Chemical Structure
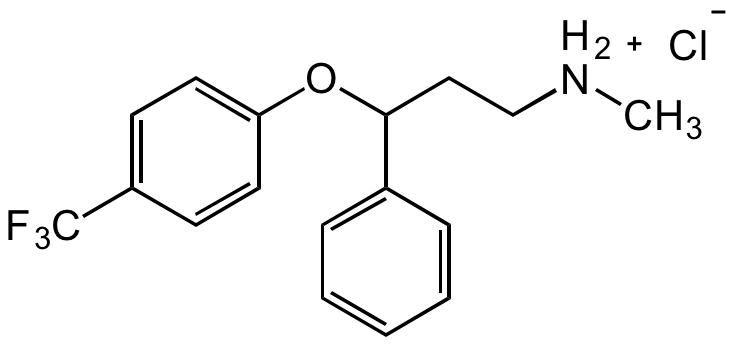
Fluoxetine hydrochloride [56296-78-7] [56296-78-7]
CDX-F0141
CAS Number56296-78-7
Product group Chemicals
Estimated Purity>98%
Molecular Weight345.79
Overview
- SupplierChemodex
- Product NameFluoxetine hydrochloride [56296-78-7] [56296-78-7]
- Delivery Days Customer2
- CAS Number56296-78-7
- CertificationResearch Use Only
- Estimated Purity>98%
- Hazard InformationDanger,Excepted quantity
- Molecular FormulaC17H18F3NO . HCl
- Molecular Weight345.79
- Scientific DescriptionChemical. CAS: 56296-78-7. Formula: C17H18F3NO . HCl. MW: 345.79. Fluoxetine is a cell-permeable selective serotonin reuptake inhibitor (SSRI), with preference for the serotonin transporter (Kd=0.81nM) over the norepinephrine transporter (Kd=240nM) and the dopamine transporter (Kd=3600nM). This drug works at presynaptic terminals where it prevents the reuptake of serotonin, resulting in the accumulation of serotonin in extracellular fluid at synapses. It functions as an antidepressant. Fluoxetine binds also to the human 5-HT transporter and is between 150- and 900- fold selective over 5-HT1A, 5-HT2A, H1, alpha1, alpha2-adrenergic, and muscarinic receptors. It has been shown to induce differentiation of neuronal precursors, enhancing neuronal characteristics. In addition, it was reported to modulate the proliferation of T-cells by increasing the Ca2+ influx and thereby influencing the activities of protein kinase A (PKA) and protein kinase C (PKC) and to regulate the phosphorylation of DARPP-32 and AMPA receptors. - Fluoxetine is a cell-permeable selective serotonin reuptake inhibitor (SSRI), with preference for the serotonin transporter (Kd=0.81nM) over the norepinephrine transporter (Kd=240nM) and the dopamine transporter (Kd=3600nM). This drug works at presynaptic terminals where it prevents the reuptake of serotonin, resulting in the accumulation of serotonin in extracellular fluid at synapses. It functions as an antidepressant. Fluoxetine binds also to the human 5-HT transporter and is between 150- and 900- fold selective over 5-HT1A, 5-HT2A, H1, alpha1, alpha2-adrenergic, and muscarinic receptors. It has been shown to induce differentiation of neuronal precursors, enhancing neuronal characteristics. In addition, it was reported to modulate the proliferation of T-cells by increasing the Ca2+ influx and thereby influencing the activities of protein kinase A (PKA) and protein kinase C (PKC) and to regulate the phosphorylation of DARPP-32 and AMPA receptors.
- SMILESC[NH2+]CCC(C1=CC=CC=C1)OC2=CC=C(C(F)(F)F)C=C2.[Cl-]
- Storage InstructionRT
- UN Number3077
- UNSPSC12352200


![Fluoxetine hydrochloride [56296-78-7] [56296-78-7]](https://www.targetmol.com/group3/M00/02/C4/CgoaEWY7N6KEUkTIAAAAAK_7_m4379.png)