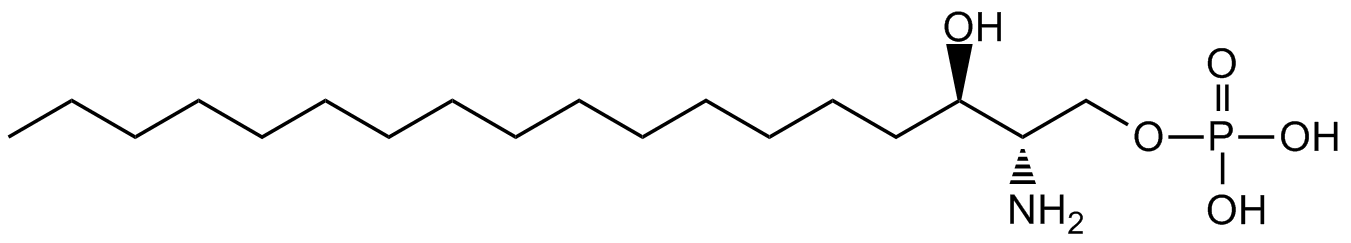
Chemical Structure
D-erythro-Dihydrosphingosine 1-phosphate [19794-97-9]

AG-CR1-0005
Overview
- SupplierAdipoGen Life Sciences
- Product NameD-erythro-Dihydrosphingosine 1-phosphate [19794-97-9]
- Delivery Days Customer10
- CAS Number19794-97-9
- CertificationResearch Use Only
- Estimated Purity>98%
- Molecular FormulaC18H40NO5P
- Molecular Weight381.5
- Scientific DescriptionChemical. CAS: 19794-97-9. Formula: C18H40NO5P. MW: 381.5. Saturated analog of sphingosine 1-phosphate (1-SP1). Ligand for sphingosine 1-phosphate (S1P/EDG) receptors. Negative control for intracellular effects of sphingosine 1-phosphate. Induces chemotaxis. Antifibrotic. - Saturated analog of sphingosine 1-phosphate (1-SP1). Ligand for sphingosine 1-phosphate (S1P/EDG) receptors [1,3]. Negative control for intracellular effects of sphingosine 1-phosphate [1]. Induces chemotaxis [2]. Antifibrotic [4].
- SMILESCCCCCCCCCCCCCCC[C@@H](O)[C@@H](N)COP(O)(O)=O
- Storage Instruction-20°C,2°C to 8°C
- UNSPSC12352200
References
- Dual actions of sphingosine-1-phosphate: extracellular through the Gi-coupled receptor Edg-1 and intracellular to regulate proliferation and survival: J.R. van Brocklyn, et al.; J. Cell Biol. 142, 229 (1998)
- Sphingosine 1-phosphate stimulates cell migration through a G(i)-coupled cell surface receptor. Potential involvement in angiogenesis: F. Wang, et al.; JBC 274, 35343 (1999)
- Sphingosine 1-phosphate-induced cell rounding and neurite retraction are mediated by the G protein-coupled receptor H218: J.R. van Brocklyn, et al. JBC 274, 4626 (1999)
- Dihydrosphingosine 1-phosphate has a potent antifibrotic effect in scleroderma fibroblasts via normalization of phosphatase and tensin homolog levels: Arthritis Rheum. 62, 2117 (2010)
