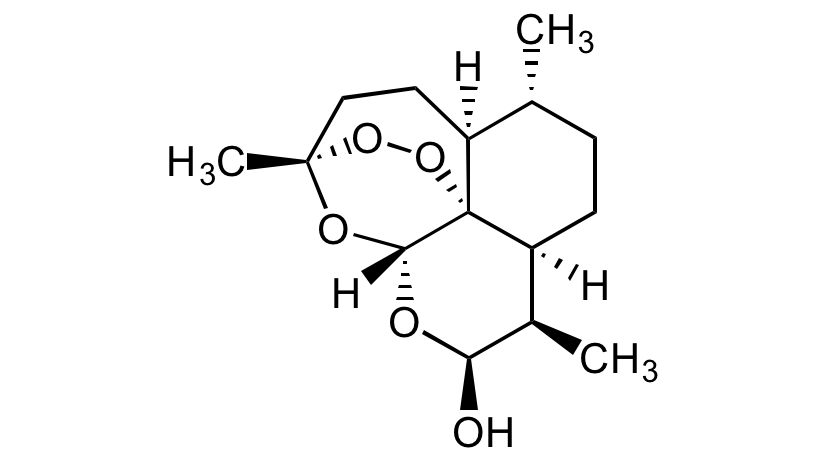
Chemical Structure
Dihydroartemisinin [71939-50-9]

AG-CN2-0468
Overview
- SupplierAdipoGen Life Sciences
- Product NameDihydroartemisinin [71939-50-9]
- Delivery Days Customer10
- CAS Number71939-50-9
- CertificationResearch Use Only
- Estimated Purity>98%
- Molecular FormulaC15H24O5
- Molecular Weight284.3
- Scientific DescriptionActive metabolite of artemisinin. Anti-malaria (Plasmodium). Anti-schistosoma. Apoptosis inducer. Anti-cancer. Anti-inflammatory Inhibits production of tumor necrosis factor-alpha (TNF-alpha), interleukin-6 (IL-6), monocyte chemotactic protein-1 (MCP-1) and nitric oxide (NO). Autophagy inducer. Functional ARX inhibitor. Enhancer of GABAA signalling. Targets Gephyrin. Sown to have anti-SARS-CoV-2 activity with an EC50 of 13.31 +/- 1.24microM, and beeing potentially useful in the treatment of COVID-19. - Chemical. CAS: 71939-50-9. Formula: C15H24O5. MW: 284.3. Isolated from Artemisia annua. Active metabolite of artemisinin. Anti-malaria (Plasmodium). Anti-schistosoma. Apoptosis inducer. Anti-cancer. Anti-inflammatory Inhibits production of tumor necrosis factor-alpha (TNF-alpha), interleukin-6 (IL-6), monocyte chemotactic protein-1 (MCP-1) and nitric oxide (NO). Autophagy inducer.
- SMILES[H][C@@]12CC[C@@H](C)[C@]3([H])CC[C@]4(C)OO[C@@]13[C@]([H])(O[C@H](O)[C@@H]2C)O4
- Storage Instruction-20°C,2°C to 8°C
- UNSPSC12352200
References
- Qinghaosu (artemisinin): an antimalarial drug from China: D.L. Klayman; Science 228, 1049 (1985)
- Comparison of in vivo and in vitro antimalarial activity of artemisinin, dihydroartemisinin and sodium artesunate in the Plasmodium berghei-rodent model: C. J. Janse, et al.; Int. J. Parasitol. 24, 589 (1994)
- The development of the antimalarial drugs with new type of chemical structure--qinghaosu and dihydroqinghaosu: Y. Tu; SE Asian J. Trop. Med. Publ. Health 35, 250 (2004)
- Artemisinin induces apoptosis in human cancer cells: N.P. Singh & H.C. Lai; Anticancer Res. 24, 2277 (2004)
- Artemisinin attenuates lipopolysaccharide-stimulated proinflammatory responses by inhibiting NF-kappaB pathway in microglia cells: C. Zhu, et al.; PLoS One 7, e35125 (2012)
- In vivo activity of dihydroartemisinin against Schistosoma mansoni schistosomula in mice: H.J. Li, et al.; SE Asian J. Trop. Med. Publ. Health 44, 379 (2013)
- Differential effect of artemisinin against cancer cell lines: M. Tilaoui, et al.; Nat. Prod. Bioprospect. 4, 189 (2014)
- Dihydroartemisinin supresses inflammation and fibrosis in bleomycine-induced pulmonary fibrosis in rats: D. Yang, et al.; Int. J. Clin. Exp. Pathol. 8, 1270 (2015)
- Dihydroartemisinin increases temozolomide efficacy in glioma cells by inducing autophagy: Z.S. Zhang, et al.; Oncol. Lett. 10, 379 (2015)
