![Ferritin, Heavy Chain (FTH) (Microglia Marker)(FTH/2081), CF405S conjugate, 0.1mg/mL [26628-22-8] Ferritin, Heavy Chain (FTH) (Microglia Marker)(FTH/2081), CF405S conjugate, 0.1mg/mL [26628-22-8]](https://biotium.com/wp-content/uploads/2021/02/view_image-434.jpeg)
Ferritin, Heavy Chain (FTH) (Microglia Marker)(FTH/2081), CF405S conjugate, 0.1mg/mL [26628-22-8]
BNC042081
ApplicationsWestern Blot, ImmunoHistoChemistry, ImmunoHistoChemistry Paraffin
Product group Antibodies
ReactivityBovine, Human, Mouse
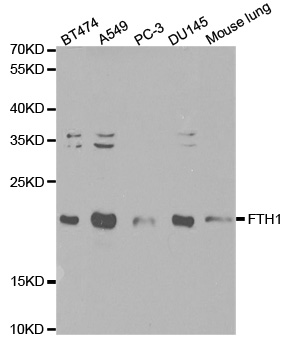
TargetFTH1
Overview
- SupplierBiotium
- Product NameFerritin, Heavy Chain (FTH) (Microglia Marker)(FTH/2081), CF405S conjugate, 0.1mg/mL [26628-22-8]
- Delivery Days Customer9
- ApplicationsWestern Blot, ImmunoHistoChemistry, ImmunoHistoChemistry Paraffin
- CAS Number26628-22-8
- CertificationResearch Use Only
- ClonalityMonoclonal
- Clone IDFTH/2081
- Concentration0.1 mg/ml
- ConjugateOther Conjugate
- Gene ID2495
- Target nameFTH1
- Target descriptionferritin heavy chain 1
- Target synonymsFHC, FTH, FTHL6, HFE5, NBIA9, PIG15, PLIF, ferritin heavy chain, H-ferritin, apoferritin, cell proliferation-inducing gene 15 protein, ferritin H subunit, ferritin, heavy polypeptide 1, placenta immunoregulatory factor, proliferation-inducing protein 15
- HostMouse
- IsotypeIgG2a
- Protein IDP02794
- Protein NameFerritin heavy chain
- Scientific DescriptionMammalian ferritins consist of 24 subunits made up of 2 types of poly-peptide chains, ferritin heavy chain and ferritin light chain, which each have unique functions. Ferritin heavy chains catalyze the first step in iron storage, the oxidationof FeI(II), whereas ferritin light chains promote the nucleation of ferrihydrite, enabling storage of Fe(III). The most prominent role of mammalian ferritins is to provide iron-buffering capacity to cells. In addition to iron buffering, heavy chain ferritin is also involved in the regulation of thymidine biosynthesis via increased expression of cytoplasmic serine hydroxymethyltransferase, which is a limiting factor in thymidylate synthesis in MCF-7 cells. Light chain ferritin is involved in cataracts by at least two mechanisms: hereditary hyperferritinemia cataract syndrome, in which light chain ferritin is overexpressed; and oxidative stress, an important factor in the development of aging-related cataracts. Primary antibodies are available purified, or with a selection of fluorescent CF® Dyes and other labels. CF® Dyes offer exceptional brightness and photostability. Note: Conjugates of blue fluorescent dyes like CF®405S and CF®405M are not recommended for detecting low abundance targets, because blue dyes have lower fluorescence and can give higher non-specific background than other dye colors.
- SourceAnimal
- ReactivityBovine, Human, Mouse
- Storage Instruction2°C to 8°C,RT
- UNSPSC41116161





![Ferritin Heavy Chain antibody [N1C3] detects Ferritin Heavy Chain protein at cytoplasm by immunohistochemical analysis. Sample: Paraffin-embedded mouse liver. Ferritin Heavy Chain stained by Ferritin Heavy Chain antibody [N1C3] (GTX101733) diluted at 1:500. Antigen Retrieval: Citrate buffer, pH 6.0, 15 min](https://www.genetex.com/upload/website/prouct_img/normal/GTX101733/GTX101733_44699_20220701_IHC-P_M_22071401_601.webp)