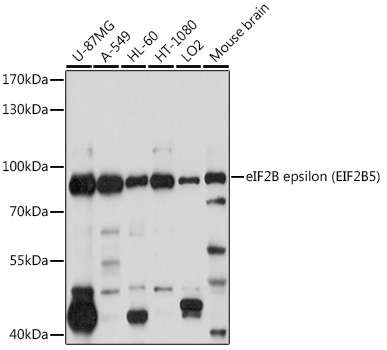
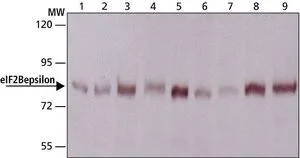
EIF2B epsilon (phospho Ser539) antibody
GTX24775
ApplicationsWestern Blot
Product group Antibodies
ReactivityHuman, Mouse, Rat
TargetEIF2B5
Overview
- SupplierGeneTex
- Product NameEIF2B epsilon (phospho Ser539) antibody
- Delivery Days Customer9
- ApplicationsWestern Blot
- CertificationResearch Use Only
- ClonalityPolyclonal
- ConjugateUnconjugated
- Gene ID8893
- Target nameEIF2B5
- Target descriptioneukaryotic translation initiation factor 2B subunit epsilon
- Target synonymsCACH, CLE, EIF-2B, EIF2Bepsilon, LVWM, VWM5, translation initiation factor eIF2B subunit epsilon, eIF-2B GDP-GTP exchange factor subunit epsilon, eIF2B GDP-GTP exchange factor subunit epsilon, eukaryotic translation initiation factor 2B, subunit 5 epsilon, 82kDa, translation initiation factor eIF-2B subunit epsilon
- HostRabbit
- IsotypeIgG
- Protein IDQ13144
- Protein NameTranslation initiation factor eIF2B subunit epsilon
- Scientific DescriptionThis gene encodes one of five subunits of eukaryotic translation initiation factor 2B (EIF2B), a GTP exchange factor for eukaryotic initiation factor 2 and an essential regulator for protein synthesis. Mutations in this gene and the genes encoding other EIF2B subunits have been associated with leukoencephalopathy with vanishing white matter. [provided by RefSeq, Nov 2009]
- ReactivityHuman, Mouse, Rat
- Storage Instruction-20°C or -80°C,2°C to 8°C
- UNSPSC12352203
References
- Tardif N, Salles J, Guillet C, et al. Muscle ectopic fat deposition contributes to anabolic resistance in obese sarcopenic old rats through eIF2α activation. Aging Cell. 2014,13(6):1001-11. doi: 10.1111/acel.12263Read this paper
- Mascher H, Ekblom B, Rooyackers O, et al. Enhanced rates of muscle protein synthesis and elevated mTOR signalling following endurance exercise in human subjects. Acta Physiol (Oxf). 2011,202(2):175-84. doi: 10.1111/j.1748-1716.2011.02274.xRead this paper
- Burd NA, Holwerda AM, Selby KC, et al. Resistance exercise volume affects myofibrillar protein synthesis and anabolic signalling molecule phosphorylation in young men. J Physiol. 2010,588(Pt 16):3119-30. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.2010.192856Read this paper
- Fry CS, Glynn EL, Drummond MJ, et al. Blood flow restriction exercise stimulates mTORC1 signaling and muscle protein synthesis in older men. J Appl Physiol (1985). 2010,108(5):1199-209. doi: 10.1152/japplphysiol.01266.2009Read this paper
- Drummond MJ, Fry CS, Glynn EL, et al. Rapamycin administration in humans blocks the contraction-induced increase in skeletal muscle protein synthesis. J Physiol. 2009,587(Pt 7):1535-46. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.2008.163816Read this paper
- Moore DR, Robinson MJ, Fry JL, et al. Ingested protein dose response of muscle and albumin protein synthesis after resistance exercise in young men. Am J Clin Nutr. 2009,89(1):161-8. doi: 10.3945/ajcn.2008.26401Read this paper
- Glover EI, Oates BR, Tang JE, et al. Resistance exercise decreases eIF2Bepsilon phosphorylation and potentiates the feeding-induced stimulation of p70S6K1 and rpS6 in young men. Am J Physiol Regul Integr Comp Physiol. 2008,295(2):R604-10. doi: 10.1152/ajpregu.00097.2008Read this paper