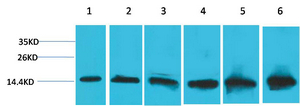
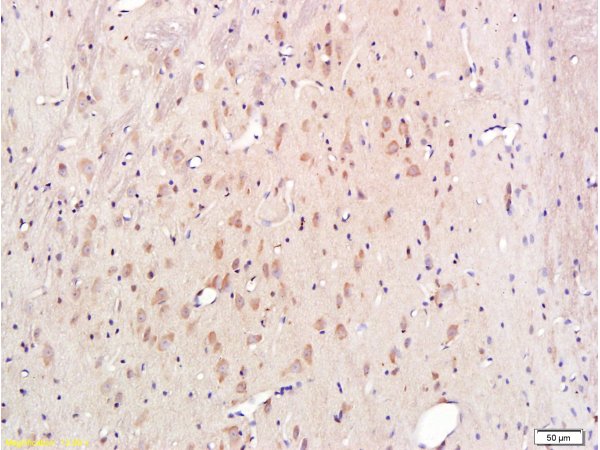
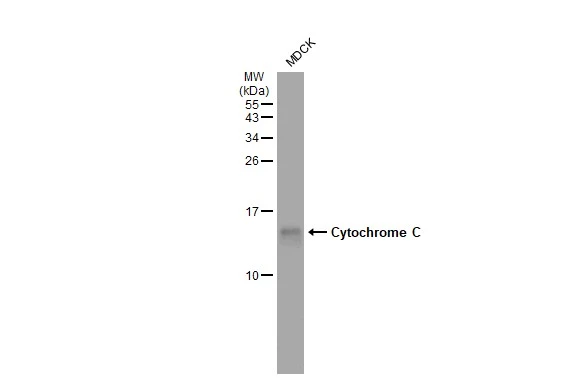
Cytochrome C (Mitochondrial Marker)(6H2.B4), 0.2mg/mL [26628-22-8]
BNUB0184
ApplicationsFlow Cytometry, ImmunoFluorescence
Product group Antibodies
ReactivityBovine, Human, Mouse, Rat
TargetCYCS
Overview
- SupplierBiotium
- Product NameCytochrome C (Mitochondrial Marker)(6H2.B4), 0.2mg/mL [26628-22-8]
- Delivery Days Customer9
- ApplicationsFlow Cytometry, ImmunoFluorescence
- CAS Number26628-22-8
- CertificationResearch Use Only
- ClonalityMonoclonal
- Clone ID6H2.B4
- Concentration0.2 mg/ml
- Gene ID54205
- Target nameCYCS
- Target descriptioncytochrome c, somatic
- Target synonymsCYC, HCS, THC4, cytochrome c
- HostMouse
- IsotypeIgG1
- Protein IDP99999
- Protein NameCytochrome c
- Scientific DescriptionCytochrome c is a well-characterized mobile electron transport protein that is essential to energy conversion in all aerobic organisms. In mammalian cells, this highly conserved protein is normally localized to the mitochondrial inter-membrane space. More recent studies have identified cytosolic cytochrome c as a factor necessary for activation of apoptosis. During apoptosis, cytochrome c is trans-located from the mitochondrial membrane to the cytosol, where it is required for activation of caspase-3 (CPP32). Overexpression of Bcl-2 has been shown to prevent the translocation of cytochrome c, thereby blocking the apoptotic process. Overexpression of Bax has been shown to induce the release of cytochrome c and to induce cell death. The release of cytochrome c from the mitochondria is thought to trigger an apoptotic cascade, whereby Apaf-1 binds to Apaf-3 (caspase-9) in a cytochrome c-dependent manner, leading to caspase-9 cleavage of caspase-3.
- SourceAnimal
- ReactivityBovine, Human, Mouse, Rat
- Storage Instruction2°C to 8°C,RT
- UNSPSC41116161