![Estrogen Receptor beta 1(ESR2/686), Biotin conjugate, 0.1mg/mL [26628-22-8] Estrogen Receptor beta 1(ESR2/686), Biotin conjugate, 0.1mg/mL [26628-22-8]](https://biotium.com/wp-content/uploads/2016/12/BNUB0686-0-1.jpg)
Estrogen Receptor beta 1(ESR2/686), Biotin conjugate, 0.1mg/mL [26628-22-8]
BNCB0686
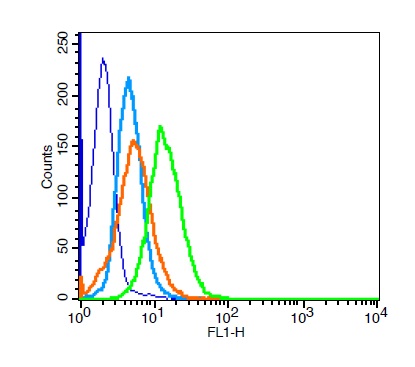
ApplicationsFlow Cytometry, ImmunoHistoChemistry, ImmunoHistoChemistry Paraffin
Product group Antibodies
ReactivityBovine, Human, Mouse
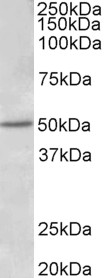
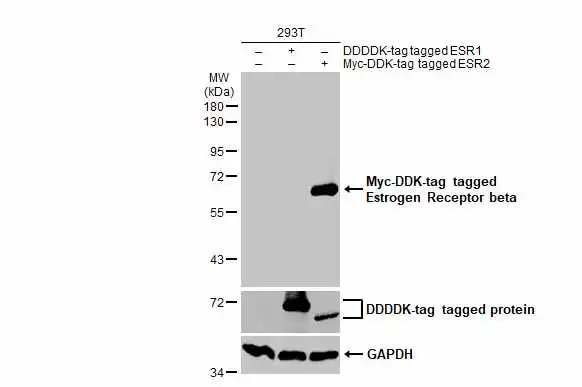
TargetESR2
Overview
- SupplierBiotium
- Product NameEstrogen Receptor beta 1(ESR2/686), Biotin conjugate, 0.1mg/mL [26628-22-8]
- Delivery Days Customer9
- ApplicationsFlow Cytometry, ImmunoHistoChemistry, ImmunoHistoChemistry Paraffin
- CAS Number26628-22-8
- CertificationResearch Use Only
- ClonalityMonoclonal
- Clone IDESR2/686
- Concentration0.1 mg/ml
- ConjugateBiotin
- Gene ID2100
- Target nameESR2
- Target descriptionestrogen receptor 2
- Target synonymsER-BETA, ESR-BETA, ESRB, ESTRB, Erb, NR3A2, ODG8, estrogen receptor beta, estrogen receptor beta 2, estrogen receptor beta 4, nuclear receptor subfamily 3 group A member 2, oestrogen receptor beta
- HostMouse
- IsotypeIgG2a
- Protein IDQ92731
- Protein NameEstrogen receptor beta
- Scientific DescriptionEstrogen receptors (ER) are members of the steroid/thyroid hormone receptor superfamily of ligand-activated transcription factors. Estrogen receptors, including ER-alpha and ER-beta, contain DNA binding and ligand binding domains and are critically involved in regulating the normal function of reproductive tissues. They are located in the nucleus, though some estrogen receptors associate with the cell surface membrane and can be rapidly activated by exposure of cells to estrogen. ER-alpha and ER-beta are differentially activated by various ligands. Receptor-ligand interactions trigger a cascade of events, including dissociation from heat shock proteins, receptor dimerization, phosphorylation and the association of the hormone activated receptor with specific regulatory elements in target genes. Evidence suggests that ER-alpha and ER-beta may be regulated by distinct mechanisms even though they share many functional characteristics.Primary antibodies are available purified, or with a selection of fluorescent CF® Dyes and other labels. CF® Dyes offer exceptional brightness and photostability. Note: Conjugates of blue fluorescent dyes like CF®405S and CF®405M are not recommended for detecting low abundance targets, because blue dyes have lower fluorescence and can give higher non-specific background than other dye colors.
- SourceAnimal
- ReactivityBovine, Human, Mouse
- Storage Instruction2°C to 8°C,RT
- UNSPSC41116161

![Estrogen Receptor beta 1(ESR2/686), Biotin conjugate, 0.1mg/mL [26628-22-8] Estrogen Receptor beta 1(ESR2/686), Biotin conjugate, 0.1mg/mL [26628-22-8]](https://biotium.com/wp-content/uploads/2016/12/BNUB0686-1-1.jpg)
![Estrogen Receptor beta 1(ESR2/686), Biotin conjugate, 0.1mg/mL [26628-22-8] Estrogen Receptor beta 1(ESR2/686), Biotin conjugate, 0.1mg/mL [26628-22-8]](https://biotium.com/wp-content/uploads/2016/12/BNUB0686-2-1.jpg)
![Estrogen Receptor beta 1(ESR2/686), Biotin conjugate, 0.1mg/mL [26628-22-8] Estrogen Receptor beta 1(ESR2/686), Biotin conjugate, 0.1mg/mL [26628-22-8]](https://biotium.com/wp-content/uploads/2016/12/BNUB0686-3-1.jpg)
![Estrogen Receptor beta 1(ESR2/686), Biotin conjugate, 0.1mg/mL [26628-22-8] Estrogen Receptor beta 1(ESR2/686), Biotin conjugate, 0.1mg/mL [26628-22-8]](https://biotium.com/wp-content/uploads/2016/12/BNUB0686-4-1.jpg)
![Estrogen Receptor beta 1(ESR2/686), Biotin conjugate, 0.1mg/mL [26628-22-8] Estrogen Receptor beta 1(ESR2/686), Biotin conjugate, 0.1mg/mL [26628-22-8]](https://biotium.com/wp-content/uploads/2016/12/BNUB0686-5-1.jpg)