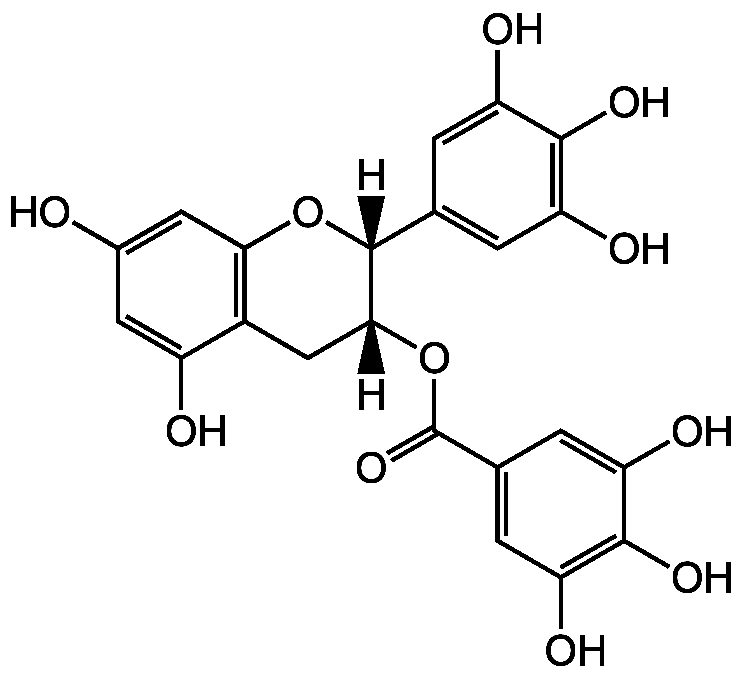
Chemical Structure
(-)-Epigallocatechin gallate [989-51-5]

AG-CN2-0063
Overview
- SupplierAdipoGen Life Sciences
- Product Name(-)-Epigallocatechin gallate [989-51-5]
- Delivery Days Customer10
- CAS Number989-51-5
- CertificationResearch Use Only
- Estimated Purity>98%
- Molecular FormulaC22H18O11
- Molecular Weight458.4
- Scientific DescriptionChemical. CAS: 989-51-5. Formula: C22H18O11. MW: 458.4. Isolated from green tea. Potent anticancer compound. Anti-angiogenic. VEGF, VE-cadherin phosphorylation, matrix metalloproteinase and urokinase-plasminogen activator (uPA) inhibitor. Anti-inflammatory. NF-kappaB inhibitor. Modulates chronic inflammatory diseases, such as type 2 diabetes, rheumatoid arthritis, inflammatory bowel disease. COX-2 and inducible nitric oxide synthase (iNOS; NOS II) inhibitor. Potent antioxidant. Protects cells from lipid peroxidation and DNA damage induced by reactive free radicals. Regulates cancer cell growth, proliferation, transformation, survival, angiogenesis, apoptosis, invasion and metastasis. Chemopreventive. Apoptosis inducer. Promotes cell cycle arrest. Modulates signal transduction pathways including JAK/STAT, MAPK, PI3K/AKT, Wnt and Notch. EGFR and HER-2 receptor signaling inhibitor. MAPKs and activator protein-1 inhibitor. mTOR suppressor. IGF-I signaling inhibitor. Proteasome inhibitor. Telomerase and DNA methyltransferase inhibitor. Selective and noncompetitive HAT inhibitor. Topoisomerase I and II inhibitor. Hedgehog signaling (Hh) modulator. PTCH and Gli1 inhibitor. Wnt signaling inhibitor. Neuroprotective. Activates HO-1 by the ARE/Nrf2 pathway, protecting neurons against oxidative damage. STAT-1 inhibitor. Shows preventive cardiovascular and metabolic (obesity, insulin resistance, hypertension and hypercholesterolemia) effects. Inhibits extracellular signal-related kinases (ERK), activates AMP-activated protein kinase (AMPK), modulates adipocyte marker proteins and down-regulates lipogenic enzymes as well as other potential targets. Fatty acid synthase (FAS) inhibitor. Autophagy stimulator. - Potent anticancer compound. Anti-angiogenic. VEGF, VE-cadherin phosphorylation, matrix metalloproteinase and urokinase-plasminogen activator (uPA) inhibitor. Anti-inflammatory. NF-kappaB inhibitor. Modulates chronic inflammatory diseases, such as type 2 diabetes, rheumatoid arthritis, inflammatory bowel disease. COX-2 and inducible nitric oxide synthase (iNOS; NOS II) inhibitor. Potent antioxidant. Protects cells from lipid peroxidation and DNA damage induced by reactive free radicals. Regulates cancer cell growth, proliferation, transformation, survival, angiogenesis, apoptosis, invasion and metastasis. Chemopreventive. Apoptosis