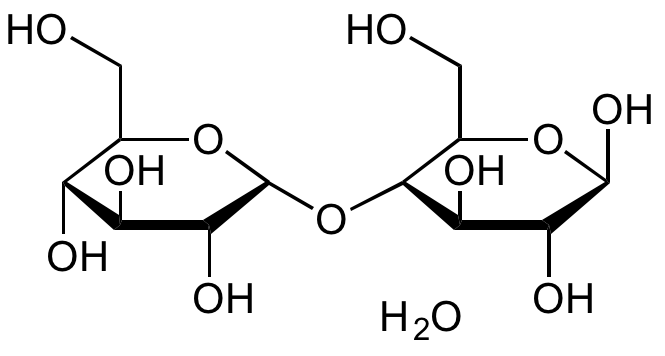
Chemical Structure
D-(+)-Maltose monohydrate [6363-53-7] [6363-53-7]
CDX-M0226
CAS Number6363-53-7
Product group Chemicals
Estimated Purity>90%
Molecular Weight342.29 . 18.02
Overview
- SupplierChemodex
- Product NameD-(+)-Maltose monohydrate [6363-53-7] [6363-53-7]
- Delivery Days Customer2
- CAS Number6363-53-7
- CertificationResearch Use Only
- Estimated Purity>90%
- Molecular FormulaC12H22O11 . H2O
- Molecular Weight342.29 . 18.02
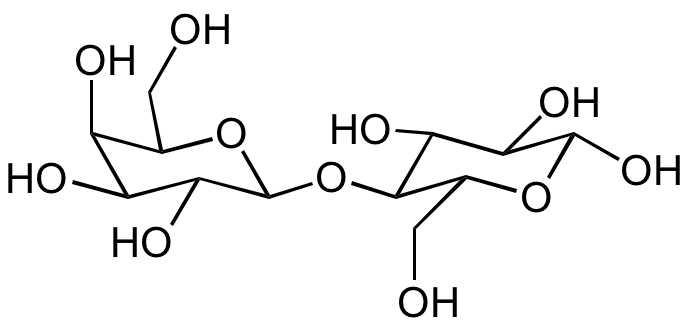
- Scientific DescriptionChemical. CAS: 6363-53-7. Formula: C12H22O11 . H2O. MW: 342.29 . 18.02. D-(+)-Maltose monohydrate is a component of starch and glycogen. It is a sugar composed of 2 alpha-D-glucose molecules coupled by an alpha(1 to 4) glycosidic bond. It is a reducing sugar with one anomeric carbon not linked in an anomeric bond. It contains a hemiacetal function and can mutarotate. Maltose is one product generated from starch and glycogen by the action of alpha-amylase. Maltose can be further hydrolyzed to glucose by the action of alpha-glucosidase (maltase), an enzyme commonly found in yeast and many other sources. It is called malt sugar when it is formed in fermenting grains during the production of alcoholic beverages. D-(+)-Maltose monohydrate is used as a sweetener with about one-third the sweetness of sucrose and as a nutrient in culture media. It is used in pharmaceutical formulations and as a parenteral supplement of sugar for diabetics. In addition it can be used in cell culture studies or may be employed as standard for the alpha-amylase and invertase assays. - D-(+)-Maltose monohydrate is a component of starch and glycogen. It is a sugar composed of 2 alpha-D-glucose molecules coupled by an alpha(1 to 4) glycosidic bond. It is a reducing sugar with one anomeric carbon not linked in an anomeric bond. It contains a hemiacetal function and can mutarotate. Maltose is one product generated from starch and glycogen by the action of alpha-amylase. Maltose can be further hydrolyzed to glucose by the action of alpha-glucosidase (maltase), an enzyme commonly found in yeast and many other sources. It is called malt sugar when it is formed in fermenting grains during the production of alcoholic beverages. D-(+)-Maltose monohydrate is used as a sweetener with about one-third the sweetness of sucrose and as a nutrient in culture media. It is used in pharmaceutical formulations and as a parenteral supplement of sugar for diabetics. In addition it can be used in cell culture studies or may be employed as standard for the alpha-amylase and invertase assays.
- SMILESOC[C@@H]1[C@@H](O)[C@H](O)[C@@H](O)[C@@H](O[C@@H]2[C@@H](CO)O[C@@H](O)[C@H](O)[C@H]2O)O1.O
- Storage InstructionRT
- UNSPSC12352200



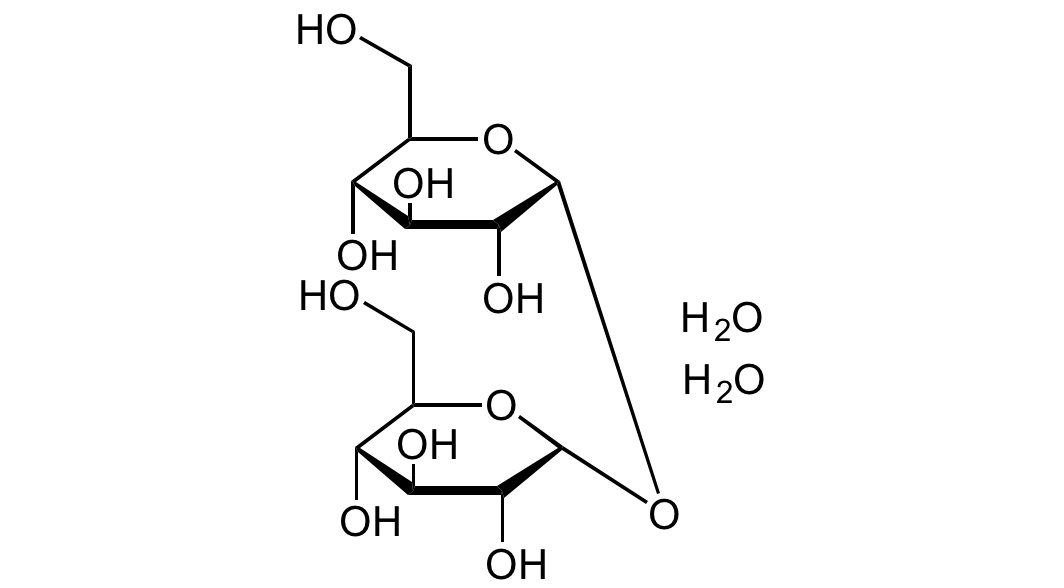
![Maltose monohydrate [6363-53-7] [6363-53-7]](https://www.targetmol.com/group3/M00/02/41/CgoaEGY7LfCENocaAAAAAM4PmfM185.png)