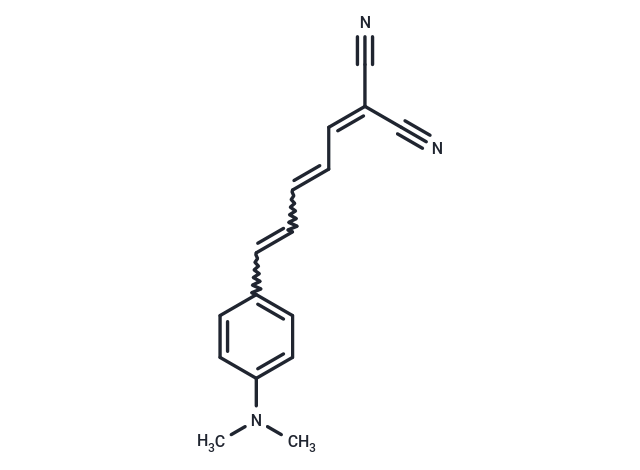
DCDAPH (Compound 2c), a novel smart near-infrared fluorescence (NIRF) probe, efficiently detects beta-amyloid (Abeta) plaques with an excitation/emission wavelength (lambda ex /lambda em) of 597/665 nm in PBS. It demonstrates high affinity for Abeta aggregates, exhibiting a dissociation constant (Kd) of 27 nM and an inhibition constant (Ki) of 37 nM. Furthermore, DCDAPH exhibits favorable blood-brain barrier permeability, qualifying it as a suitable agent for both in vitro and in vivo detection of Abeta plaques [1].