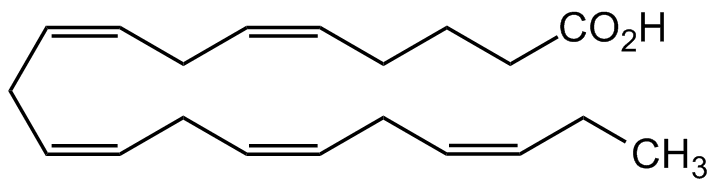
Chemical Structure
Eicosapentaenoic acid [10417-94-4] [10417-94-4]
CDX-C0465
CAS Number10417-94-4
Product group Chemicals
Estimated Purity>97%
Molecular Weight302.45
Overview
- SupplierChemodex
- Product NameEicosapentaenoic acid [10417-94-4] [10417-94-4]
- Delivery Days Customer2
- CAS Number10417-94-4
- CertificationResearch Use Only
- Estimated Purity>97%
- Molecular FormulaC20H30O2
- Molecular Weight302.45
- Scientific DescriptionChemical. CAS: 10417-94-4. Formula: C20H30O2. MW: 302.45. Eicosapentaenoic acid (EPA) is one of several omega-3 fatty acids abundantly available in marine organisms. EPA has antioxidant, anti-inflammatory, cardiovascular, anticancer and antiobesity activities. EPA is a polyunsaturated fatty acid (PUFA) that acts as a precursor. When omega-3 fatty acids, like EAP is incorporated into the cell membrane, it induces production of eicosanoids and resolvins which then compete with arachidonic acid for the activity of phospholipase A2. Fatty acids are then liberated inside the cytosol and via cyclooxygenase-2 (COX-2), 5-lipoxygenase and thromboxane synthetase activity get degraded into prostaglandins, leukotrienes, and thromboxanes, responsible for decreasing the synthesis of eicosanoids derived from arachidonic acid (AA), like PGI2, PGF2alpha, PGE2, and LTB4 (pro-inflammatory) and increase the synthesis of LT5, thromboxane-3 and PGE3 (weak effects on inflammation). It has been shown that omega-3 fatty acids potentially exert their anti-inflammatory effect via toll-like receptor 4 (TLR4) pathway and G-protein coupled receptor 120 (GPR120) pathway to inhibit the NF-kappaB and consequently the inflammatory cascade. EPA plays a role in mediating inflammatory processes and immunomodulation for both innate and acquired immune systems and might be interesting vor cytokine storm prevention. EPA has been shown to stimulate ERK1/2 and C/EBPbeta phosphorylation, and induces demethylation of CpG island B in U937 leukemia cells. Attenuates proliferation of U9137 cells, and induces cell cycle arrest and apoptosis in pancreatic cells in vitro. EPA binds and activates PPARalpha and enhances insulin sensitivity. It also has shown positive impacts on gut microbiota flora, leading to its antiobesity and anti-inflammatory activities. EPA has been shown to offer protection against coronary heart disease, thrombosis, ischemic brain injury, scaly dermatitis and some inflammatory diseases. - Eicosapentaenoic acid (EPA) is one of several omega-3 fatty acids abundantly available in marine organisms. EPA has antioxidant, anti-inflammatory, cardiovascular, anticancer and antiobesity activities. EPA is a polyunsaturated fatty acid (PUFA) that acts as a precursor. When omega-3 fatty acids, like EAP is incorporated into the cell membrane, it induces production of eicosanoids and resolvins which then compete with arachidonic acid for the activity of phospholipase A2. Fatty acids are then liberated inside the cytosol and via cyclooxygenase-2 (COX-2), 5-lipoxygenase and thromboxane synthetase activity get degraded into prostaglandins, leukotrienes, and thromboxanes, responsible for decreasing the synthesis of eicosanoids derived from arachidonic acid (AA), like PGI2, PGF2alpha, PGE2, and LTB4 (pro-inflammatory) and increase the synthesis of LT5, thromboxane-3 and PGE3 (weak effects on inflammation). It has been shown that omega-3 fatty acids potentially exert their anti-inflammatory effect via toll-like receptor 4 (TLR4) pathway and G-protein coupled receptor 120 (GPR120) pathway to inhibit the NF-kappaB and consequently the inflammatory cascade. EPA plays a role in mediating inflammatory processes and immunomodulation for both innate and acquired immune systems and might be interesting vor cytokine storm prevention. EPA has been shown to stimulate ERK1/2 and C/EBPbeta phosphorylation, and induces demethylation of CpG island B in U937 leukemia cells. Attenuates proliferation of U9137 cells, and induces cell cycle arrest and apoptosis in pancreatic cells in vitro. EPA binds and activates PPARalpha and enhances insulin sensitivity. It also has shown positive impacts on gut microbiota flora, leading to its antiobesity and anti-inflammatory activities. EPA has been shown to offer protection against coronary heart disease, thrombosis, ischemic brain injury, scaly dermatitis and some inflammatory diseases.
- SMILESCC/C=C\C/C=C\C/C=C\C/C=C\C/C=C\CCCC(O)=O
- Storage Instruction-20°C,2°C to 8°C
- UNSPSC12352200


![Eicosapentaenoic Acid [10417-94-4] [10417-94-4]](https://www.targetmol.com/group3/M00/38/02/CgoaEWayVRyEGCj7AAAAAO1C_KI259.png)