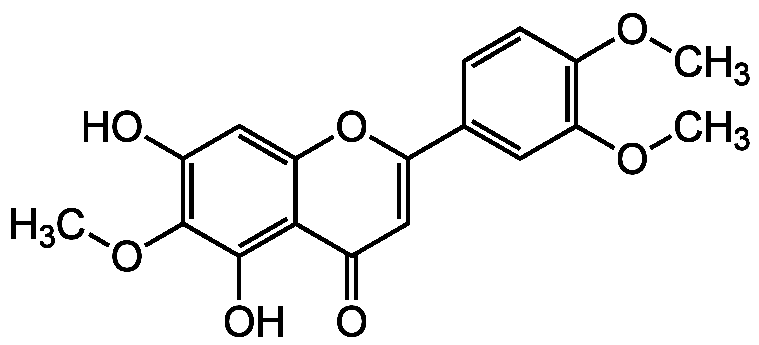
Chemical Structure
Eupatilin [22368-21-4]

AG-CN2-0432
Overview
- SupplierAdipoGen Life Sciences
- Product NameEupatilin [22368-21-4]
- Delivery Days Customer10
- CAS Number22368-21-4
- CertificationResearch Use Only
- Estimated Purity>98%
- Hazard InformationWarning
- Molecular FormulaC18H16O7
- Molecular Weight344.3
- Scientific DescriptionChemical. CAS: 22368-21-4. Formula: C18H16O7. MW: 344.3. Isolated from Artemisia sp. Selective inhibitor of 5-lipoxygenase. Apoptosis and cell cycle arrest inducer. Anticancer compound. Inhibits ERK1/2, JNK, and NF-kappaB activation and expression of Raf-1 and Ras. Anti-proliferative compound. Anti-inflammatory and immunosuppressive. Anti-apoptotic compound in hepatocytes. Antioxidant. Antidiabetic. Enhances hepatic and plasma glucose metabolism and increases insulin secretion in type 2 diabetic mice. Inhibits angiogenesis by blocking STAT3 and VEGF expression. Neuroprotective. PI3K Class I, MKK3/6 and MKK4 inhibitor. Shown to inhibit osteoporosis dually through transcriptional suppression and actin rearrangement. - Selective inhibitor of 5-lipoxygenase. Anti-proliferative and anticancer compound. Apoptosis and cell cycle arrest inducer. Inhibits ERK1/2, JNK, and NF-kappaB activation and expression of Raf-1 and Ras. PI3K Class I, MKK3/6 and MKK4 inhibitor. Inhibits angiogenesis by blocking STAT3 and VEGF expression. Anti-inflammatory and immunosuppressive agent. Antioxidant. Antidiabetic. Enhances hepatic and plasma glucose metabolism and increases insulin secretion in type 2 diabetic mice. Selective PPARalpha agonist. Neuroprotective.
- SMILESCOC1=C(C=C(C=C1)C2=CC(=O)C3=C(C(=C(C=C3O2)O)OC)O)OC
- Storage Instruction-20°C,2°C to 8°C
- UNSPSC12352200
References
- Selective inhibition of 5-lipoxygenase by natural compounds isolated from Chinese plants, Artemisia rubripes Nakai: Y. Koshihara, et al.; FEBS Lett. 158, 41 (1983)
- Eupatilin, a pharmacologically active flavone derived from Artemisia plants, induces apoptosis in human promyelocytic leukemia cells: H.J. Seo & Y.J. Surh; Mutat. Res. 496, 191-8 (2001)
- Eupatilin, a pharmacologically active flavone derived from Artemisia plants, induces cell cycle arrest in ras-transformed human mammary epithelial cells: D.H. Kim, et al.; Biochem. Pharmacol. 68, 1081 (2004)
- Eupatilin blocks mediator release via tyrosine kinase inhibition in activated guinea pig lung mast cells: J.Y Kim, et al.; J. Toxicol. Environ. Health A. 68, 2063 (2005)
- Eupatilin has an antiapoptotic action on hepatocytes, in contrast to apoptotic actions on other cells: T. Mine; J. Gastroenterol. 41, 818 (2006)
- Eupatilin protects gastric epithelial cells from oxidative damage and down-regulates genes responsible for the cellular oxidative stress: E.J. Choi, et al.; Pharm. Res. 25, 1355 (2008)
- Eupatilin inhibits H(2)O(2)-induced apoptotic cell death through inhibition of mitogen-activated protein kinases and nuclear factor-kappaB: S. Lee, et al.; Food Chem. Toxicol. 46, 2865 (2008)
- Eupatilin, isolated from Artemisia princeps Pampanini, enhances hepatic glucose metabolism and pancreatic beta-cell function in type 2 diabetic mice: Y.J. Kang, et al.; Diabetes Res. Clin. Pract. 82, 25 (2008)
- Eupatilin exhibits a novel anti-tumor activity through the induction of cell cycle arrest and differentiation of gastric carcinoma AGS cells: E.J. Choi, et al.; Differentiation 77, 412 (2009)
- Eupatilin inhibits T-cell activation by modulation of intracellular calcium flux and NF-kappaB and NF-AT activity: Y.D. Kim, et al.; J. Cell Biochem. 108, 225 (2009)
