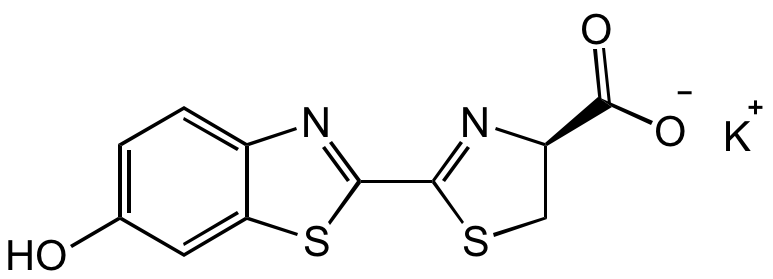
Chemical Structure
D-Luciferin potassium salt [115144-35-9]
CDX-L0009
CAS Number115144-35-9
Product group Chemicals
Estimated Purity>95%
Molecular Weight318.41
Overview
- SupplierChemodex
- Product NameD-Luciferin potassium salt [115144-35-9]
- Delivery Days Customer2
- CAS Number115144-35-9
- CertificationResearch Use Only
- Estimated Purity>95%
- Molecular FormulaC11H7KN2O3S2
- Molecular Weight318.41
- Scientific DescriptionChemical. CAS: 115144-35-9. Formula: C11H7KN2O3S2. MW: 318.41. D-Luciferin is the most popular and versatile bioluminescent substrate. Firefly luciferase produces light by the ATP-dependent oxidation (Mg2+ as cofactor) of luciferin. It emits a characteristic yellow-green emission in the presence of oxygen, which shifts to red light in vivo. The 560nm chemiluminescence from this reaction peaks within seconds, with light output that is proportional to luciferase activity when luciferin and ATP are present in excess. Firefly luciferase has long been conjugated to antibodies and used as a label in immunoassays using luciferin as the substrate for detection. One particular advantage to the enzyme is that there is low endogenous luciferase activity in mammalian tissues besides its high sensitivity. Through the utilization of ATP, the reaction can be further used to indicate the presence of energy or life in order to function as a life-death stain. Luciferin is a common reagent used throughout the biotechnology field and specifically for in vivo imaging. Luciferase labeled tumor cells, stem cells or infectious diseases are often inoculated into research animals such as rats or mice for investigation. The injection of luciferin allows for the real-time, non-invasive monitoring of disease progression and/or drug efficacy in these model systems through Bioluminescence Imaging (BLI). Luciferin is also commonly used for in vitro research, including luciferase and ATP assays, gene reporter assays, high throughput sequencing and various contamination assays (e.g. determine cell viability and bacteria counting). - D-Luciferin is the most popular and versatile bioluminescent substrate. Firefly luciferase produces light by the ATP-dependent oxidation (Mg2+ as cofactor) of luciferin. It emits a characteristic yellow-green emission in the presence of oxygen, which shifts to red light in vivo. The 560nm chemiluminescence from this reaction peaks within seconds, with light output that is proportional to luciferase activity when luciferin and ATP are present in excess. Firefly luciferase has long been conjugated to antibodies and used as a label in immunoassays using luciferin as the substrate for detection. One particular advantage to the enzyme is that there is low endogenous luciferase activity in mammalian tissues besides its high sensitivity. Through the utilization of ATP, the reaction can be further used to indicate the presence of energy or life in order to function as a life-death stain. Luciferin is a common reagent used throughout the biotechnology field and specifically for in vivo imaging. Luciferase labeled tumor cells, stem cells or infectious diseases are often inoculated into research animals such as rats or mice for investigation. The injection of luciferin allows for the real-time, non-invasive monitoring of disease progression and/or drug efficacy in these model systems through Bioluminescence Imaging (BLI). Luciferin is also commonly used for in vitro research, including luciferase and ATP assays, gene reporter assays, high throughput sequencing and various contamination assays (e.g. determine cell viability and bacteria counting).
- SMILESOC1=CC=C2C(SC(C3=N[C@@H](C([O-])=O)CS3)=N2)=C1.[K+]
- Storage Instruction-20°C,2°C to 8°C
- UNSPSC12162000


![D-Luciferin potassium [115144-35-9]](https://www.targetmol.com/group3/M00/02/C9/CgoaEGY7Pe-EQ9OKAAAAAMjZ_Nw803.png)