Chemical Structure
Curvularin
AG-CN2-0147
Overview
- SupplierAdipoGen Life Sciences
- Product NameCurvularin
- Delivery Days Customer10
- CAS Number10140-70-2
- CertificationResearch Use Only
- Estimated Purity>95%
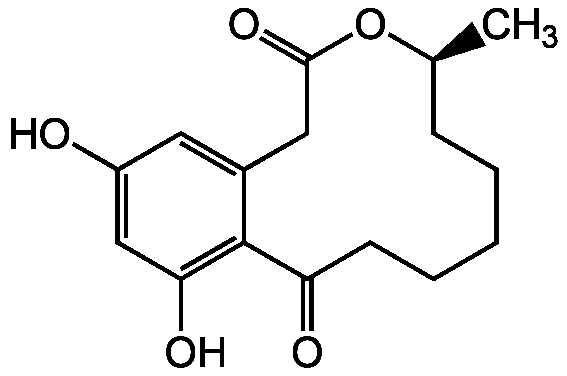
- Molecular FormulaC16H20O5
- Molecular Weight292.3
- Scientific DescriptionAntibiotic [1]. Antiprotozoal [1]. Antifungal and phytotoxic compound [1, 6]. Anti-inflammatory [7]. TGF-beta signaling inhibitor [8] Anticancer compound [2, 9]. Inhibits expression of inducible nitric oxide synthase (iNOS; NOSII) [4, 5]. Cell division inhibitor [3]. Acetylcholinesterase (AChE) inhibitor [9]. - Chemical. CAS: 10140-70-2. Formula: C16H20O5. MW: 292.3. Isolated from Penicillium sp. FKI-1938 Antibiotic. Antiprotozoal. Antifungal and phytotoxic compound. Anti-inflammatory. TGF-beta signaling inhibitor Anticancer compound. Inhibits expression of inducible nitric oxide synthase (iNOS; NOSII). Cell division inhibitor. Acetylcholinesterase (AChE) inhibitor.
- SMILESC[C@H]1CCCCCC(=O)C2=C(O)C=C(O)C=C2CC(=O)O1
- Storage Instruction-20°C,2°C to 8°C
- UNSPSC12352200

![Curvularin [10140-70-2]](https://www.targetmol.com/group3/M00/38/06/CgoaEWayVVeEXGR5AAAAANUMhR8069.png)