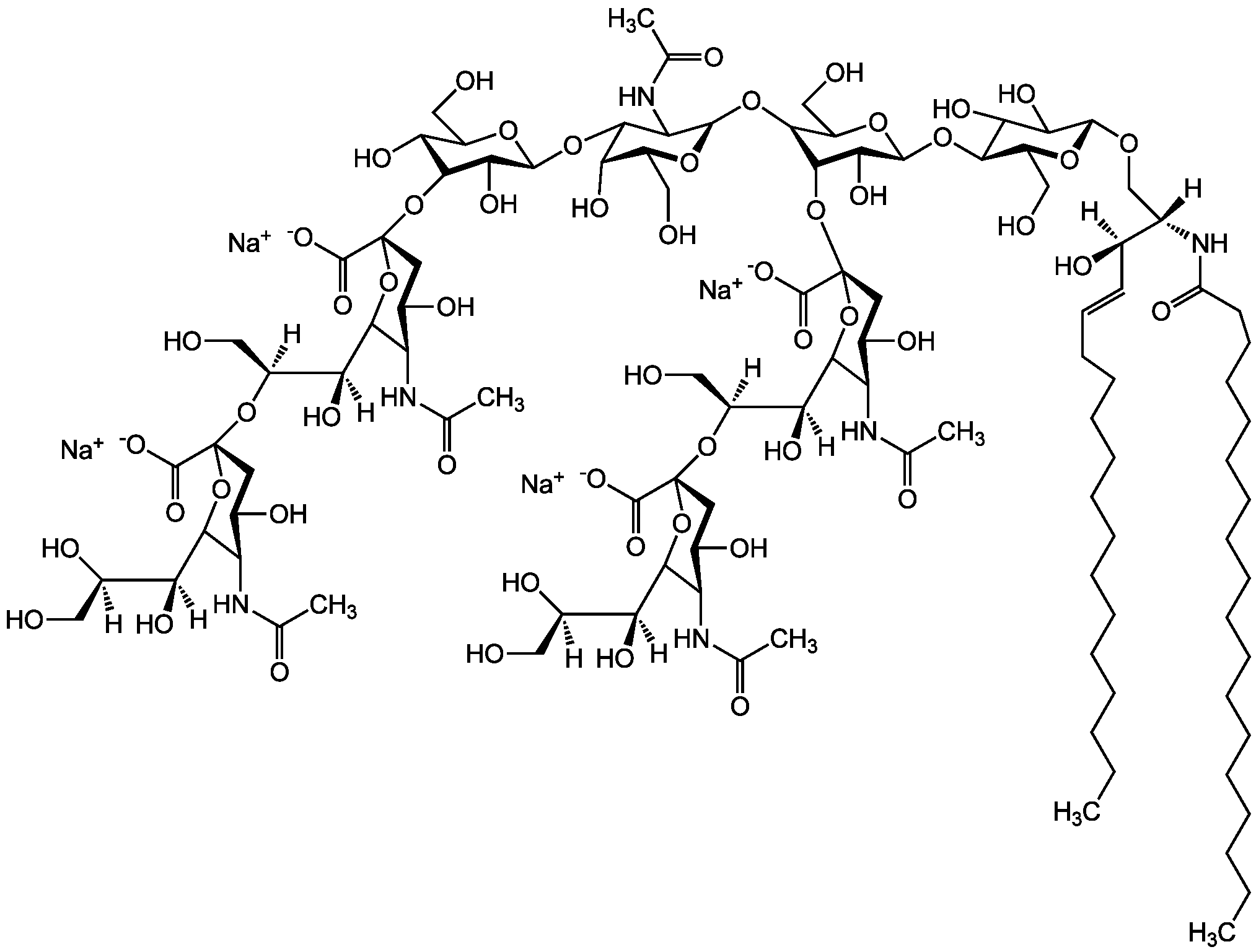
Chemical Structure
Ganglioside GQ1b . tetrasodium salt (bovine brain) [68652-37-9]

AG-CN2-9007
CAS Number68652-37-9
Product group Chemicals
Estimated Purity>98%
Molecular Weight2416.6 . 92.0 (calculated on sphingosine C18:1 and stearic acid)
Overview
- SupplierAdipoGen Life Sciences
- Product NameGanglioside GQ1b . tetrasodium salt [68652-37-9]
- Delivery Days Customer10
- CAS Number68652-37-9
- CertificationResearch Use Only
- Estimated Purity>98%
- Molecular FormulaC106H178N6O55 . 4Na
- Molecular Weight2416.6 . 92.0 (calculated on sphingosine C18:1 and stearic acid)
- Scientific DescriptionChemical. CAS: 68652-37-9. Formula: C106H178N6O55 . 4Na. MW: 2416.6 . 92.0 (calculated on sphingosine C18:1 and stearic acid). Isolated from bovine brain. Gangliosides are acidic glycosphingolipids that form lipid rafts in the outer leaflet of the cell plasma membrane, especially in neuronal cells in the central nervous system. They participate in cellular proliferation, differentiation, adhesion, signal transduction, cell-to-cell interactions, tumorigenesis and metastasis. The accumulation of gangliosides has been linked to several diseases. Ganglioside GQ1b specifically promotes neural differentiation of human neuroblastoma cells. Anti-GQ1b antibodies are present in serum from Miller-Fisher syndrome patients. - Gangliosides are acidic glycosphingolipids that form lipid rafts in the outer leaflet of the cell plasma membrane, especially in neuronal cells in the central nervous system. They participate in cellular