Chemical Structure
clasto-Lactacystin beta-lactone [154226-60-5]

AG-CN2-0442
Overview
- SupplierAdipoGen Life Sciences
- Product Nameclasto-Lactacystin beta-lactone [154226-60-5]
- Delivery Days Customer10
- CAS Number154226-60-5
- CertificationResearch Use Only
- Estimated Purity>95%
- Molecular FormulaC10H15NO4
- Molecular Weight213.2
- Scientific DescriptionChemical. CAS: 154226-60-5. Formula: C10H15NO4. MW: 213.2. Potent and selective irreversible and cell permeable proteasome inhibitor. Inhibits the chymotrypsin-like, trypsin-like and caspase-like peptidase activity of the proteasome. The active metabolite of lactacystin (Prod. No. AG-CN2-0104) with higher potency since it does not require hydrolysis in order to become cell permeable. Calpain and cathepsin inhibitor. Apoptosis inducer. Anticancer compound. Induces differentiation and inhibits cell cycle progression in several tumor cell lines. Induces neuritogenesis. Autophagy inducer. - Potent and selective irreversible and cell permeable proteasome inhibitor. Inhibits the chymotrypsin-like, trypsin-like and caspase-like peptidase activity of the proteasome. The active metabolite of lactacystin (Prod. No. AG-CN2-0104) with higher potency since it does not require hydrolysis in order to become cell permeable. Calpain and cathepsin inhibitor. Apoptosis inducer. Anticancer compound. Induces differentiation and inhibits cell cycle progression in several tumor cell lines. Induces neuritogenesis. Autophagy inducer.
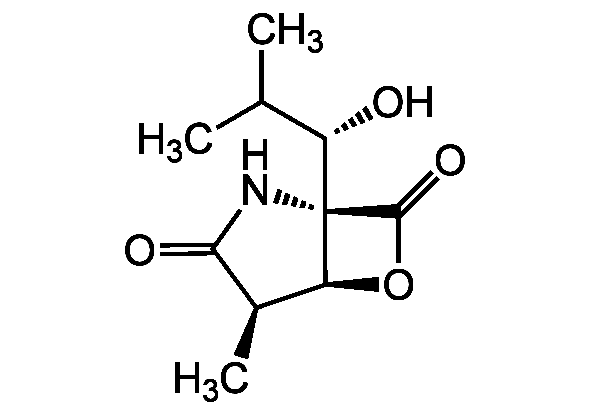
- SMILESCC(C)[C@H](O)C12NC(=O)[C@H](C)[C@@H]1OC2=O
- Storage Instruction-20°C,2°C to 8°C
- UNSPSC12352200
References
- Inhibition of proteasome activities and subunit-specific amino-terminal threonine modification by lactacystin: G. Fenteany, et al.; Science 268, 726 (1995)
- Lactacystin and clasto-lactacystin beta-lactone modify multiple proteasome beta-subunits and inhibit intracellular protein degradation and major histocompatibility complex class I antigen presentation: A. Craiu, et al.; J. Biol. Chem. 272, 56 (1997)
- Mechanistic studies on the inactivation of the proteasome by lactacystin in cultured cells: L.R. Dick, et al.; J. Biol. Chem. 272, 182 (1997)
- Lactacystin, proteasome function, and cell fate: G. Fenteany & S.L. Schreiber; J. Biol. Chem. 273, 8545 (1998) (Review)
- Prediction of the mechanism of action of omuralide (clasto-lactacystin beta-lactone) on human cathepsin A based on a structural model of the yeast proteasome beta5/PRE2-subunit/omuralide complex: S. Aikawa, et al.; Biochim. Biophys. Acta 1764, 1372 (2006)
- Importance of the different proteolytic sites of the proteasome and the efficacy of inhibitors varies with the protein substrate: A.F. Kisselev, et al.; J. Biol. Chem. 281, 8582 (2006)
- Effect of proteasome inhibitor clasto-lactacystin-beta-lactone on the proteome of the haloarchaeon Haloferax volcanii: P.A. Kirkland, et al.; Microbiology 153, 2271 (2007)
