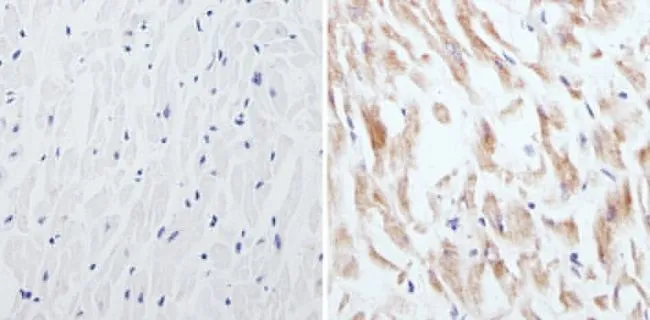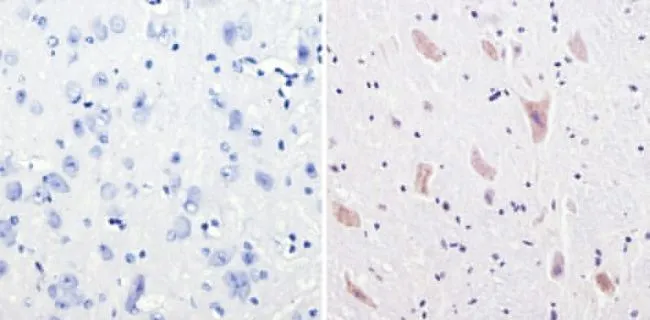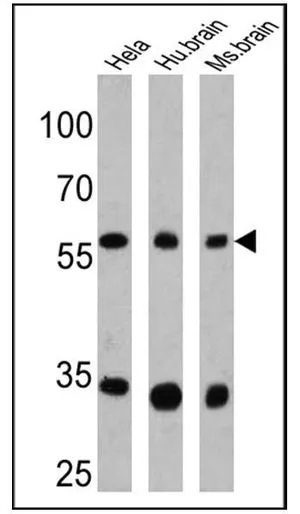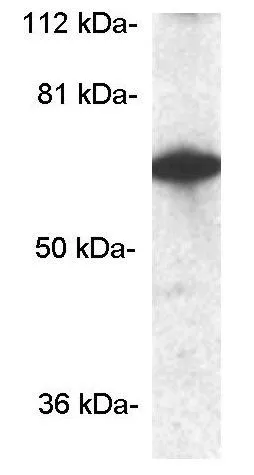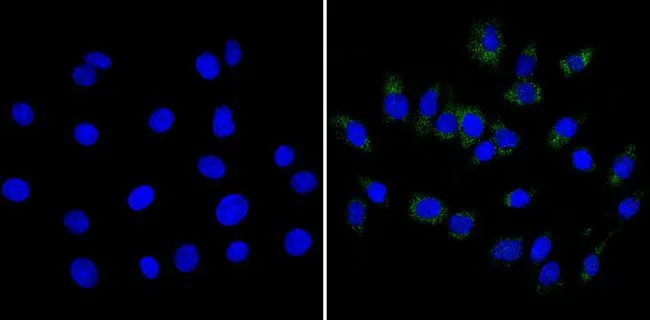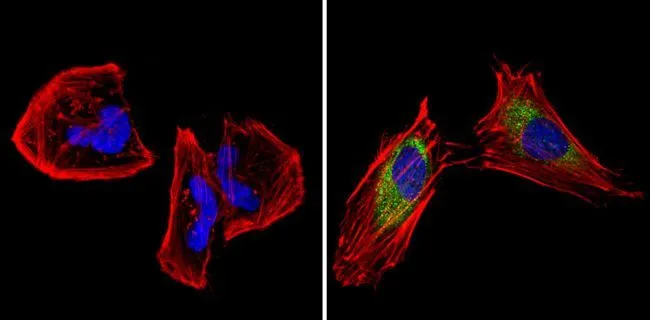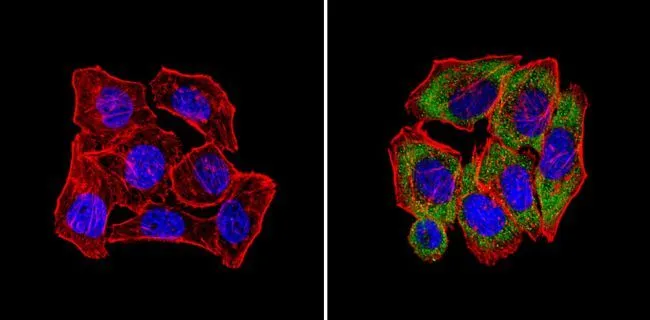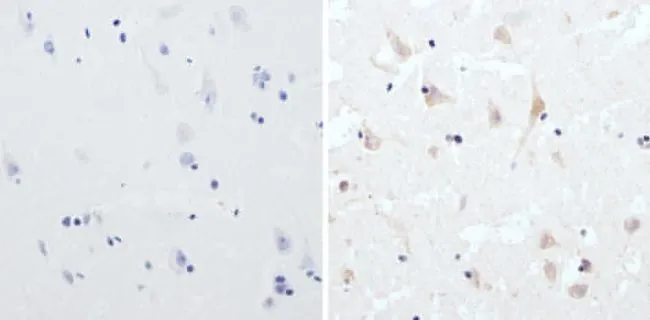
IHC-P analysis of human brain tissue using GTX23465 CPEB1 antibody. Right : Primary antibody Left : Negative control without primary antibody Antigen retrieval : 10mM sodium citrate (pH 6.0), microwaved for 8-15 min Dilution : 1:100
CPEB1 antibody
GTX23465
ApplicationsImmunoFluorescence, ImmunoPrecipitation, Western Blot, ImmunoCytoChemistry, ImmunoHistoChemistry, ImmunoHistoChemistry Paraffin
Product group Antibodies
ReactivityHuman, Mouse, Rat
TargetCpeb1
Overview
- SupplierGeneTex
- Product NameCPEB1 antibody
- Delivery Days Customer9
- Application Supplier NoteWB: 1:100-1:1000. ICC/IF: 1:50-1:500. IHC-P: 1:50-1:500. *Optimal dilutions/concentrations should be determined by the researcher.Not tested in other applications.
- ApplicationsImmunoFluorescence, ImmunoPrecipitation, Western Blot, ImmunoCytoChemistry, ImmunoHistoChemistry, ImmunoHistoChemistry Paraffin
- CertificationResearch Use Only
- ClonalityPolyclonal
- Concentration1 mg/ml
- ConjugateUnconjugated
- Gene ID12877
- Target nameCpeb1
- Target descriptioncytoplasmic polyadenylation element binding protein 1
- Target synonymsAU024112; Cpeb; CPE-binding protein 1; Cpe-bp1; cytoplasmic polyadenylation element-binding protein 1; mCPEB; mCpeb-1
- HostRabbit
- IsotypeIgG
- Protein IDP70166
- Protein NameCytoplasmic polyadenylation element-binding protein 1
