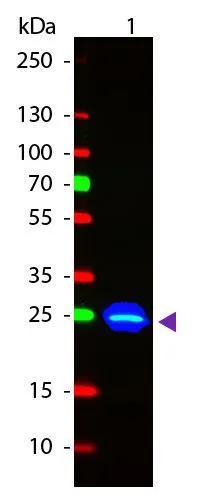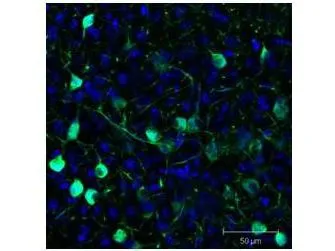
Immunofluorescence Microscopy of GFP-GOAT-Antibody. Tissue: Sf-1:Cre mice crossed to the Z/EG reporter line. Mouse brain (coronal view, 20X magnification). Fixation: 4%PFA/PBS with o/n fixation, and subsequently transferred to a 30% sucrose solution. Antigen retrieval: frozen in OCT freezing medium (Sakura) and cryostat sectioned at 40 microns. Primary antibody: Goat anti-GFP (GTX26662) was used at 1:500 dilution in free floating imunnohistochemistry to detect GFP. Secondary antibody: Fluorchrome conjugated Anti-goat IgG secondary antibody was used for detection at 1:500 at 1:10,000 for 45 min at RT. Localization: Sf-1+ neurons and their processes of the ventromedial nucleus of the hypothalamus. Staining: eGFP as green fluorescent signal and sections were counterstained with DAPI.
GFP antibody (FITC)
GTX26662
ApplicationsDot Blot, Flow Cytometry, ImmunoFluorescence, Western Blot, ImmunoCytoChemistry, ImmunoHistoChemistry, ImmunoHistoChemistry Frozen, ImmunoHistoChemistry Paraffin, Other Application
Product group Antibodies
ReactivityOther Species
Overview
- SupplierGeneTex
- Product NameGFP antibody (FITC)
- Delivery Days Customer9
- Antibody SpecificityNo reaction was observed against Human, Mouse and Rat Serum Proteins.
- Application Supplier NoteWB: >1:10000. ICC/IF: 1:500-1:2500. *Optimal dilutions/concentrations should be determined by the researcher.Not tested in other applications.
- ApplicationsDot Blot, Flow Cytometry, ImmunoFluorescence, Western Blot, ImmunoCytoChemistry, ImmunoHistoChemistry, ImmunoHistoChemistry Frozen, ImmunoHistoChemistry Paraffin, Other Application
- CertificationResearch Use Only
- ClonalityPolyclonal
- Concentration1 mg/ml
- ConjugateFITC
- HostGoat
- IsotypeIgG
- Scientific DescriptionThe jellyfish Aequorea victoria contains green fluorescent protein (GFP) that emits light in the bioluminescence reaction of the animal. GFP has been used widely as a reporter protein for gene expression in eukaryotic and prokaryotic organisms, and as a protein tag in cell culture and in multicellular organisms. As a fusion tag, GFP can be used to localize proteins, to study their movement or to research the dynamics of the subcellular compartments where these proteins are targeted. GFP technology has revealed considerable new insights into the physiological activities of living cells.
