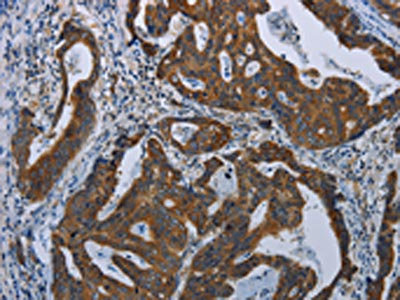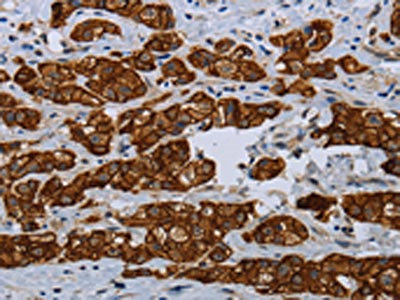
The image on the left is immunohistochemistry of paraffin-embedded Human breast cancer tissue using CSB-PA127808(COX6B2 Antibody) at dilution 1/35, on the right is treated with fusion protein. (Original magnification: x200)
COX6B2 Antibody
CSB-PA127808
ApplicationsWestern Blot, ELISA, ImmunoHistoChemistry
Product group Antibodies
ReactivityHuman, Mouse
TargetCOX6B2
Overview
- SupplierCusabio
- Product NameCOX6B2 Antibody
- Delivery Days Customer20
- ApplicationsWestern Blot, ELISA, ImmunoHistoChemistry
- CertificationResearch Use Only
- ClonalityPolyclonal
- ConjugateUnconjugated
- Gene ID125965
- Target nameCOX6B2
- Target descriptioncytochrome c oxidase subunit 6B2
- Target synonymscancer/testis antigen 59; COX VIb-2; COXVIB2; CT59; cytochrome c oxidase subunit 6B2; cytochrome c oxidase subunit VIb polypeptide 2 (testis); cytochrome c oxidase subunit VIb, testes-specific
- HostRabbit
- IsotypeIgG
- Protein IDQ6YFQ2
- Protein NameCytochrome c oxidase subunit 6B2
- Scientific DescriptionCytochrome c oxidase is the terminal enzyme of the electron transfer chain in aerobic bacteria as well as in the mitochondria of plants and animals. Bacterial cytochrome c oxidases are composed of three different subunits and include two hemes a and two copper atoms as prosthetic groups. The enzyme from eukaryotes is more complex and includes three subunits encoded on mitochondrial DNA, which are the homologues of the subunits of the bacterial enzyme, and in addition contains a number of subunits encoded in the nucleus. It is generally agreed that the mitochondrially coded subunits with their associated prosthetic groups are the functional core of the enzyme. The role of the nuclear coded subunits in cytochrome c oxidase function remains a matter of conjecture. cytochrome c oxidase subunit VIb polypeptide 2 Connects the two COX monomers into the physiological dimeric form.
- ReactivityHuman, Mouse
- Storage Instruction-20°C or -80°C
- UNSPSC12352203