Chemical Structure
Dichloroacetate [CDA] . sodium salt [2156-56-1] [2156-56-1]
AG-CR1-3684
CAS Number2156-56-1
Product group Chemicals
Estimated Purity>98%
Molecular Weight127.9 . 23.0
Overview
- SupplierAdipoGen Life Sciences
- Product NameDichloroacetate [CDA] . sodium salt [2156-56-1] [2156-56-1]
- Delivery Days Customer10
- CAS Number2156-56-1
- CertificationResearch Use Only
- Estimated Purity>98%
- Hazard InformationWarning
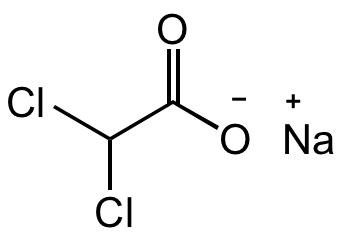
- Molecular FormulaC2HCl2O2 . Na
- Molecular Weight127.9 . 23.0
- Scientific DescriptionChemical. CAS: 2156-56-1. Formula: C2HCl2O2 . Na. MW: 127.9 . 23.0. Synthetic. Analog of acetic acid. Mitochondrial pyruvate dehydrogenase kinase (PDK) inhibitor, consequently activating pyruvate dehydrogenase (PDH). Decreases glycolysis. Shifts pyruvate metabolism from glycolysis and lactate production to glucose oxidation in the mitochondria. Antitumor agent. Decreases tumor growth in vitro and in vivo. Induces mitochondrial-dependent apoptosis. Useful agent for immunometabolism research. Glucose entering the cell is metabolized by glycolysis to pyruvate. Most of the pyruvate in non-cancerous cells enters the mitochondria under aerobic conditions and a small fraction is metabolized to lactate. PDH in mitochondria converts pyruvate into acetyl-CoA, which enters the TCA cycle. In cancer cells, the oxidative (mitochondrial) pathway of glucose utilization is suppressed and most of the pyruvate is converted into lactate (Warburg effect). The relative activities of LDH and PDH therefore determine the fate of pyruvate. PDK inhibits PDH through phosphorylation and regulates its activities, resulting in suppression of the TCA cycle and mitochondrial respiration. This renders PDK a promising target for the treatment of various cancers. - Mitochondrial pyruvate dehydrogenase kinase (PDK) inhibitor, consequently activating pyruvate dehydrogenase (PDH). Decreases glycolysis. Shifts pyruvate metabolism from glycolysis and lactate production to glucose oxidation in the mitochondria. Antitumor agent. Decreases tumor growth in vitro and in vivo. Induces mitochondrial-dependent apoptosis. Useful agent for immunometabolism research. Glucose entering the cell is metabolized by glycolysis to pyruvate. Most of the pyruvate in non-cancerous cells enters the mitochondria under aerobic conditions and a small fraction is metabolized to lactate. PDH in mitochondria converts pyruvate into acetyl-CoA, which enters the TCA cycle. In cancer cells, the oxidative (mitochondrial) pathway of glucose utilization is suppressed and most of the pyruvate is converted into lactate (Warburg effect). The relative activities of LDH and PDH therefore determine the fate of pyruvate. PDK inhibits PDH through phosphorylation and regulates its activities, resulting in suppression of the TCA cycle and mitochondrial respiration. This renders PDK a promising target for the treatment of various cancers.
- SMILESClC(Cl)C([O-])=O.[Na+]
- Storage Instruction2°C to 8°C,RT
- UNSPSC12352200


![Sodium dichloroacetate [2156-56-1] [2156-56-1]](https://www.targetmol.com/group3/M00/03/0D/CgoaEWY7QD2EHsUOAAAAAGy2hdA033.png)