- ReactivityOther Species
- Storage Instruction-20°C,2°C to 8°C
- UNSPSC12352203
References
- let-7 miRNAs inhibit CHD7 expression and control auditory-sensory progenitor cell behavior in the developing inner ear. Evsen L et al., 2020 Aug 14, DevelopmentRead more
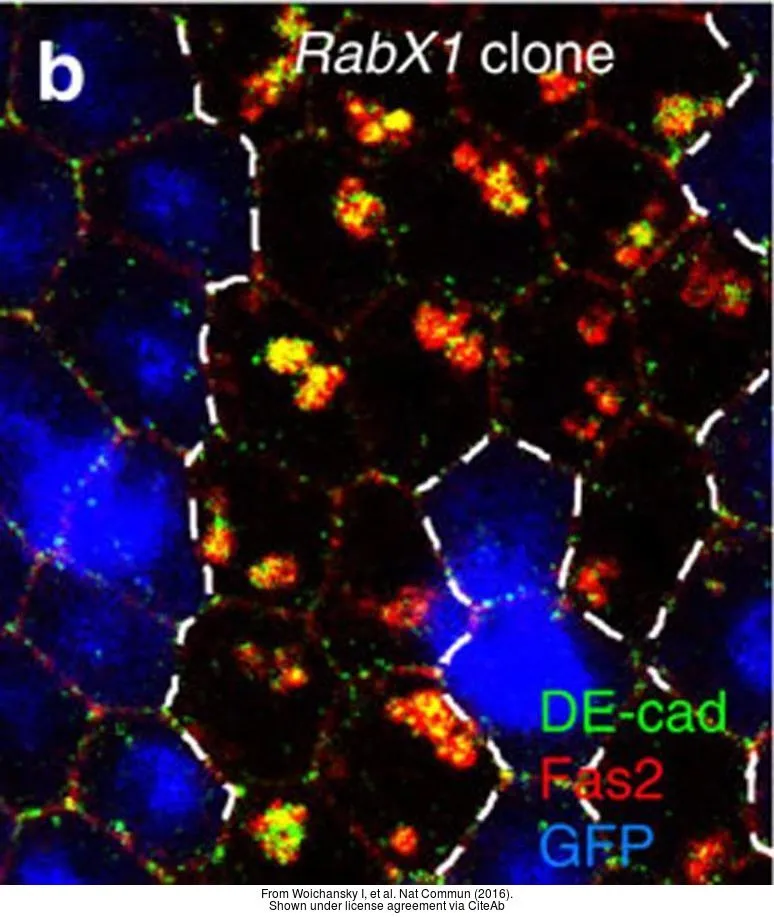
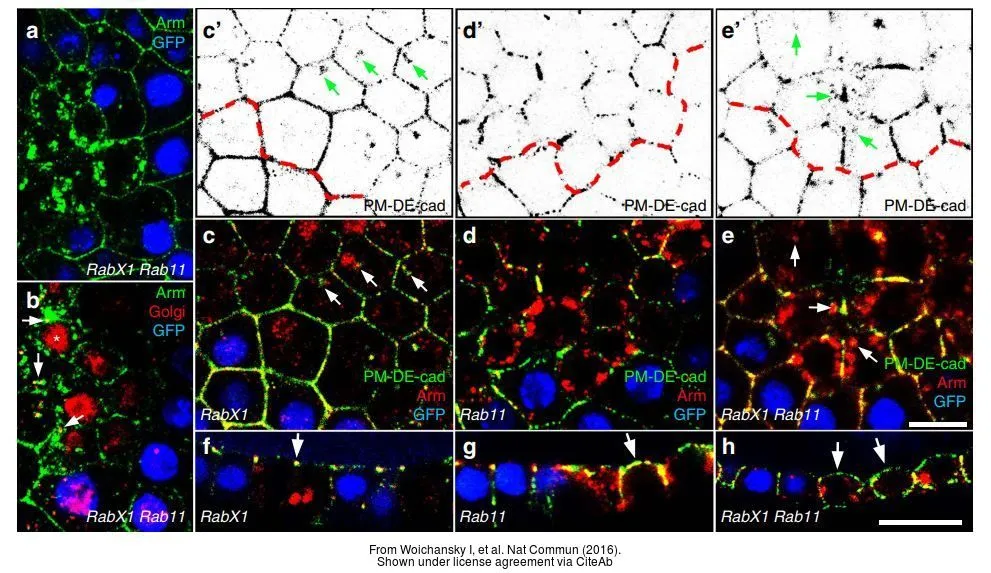
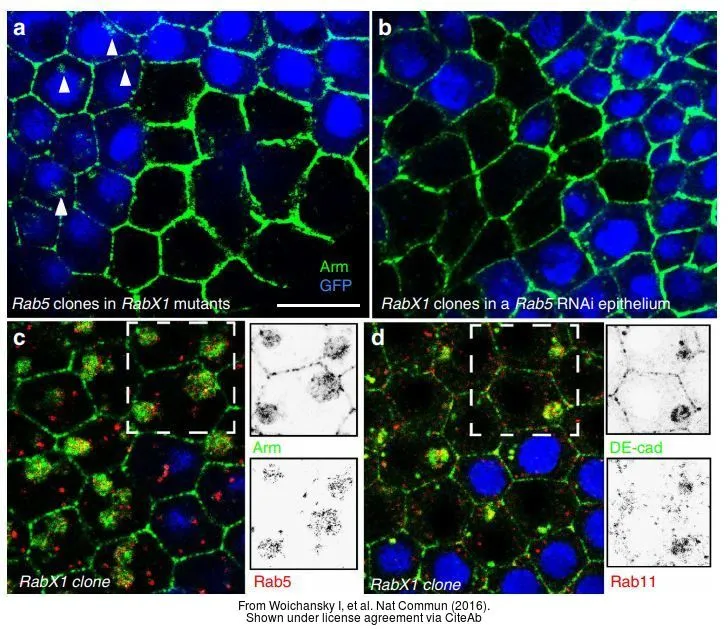
- RabX1 Organizes a Late Endosomal Compartment that Forms Tubular Connections to Lysosomes Consistent with a Kiss and Run Mechanism. Laiouar S et al., 2020 Apr 6, Curr BiolRead more
