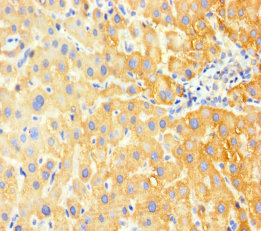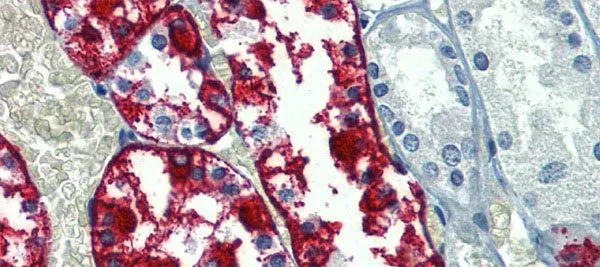
IHC-P analysis of human kidney tissue using GTX46748 G6PC antibody at 5μg/ml.
G6PC antibody, N-term
GTX46748
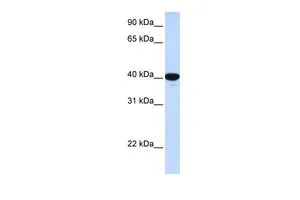
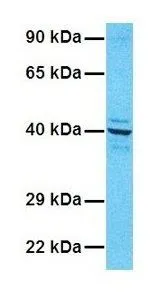
ApplicationsWestern Blot, ImmunoHistoChemistry, ImmunoHistoChemistry Paraffin
Product group Antibodies
ReactivityHuman
TargetG6PC1
Overview
- SupplierGeneTex
- Product NameG6PC antibody, N-term
- Delivery Days Customer9
- Application Supplier NoteWB: 0.2-2.5 ug/ml. IHC-P: 2-10 ug/ml. *Optimal dilutions/concentrations should be determined by the researcher.Not tested in other applications.
- ApplicationsWestern Blot, ImmunoHistoChemistry, ImmunoHistoChemistry Paraffin
- CertificationResearch Use Only
- ClonalityPolyclonal
- Concentration0.5-1 mg/ml
- ConjugateUnconjugated
- Gene ID2538
- Target nameG6PC1
- Target descriptionglucose-6-phosphatase catalytic subunit 1
- Target synonymsG6PC, G6PT, G6Pase, GSD1, GSD1a, glucose-6-phosphatase catalytic subunit 1, G-6-Pase, G6Pase-alpha, glucose-6-phosphatase alpha
- HostRabbit
- IsotypeIgG
- Protein IDP35575
- Protein NameGlucose-6-phosphatase catalytic subunit 1
- Scientific DescriptionGlucose-6-phosphatase (G6Pase) is a multi-subunit integral membrane protein of the endoplasmic reticulum that is composed of a catalytic subunit and transporters for G6P, inorganic phosphate, and glucose. This gene (G6PC) is one of the three glucose-6-phosphatase catalytic-subunit-encoding genes in human: G6PC, G6PC2 and G6PC3. Glucose-6-phosphatase catalyzes the hydrolysis of D-glucose 6-phosphate to D-glucose and orthophosphate and is a key enzyme in glucose homeostasis, functioning in gluconeogenesis and glycogenolysis. Mutations in this gene cause glycogen storage disease type I (GSD1). This disease, also known as von Gierke disease, is a metabolic disorder characterized by severe hypoglycemia associated with the accumulation of glycogen and fat in the liver and kidneys.[provided by RefSeq, Feb 2011]
- ReactivityHuman
- Storage Instruction-20°C or -80°C,2°C to 8°C
- UNSPSC41116161
References
- MicroRNA-130a can inhibit hepatitis B virus replication via targeting PGC1alpha and PPARgamma. Huang JY et al., 2015 Mar, RNARead this paper