- Scientific DescriptionThe regulated translation of messenger RNA is essential for cell-cycle progression, establishment of the body plan during early development, and modulation of key activities in the central nervous system. Cytoplasmic polyadenylation, which is one mechanism of controlling translation, is driven by CPEB (cytoplasmic polyadenylation element binding protein), a highly conserved, sequence-specific RNA-binding protein that binds to the cytoplasmic polyadenylation element, and modulates translational repression and mRNA localization. In both vertebrates and invertebrates, the expression of several maternal mRNAs is regulated by cytoplasmic polyadenylation. In Xenopus oocytes, where most of the biochemical details of this process have been examined, polyadenylation is controlled by CPEB. Early metazoan development is programmed by maternal mRNAs inherited by the egg at the time of fertilization. These mRNAs are not translated en masse at any one time or at any one place, but instead their expression is regulated both temporally and spatially. Mammalian neurons, particularly in the synapto-dendritic compartment, also contain localized mRNAs such as that encoding alpha-CaMKII. Here, synaptic activation drives local translation, an event that is involved in synaptic plasticity and possibly long-term memory storage. Synaptic translation of alpha-CaMKII mRNA also appears to be controlled by CPEB, which is enriched in the postsynaptic density. Therefore, CPEB-controlled local translation may influence such seemingly disparate processes as the cell cycle and synaptic plasticity.
- ReactivityHuman, Mouse, Rat
- Storage Instruction-20°C or -80°C,2°C to 8°C
- UNSPSC12352203