proliferation, differentiation, adhesion, signal transduction, cell-to-cell interactions, tumorigenesis and metastasis. The accumulation of gangliosides has been linked to several diseases. Ganglioside GQ1b specifically promotes neural differentiation of human neuroblastoma cells. Anti-GQ1b antibodies are present in serum from Miller-Fisher syndrome patients.
- SMILES[Na+].[Na+].[Na+].[Na+].[H][C@@](O)(CO)[C@]([H])(O)C1O[C@@](CC(O)[C@H]1NC(C)=O)(O[C@@]([H])(CO)[C@]([H])(O)C1O[C@@](CC(O)[C@H]1NC(C)=O)(O[C@H]1[C@H](O)C(CO)O[C@@H](OC2[C@@H](O)[C@H](CO)O[C@H](O[C@H]3C(CO)O[C@@H](O[C@H]4C(O)C(O)[C@H](OC[C@]([H])(NC(=O)CCCCCCCCCCCCCCCCC)[C@]([H])(O)\C=C\CCCCCCCCCCCCC)O[C@H]4CO)C(O)[C@H]3O[C@@]3(CC(O)[C@@H](NC(C)=O)C(O3)[C@@]([H])(O)[C@]([H])(CO)O[C@@]3(CC(O)[C@@H](NC(C)=O)C(O3)[C@@]([H])(O)[C@]([H])(O)CO)C([O-])=O)C([O-])=O)C2NC(C)=O)C1O)C([O-])=O)C([O-])=O
- Storage Instruction-20°C,2°C to 8°C
- UNSPSC12352200
References
- Role of membrane gangliosides in the binding and action of bacterial toxins: P.H. Fishman; J. Membr. Biol. 69, 85 (1982)
- A novel glycosignaling system: GQ1b-dependent neuritogenesis of human neuroblastoma cell line, GOTO, is closely associated with GQ1b-dependent ecto-type protein phosphorylation. S. Tsuji, et al.; Neurochem. 21, 549 (1992)
- Dynamic and structural properties of sphingolipids as driving force to the formation of membrane domains: S. Sonnino, et al.; Chem. Rev. 106, 2111 (2006)
- Fisher syndrome: clinical features, immunopathogenesis and management. M. Mori, et al.; Expert Rev. Neurother. 12, 39 (2012)