inducer. Promotes cell cycle arrest. Modulates signal transduction pathways including JAK/STAT, MAPK, PI3K/AKT, Wnt and Notch. EGFR and HER-2 receptor signaling inhibitor. MAPKs and activator protein-1 inhibitor. Potent DYRK1A inhibitor (IC50=330nM). mTOR suppressor. IGF-I signaling inhibitor. Proteasome inhibitor. Telomerase and DNA methyltransferase inhibitor. Selective and noncompetitive HAT inhibitor. Topoisomerase I and II inhibitor. Hedgehog signaling (Hh) modulator. PTCH and Gli1 inhibitor. Wnt signaling inhibitor. Neuroprotective. Activates HO-1 by the ARE/Nrf2 pathway, protecting neurons against oxidative damage. STAT-1 inhibitor. Shows preventive cardiovascular and metabolic (obesity, insulin resistance, hypertension and hypercholesterolemia) effects. Inhibits extracellular signal-related kinases (ERK), activates AMP-activated protein kinase (AMPK), modulates adipocyte marker proteins and down-regulates lipogenic enzymes as well as other potential targets. Fatty acid synthase (FAS) inhibitor. Autophagy stimulator.
- SMILES[H][C@]1(CC2=C(O[C@]1([H])C1=CC(O)=C(O)C(O)=C1)C=C(O)C=C2O)OC(=O)C1=CC(O)=C(O)C(O)=C1
- Storage Instruction-20°C,2°C to 8°C
- UNSPSC12352200
References
- Molecular mechanisms underlying chemopreventive activities of anti-inflammatory phytochemicals: down-regulation of COX-2 and iNOS through suppression of NF-kappa B activation: Y.J. Surh, et al.; Mutat. Res. 480-481, 243 (2001) (Review)
- Targeting multiple signaling pathways by green tea polyphenol (-)-epigallocatechin-3-gallate: N. Khan, et al.; Cancer Res. 66, 2500 (2006) (Review)
- Inhibition of fatty acid synthase by polyphenols: W.X. Tian; Curr. Med. Chem. 13, 967 (2006) (Review)
- Green tea polyphenols as a natural tumour cell proteasome inhibitor: Q.P. Dou, et al.; Inflammopharmacology 16, 208 (2008) (Review)
- Chemoprevention with phytochemicals targeting inducible nitric oxide synthase: A. Murakami; Forum Nutr. 61, 193 (2009) (Review)
- Molecular basis for cancer chemoprevention by green tea polyphenol EGCG: H. Tachibana; Forum Nutr. 61, 156 (2009) (Review)
- Apoptosis by dietary agents for prevention and treatment of prostate cancer: N. Khan, et al.; Endocr. Relat. Cancer 17, R39 (2010) (Review)
- Targeting polyamines and biogenic amines by green tea epigallocatechin-3-gallate: E. Melgarejo, et al.; Amino Acids 38, 519 (2010) (Review)
- Green tea polyphenol epigallocatechin-3-gallate: inflammation and arthritis: R. Singh, et al.; Life Sci. 86, 907 (2010) (Review)
- Regulation of survival, proliferation, invasion, angiogenesis, and metastasis of tumor cells through modulation of inflammatory pathways by nutraceuticals: S.C. Gupta, et al.; Cancer Metastasis Rev. 29, 405 (2010) (Review)
