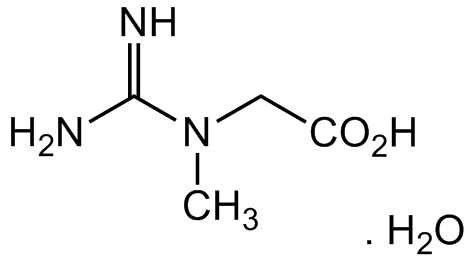
Chemical Structure
Creatine . monohydrate [6020-87-7] [6020-87-7]
AG-CR1-3679
CAS Number6020-87-7
Product group Chemicals
Estimated Purity>98%
Molecular Weight131.1 . 18.0
Overview
- SupplierAdipoGen Life Sciences
- Product NameCreatine . monohydrate [6020-87-7] [6020-87-7]
- Delivery Days Customer10
- CAS Number6020-87-7
- CertificationResearch Use Only
- Estimated Purity>98%
- Molecular FormulaC4H9N3O2 . H2O
- Molecular Weight131.1 . 18.0
- Scientific DescriptionA nitrogenous organic acid that occurs naturally in vertebrates. Can be acquired through dietary consumption or formed from L-arginine, glycine and L-methionine in a multi-step reaction that occurs in the kidney and liver. High-energy reservoir for the rapid regeneration of ATP. Its main role is to facilitate recycling of adenosine triphosphate (ATP) primarily in muscle and brain tissue via the action of creatine kinase(s). Supplementation is investigated for the use in myopathies and enhancement of sports performance, primarily by increasing muscle mass. It is also investigated as a treatment of neuromuscular diseases, where it may aid in neuroprotection and by improving the cellular bioenergetic state. Antioxidant compound. Thermogenesis enhancer in beige adipocytes. Creatine cycling is important for thermogenesis and an altered creatine cycle could lead to obesity. Enhancer of energy expenditure through stimulation of mitochondrial ATP turnover. - Chemical. CAS: 6020-87-7. Formula: C4H9N3O2 . H2O. MW: 131.1 . 18.0. Synthetic. A nitrogenous organic acid that occurs naturally in vertebrates. Can be acquired through dietary consumption or formed from L-arginine, glycine and L-methionine in a multi-step reaction that occurs in the kidney and liver. High-energy reservoir for the rapid regeneration of ATP. Its main role is to facilitate recycling of adenosine triphosphate (ATP) primarily in muscle and brain tissue via the action of creatine kinase(s). Supplementation is investigated for the use in myopathies and enhancement of sports performance, primarily by increasing muscle mass. It is also investigated as a treatment of neuromuscular diseases, where it may aid in neuroprotection and by improving the cellular bioenergetic state. Antioxidant compound. Thermogenesis enhancer in beige adipocytes. Creatine cycling is important for thermogenesis and an altered creatine cycle could lead to obesity. Enhancer of energy expenditure through stimulation of mitochondrial ATP turnover.
- SMILESNC(N(C)CC(O)=O)=N.O
- Storage Instruction2°C to 8°C
- UNSPSC12352200

![Creatine monohydrate [6020-87-7] [6020-87-7]](https://www.targetmol.com/group3/M00/03/00/CgoaEGY7Q_aEIgqMAAAAAM5cF9U877.png)