- Induced pluripotent stem cell-derived endothelial cells promote angiogenesis and accelerate wound closure in a murine excisional wound healing model. Clayton ZE et al., 2018 Aug 31, Biosci RepRead more
- Evaluation of synthetic vascular grafts in a mouse carotid grafting model. Chan AH et al., 2017, PLoS OneRead more
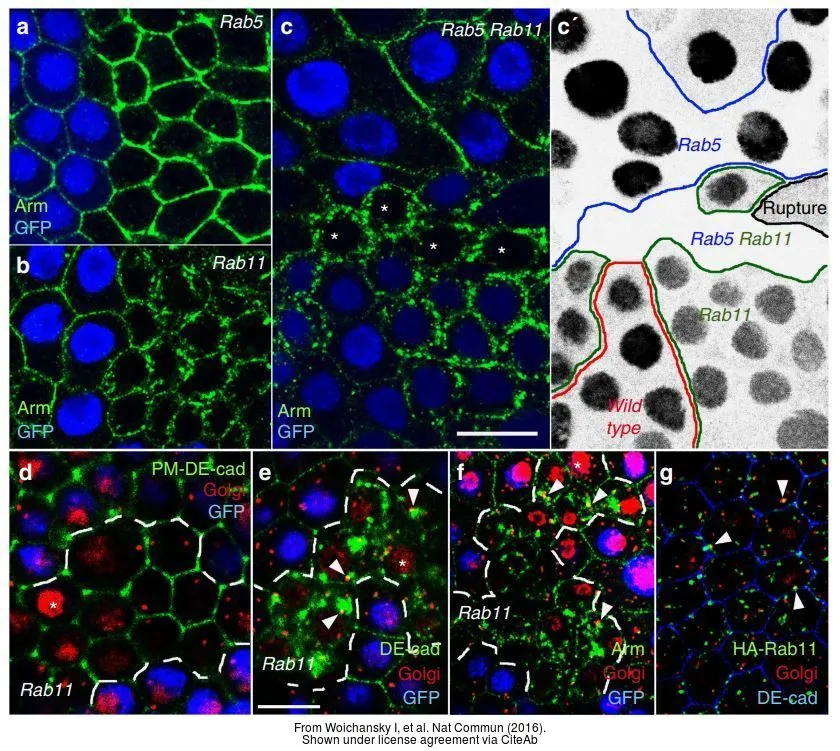
- Three mechanisms control E-cadherin localization to the zonula adherens. Woichansky I et al., 2016 Mar 10, Nat CommunRead more
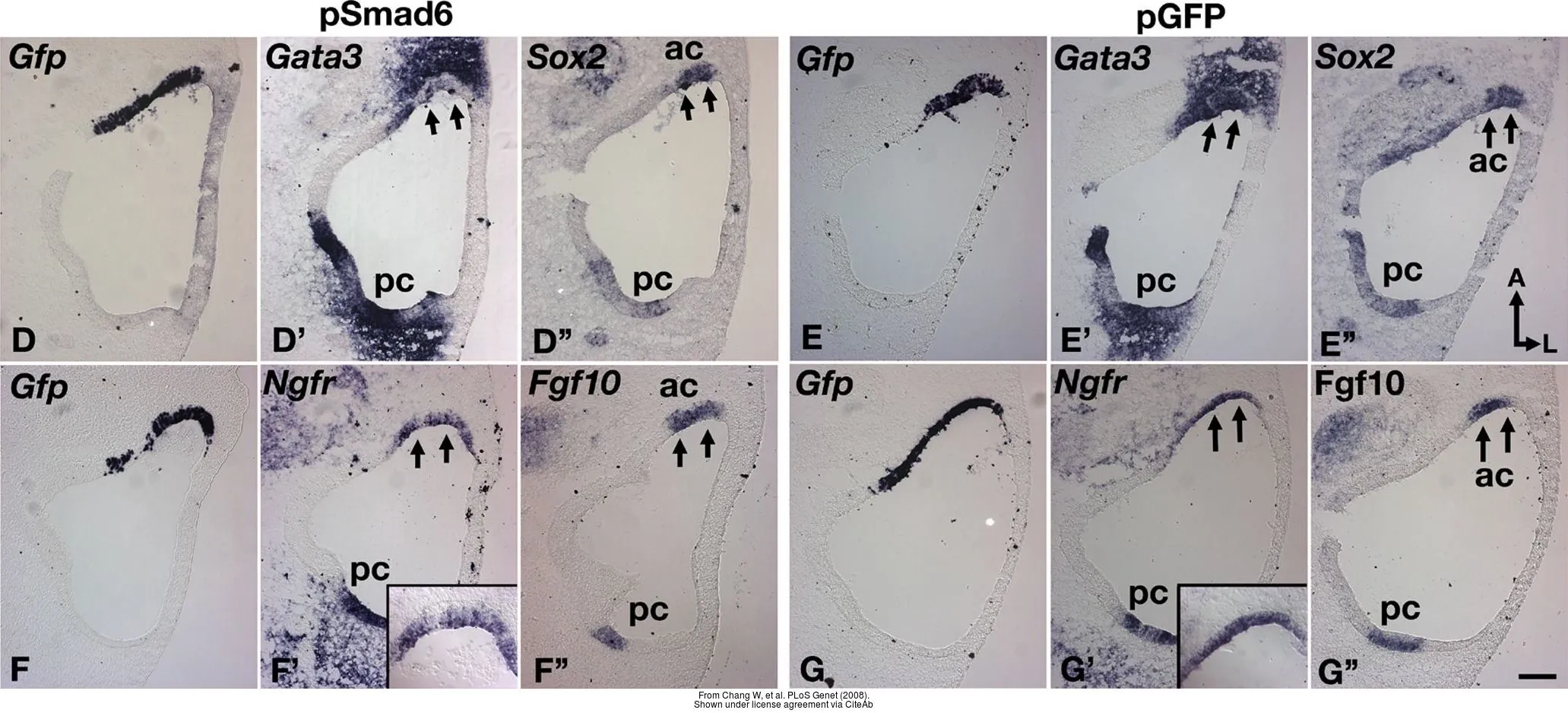
- Pou3f4-mediated regulation of ephrin-b2 controls temporal bone development in the mouse. Raft S et al., 2014, PLoS OneRead more
- Cytoplasmic localization of p21 protects trophoblast giant cells from DNA damage induced apoptosis. de Renty C et al., 2014, PLoS OneRead more
- A genome-scale in vivo RNAi analysis of epithelial development in Drosophila identifies new proliferation domains outside of the stem cell niche. Berns N et al., 2014 Jun 15, J Cell SciRead more
- Ephrin-B2 governs morphogenesis of endolymphatic sac and duct epithelia in the mouse inner ear. Raft S et al., 2014 Jun 1, Dev BiolRead more
- SLC26A4 targeted to the endolymphatic sac rescues hearing and balance in Slc26a4 mutant mice. Li X et al., 2013, PLoS GenetRead more