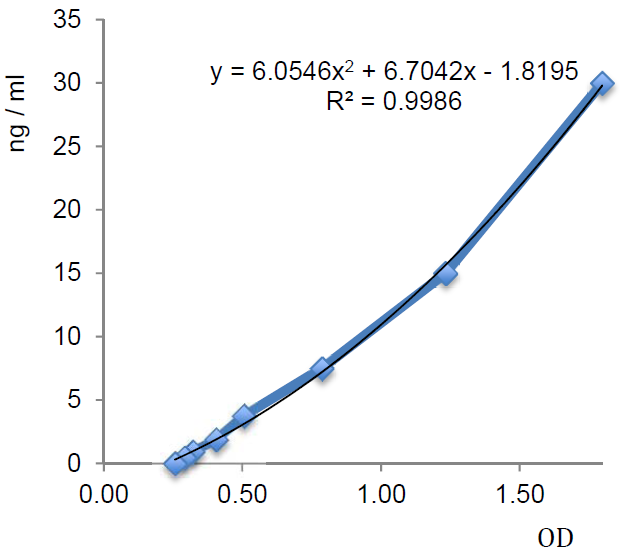
Standard Curve
DLK1, Soluble (human) ELISA Kit
AG-45A-0032Y
ReactivityHuman
Product group Assays
Overview
- SupplierAdipoGen Life Sciences
- Product NameDLK1, Soluble (human) ELISA Kit
- Delivery Days Customer10
- ApplicationsELISA
- Assay Detection Range0.47 to 30ng/ml
- Assay Sensitivity336pg/ml
- CertificationResearch Use Only
- Protein IDP80370
- Protein NameProtein delta homolog 1
- Scientific DescriptionELISA Assay. Detects human DLK1. Does not cross-react with human DLL1 or human DNER. Colorimetric assay. Sample Types: Cell Culture Supernatant, Serum. Range: 0.47 to 30ng/ml. Sensitivity: 336pg/ml. The Notch signaling pathway is essential for appropriate cell differentiation and cell fate decisions. DLK1 (Protein delta homolog 1; Preadipocyte factor 1; Pref-1) is a regulator of adipocyte differentiation found in serum and urine. DLK1 might be a decoy ligand. Serum or plasma levels of soluble DLK1 affect negatively or positively adipogenesis and control mesenchymal cell fate. DLK1 is frequently upregulated in myelodysplastic syndrome (MDS) patients compared to non-leukemic individuals. - The Notch signaling pathway is essential for appropriate cell differentiation and cell fate decisions. DLK1 (Protein delta homolog 1; Preadipocyte factor 1; Pref-1) is a regulator of adipocyte differentiation found in serum and urine. DLK1 shifts nutrient metabolism towards FA oxidation. Serum or plasma levels of soluble DLK1 affect negatively or positively adipogenesis and control mesenchymal cell fate. DLK1 is frequently upregulated in myelodysplastic syndrome (MDS) patients compared to non-leukemic individuals. Fetus is the source of maternal circulating DLK1 during pregnancy. It has been recently reported that measurement of DLK1 in maternal blood may be a valuable method for diagnosing human disorders associated with impaired DLK1 expression, and to predict poor intrauterine growth and complications of pregnancy.
- ReactivityHuman
- Storage Instruction2°C to 8°C
- UNSPSC41116100
- SpeciesHuman