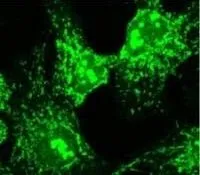
ICC/IF analysis of HeLa cells using GTX22913 COPA antibody.
COPA antibody
GTX22913
ApplicationsImmunoFluorescence, ImmunoPrecipitation, Western Blot, ImmunoCytoChemistry
Product group Antibodies
ReactivityHuman, Primate, Rat
TargetCopa
Overview
- SupplierGeneTex
- Product NameCOPA antibody
- Delivery Days Customer9
- Application Supplier NoteWB: 1 microg/ml. ICC/IF: 3 microg/ml. *Optimal dilutions/concentrations should be determined by the researcher.Not tested in other applications.
- ApplicationsImmunoFluorescence, ImmunoPrecipitation, Western Blot, ImmunoCytoChemistry
- CertificationResearch Use Only
- ClonalityPolyclonal
- Concentration1 mg/ml
- ConjugateUnconjugated
- Gene ID304978
- Target nameCopa
- Target descriptionCOPI coat complex subunit alpha
- Target synonymscoatomer protein complex subunit alpha; coatomer subunit alpha
- HostRabbit
- IsotypeIgG
- Scientific DescriptionCoatomer proteins are involved in regulating transport between the endoplasmic reticulum (ER) and the Golgi complex and in intra-Golgi transport. There exist two coatomer-protein mechanisms (COPI and COPII) and although they have mechanistic parallels, they are molecularly distinct. The COPI coat is comprised of seven subunits (alpha-, beta-, beta-, gamma-, delta-, epsilon-, and zeta-COP) in a complex called coatomer. Assembly of the coatomer (COPI) onto non-clathrin coated vesicles is regulated by ADP-ribosylation factor (ARF). Vesicle formation, budding, fusion, and disassembly is dependent on GDP-GTP exchange, COPI, and ARF. COPI has been shown to facilitate retrograde intracellular transport from the ER to the Golgi complex. By contrast, COPII facilitates anterograde transport between these subcellular organelles. COPII has been shown to be independently and selectively recruited to the ER relative to COPI subunits.
- ReactivityHuman, Primate, Rat
- Storage Instruction-20°C or -80°C,2°C to 8°C
- UNSPSC12352203
References
- Death-receptor activation halts clathrin-dependent endocytosis. Austin CD et al., 2006 Jul 5, Proc Natl Acad Sci U S ARead more
