[C@@H]1[C@H](C(N)=O)O1
- Storage Instruction-20°C,2°C to 8°C
- UNSPSC12352200
References
- Studies on cerulenin, 3. Isolation and physico-chemical properties of cerulenin: Y. Sato, et al.; J. Antibiot. (Tokyo) 200, 344 (1967)
