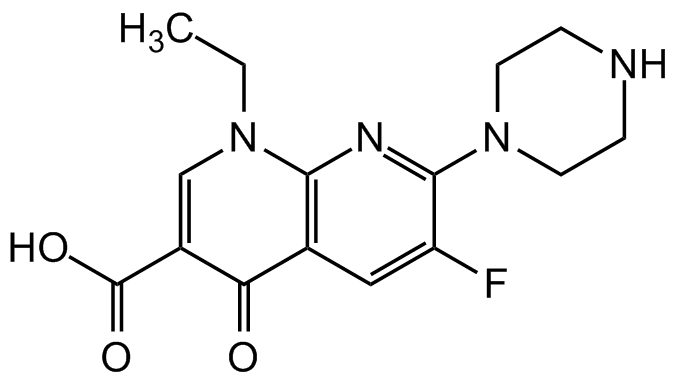
Chemical Structure
Enoxacin
AG-CR1-3539
CAS Number74011-58-8
Product group Chemicals
Estimated Purity>98%
Molecular Weight320.3
Overview
- SupplierAdipoGen Life Sciences
- Product NameEnoxacin
- Delivery Days Customer10
- CAS Number74011-58-8
- CertificationResearch Use Only
- Estimated Purity>98%
- Molecular FormulaC15H17FN4O3
- Molecular Weight320.3
- Scientific DescriptionChemical. CAS: 74011-58-8. Formula: C15H17FN4O3. MW: 320.3. Enoxacin is a cell permeable fluoroquinolone broad-spectrum antibacteral agent. It is active against clinical isolates of a variety of Gram-positive and Gram-negative bacteria. Fluoroquinolones are a group of broad-spectrum antibiotics that inhibit DNA synthesis. They prevent unwinding of double-stranded DNA by binding DNA gyrase or DNA topoisomerase IV, prevent the formation of single-stranded DNA and inhibit bacterial replication. Enoxacin is used to treat urinary tract infections and gonorrhea. Osteoclastogenesis inhibitor. Shown to decrease RANKL-induced JNK signaling and inhibiting osteoclast formation. Additionally, Enoxacin inhibits vacuolar H+ ATPase activity, preventing bone resorption. Enoxacin is a unique small molecule enhancer of microRNA (SMER) maturation. MicroRNAs (miRNAs) are small RNA molecules that regulate gene expression at the posttranscriptional level and are critical for many cellular pathways. The disruption of miRNAs and their processing machineries also contributes to the development of human tumors. The RNA interference (RNAi) represents the foundation underlying complex biological mechanisms that are dysregulated in many diseases. Enoxacin exerts an antiviral activity and could be a promising candidate for COVID-19 treatment through enhancing the RNAi pathway as an inflammation-free innate immune defense against viral infections and through inhibition of viral helicases. Shows antiviral activity against SARS-CoV-2 and MERS-CoV. Enoxacin enhances the production of miRNAs with tumor suppressor functions by binding to the miRNA biosynthesis protein TAR RNA-binding protein 2 (TRBP). Restoring the global expression of miRNAs by Enoxacin has been attributed to its anti-tumor properties. Enoxacin counteracts obesity by promoting thermogenic signaling and inducing oxidative metabolism in adipose tissue and skeletal muscle through miRNA-mediated regulation. Enoxacin increased lifespan in C. elegans by inhibiting miR-34-5p levels, interfering with the redox balance and promoting healthspan. - Enoxacin is a cell permeable fluoroquinolone broad-spectrum antibacterial agent. It is active against clinical isolates of a variety of Gram-positive and Gram-negative bacteria. Fluoroquinolones are a group of broad-spectrum antibiotics that inhibit DNA synthesis. They prevent unwinding of double-stranded DNA by binding DNA gyrase or DNA topoisomerase IV, prevent the formation of single-stranded DNA and inhibit bacterial replication. Enoxacin is used to treat urinary tract infections and gonorrhea. Osteoclastogenesis inhibitor. Shown to decrease RANKL-induced JNK signaling and inhibiting osteoclast formation. Additionally, Enoxacin inhibits vacuolar H+ ATPase activity, preventing bone resorption. Enoxacin is a unique small molecule enhancer of microRNA (SMER) maturation. MicroRNAs (miRNAs) are small RNA molecules that regulate gene expression at the posttranscriptional level and are critical for many cellular pathways. The disruption of miRNAs and their processing machineries also contributes to the development of human tumors. The RNA interference (RNAi) represents the foundation underlying complex biological mechanisms that are dysregulated in many diseases. Enoxacin exerts an antiviral activity and could be a promising candidate for COVID-19 treatment through enhancing the RNAi pathway as an inflammation-free innate immune defense against viral infections and through inhibition of viral helicases. Shows antiviral activity against SARS-CoV-2 and MERS-CoV. Enoxacin enhances the production of miRNAs with tumor suppressor functions by binding to the miRNA biosynthesis protein TAR RNA-binding protein 2 (TRBP). Restoring the global expression of miRNAs by Enoxacin has been attributed to its anti-tumor properties. Enoxacin counteracts obesity by promoting thermogenic signaling and inducing oxidative metabolism in adipose tissue and skeletal muscle through miRNA-mediated regulation. Enoxacin increased lifespan in C. elegans by inhibiting miR-34-5p levels, interfering with the redox balance and promoting healthspan.
- SMILESCCN(C=C(C(O)=O)C1=O)C2=C1C=C(F)C(N3CCNCC3)=N2
- Storage Instruction-20°C,2°C to 8°C
- UNSPSC12352200

![Enoxacin [74011-58-8]](https://www.targetmol.com/group3/M00/03/5B/CgoaEWY7SQyEBIn4AAAAAFhx5tY793.png)
