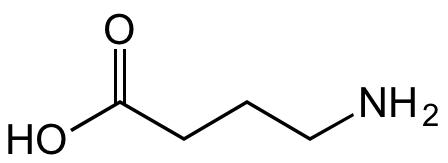
Chemical Structure
GABA [gamma-Aminobutyric acid] [56-12-2]
AG-CR1-3664
CAS Number56-12-2
Product group Chemicals
Estimated Purity>98%
Molecular Weight103.12
Overview
- SupplierAdipoGen Life Sciences
- Product NameGABA [gamma-Aminobutyric acid] [56-12-2]
- Delivery Days Customer10
- CAS Number56-12-2
- CertificationResearch Use Only
- Estimated Purity>98%
- Molecular FormulaC4H9NO2
- Molecular Weight103.12
- Scientific DescriptionAmino acid that functions as the major inhibitory neurotransmitter in the mammalian central nervous system and also functions as a neuromodulator in some peripheral tissues. GABAA and GABAB receptor agonist that increases Cl- conductance. GABA acts at inhibitory synapses in the brain by binding to specific transmembrane receptors in the plasma membrane of both pre- and postsynaptic neuronal processes. This binding causes the opening of ion channels to allow the flow of either negatively charged chloride ions into the cell or positively charged potassium ions out of the cell. This action results in a negative change in the transmembrane potential, usually causing hyperpolarization. GABAergic neurons are involved in myorelaxation, anxiolytic treatment, sedation and anaesthetics. GABA can also influence heart rate and blood pressure and function as a immunomodulator. GABA signaling stimulates alpha-cell-mediated beta-like cell neogenesis. GABA induced insulin-producing beta-like cell neogenesis. - Chemical. CAS: 56-12-2. Formula: C4H9NO2. MW: 103.12. Amino acid that functions as the major inhibitory neurotransmitter in the mammalian central nervous system and also functions as a neuromodulator in some peripheral tissues. GABAA and GABAB receptor agonist that increases Cl- conductance. GABA acts at inhibitory synapses in the brain by binding to specific transmembrane receptors in the plasma membrane of both pre- and postsynaptic neuronal processes. This binding causes the opening of ion channels to allow the flow of either negatively charged chloride ions into the cell or positively charged potassium ions out of the cell. This action results in a negative change in the transmembrane potential, usually causing hyperpolarization. GABAergic neurons are involved in myorelaxation, anxiolytic treatment, sedation and anaesthetics. GABA can also influence heart rate and blood pressure and function as a immunomodulator. GABA signaling stimulates alpha-cell-mediated beta-like cell neogenesis. GABA induced insulin-producing beta-like cell neogenesis.
- SMILESOC(CCCN)=O
- Storage InstructionRT
- UNSPSC12352200

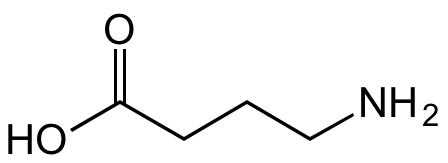

![gamma-Aminobutyric acid [56-12-2]](https://www.targetmol.com/group3/M00/26/B3/CgoaEWZhxt2EUD_AAAAAAFniq0w810.png)