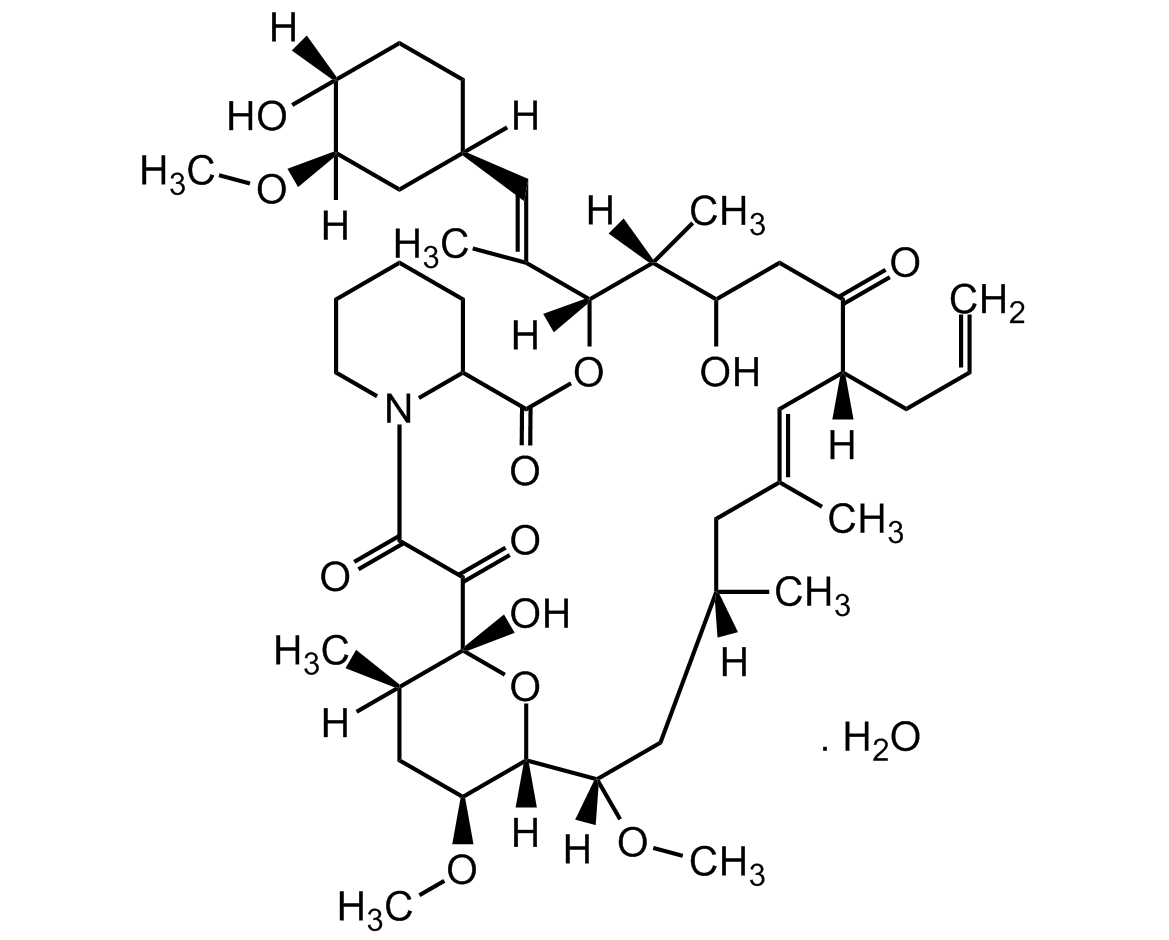
Chemical Structure
FK-506 [Tacrolimus] [109581-93-3]
AG-CN2-0047
CAS Number109581-93-3
Product group Chemicals
Estimated Purity>98%
Molecular Weight804.0 . 18.0
Overview
- SupplierAdipoGen Life Sciences
- Product NameFK-506 [Tacrolimus] [109581-93-3]
- Delivery Days Customer10
- CAS Number109581-93-3
- CertificationResearch Use Only
- Estimated Purity>98%
- Hazard InformationDanger,Excepted quantity
- Molecular FormulaC44H69NO12 . H2O
- Molecular Weight804.0 . 18.0
- Scientific DescriptionChemical. CAS: 109581-93-3. Formula: C44H69NO12 . H2O. MW: 804.0 . 18.0. Isolated from Streptomyces FCZ0311. Potent immunosuppressant (as cyclosporin A and rapamycin). Suppresses proliferation of cytotoxic T cells and inhibits the production of T cell-derived mediators such as interleukin-2 (IL-2). Forms a complex with FK-506 binding protein 12 (FKBP12). Inhibits the activity of the calcium/calmodulin-dependent protein phosphatase 2B (PP2B; calcineurin), leading to disruption of T cell activation. Prevents rejection of transplanted organs. Anti-inflammatory compound in the treatment of several inflammatory skin diseases (e.g. atopic dermatitis) and with potential anti-rheumatic activity (rheumatoid arthritis). Neuroprotective. Regulates nitric oxide neurotoxicity. Neurotransmitter. Ca2+ release compound. NF-kappaB suppressor by induction of unfolded protein response (UPR). Anti-cancer compound. Apoptosis inducer. - Potent immunosuppressant (as cyclosporin A and rapamycin) [1-3]. Suppresses proliferation of cytotoxic T cells and inhibits the production of T cell-derived mediators such as interleukin-2 (IL-2) [2, 4]. Forms a complex with FK-506 binding protein 12 (FKBP12). Inhibits the activity of the calcium/calmodulin-dependent protein phosphatase 2B (PP2B; calcineurin), leading to disruption of T cell activation [2, 4, 6, 7]. Prevents rejection of transplanted organs [3]. Anti-inflammatory compound in the treatment of several inflammatory skin diseases (e.g. atopic dermatitis) and with potential anti-rheumatic activity (rheumatoid arthritis) [5, 9]. Neuroprotective. Regulates nitric oxide neurotoxicity. Neurotransmitter. Ca2+ release compound [8]. NF-kappaB suppressor by induction of unfolded protein response (UPR) [11]. Anti-cancer compound. Apoptosis inducer [10, 12].
- SMILES[H]O[H].[H][C@]1(CC[C@@]([H])(O)[C@@]([H])(C1)OC)\C=C(/C)[C@@]1([H])OC(=O)C2CCCCN2C(=O)C(=O)[C@]2(O)O[C@@]([H])([C@H](C[C@@]2([H])C)OC)[C@]([H])(C[C@@]([H])(C)C\C(C)=C\[C@@]([H])(CC=C)C(=O)CC(O)[C@@]1([H])C)OC
- Storage Instruction-20°C,2°C to 8°C
- UN NumberUN 2811
- UNSPSC12352200


![Tacrolimus monohydrate [109581-93-3]](https://www.targetmol.com/group3/M00/02/8E/CgoaEGY7NuWEKCcGAAAAAKHvtBg957.png)