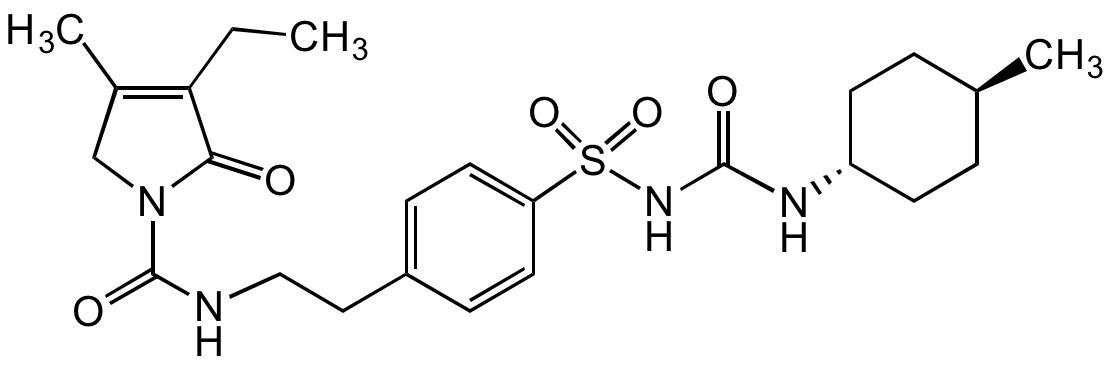
Chemical Structure
Glimepiride [93479-97-1]
CDX-G0208
CAS Number93479-97-1
Product group Chemicals
Estimated Purity>98%
Molecular Weight490.62
Overview
- SupplierChemodex
- Product NameGlimepiride [93479-97-1]
- Delivery Days Customer2
- CAS Number93479-97-1
- CertificationResearch Use Only
- Estimated Purity>98%
- Hazard InformationWarning
- Molecular FormulaC24H34N4O5S
- Molecular Weight490.62
- Scientific DescriptionChemical. CAS: 93479-97-1. Formula: C24H34N4O5S. MW: 490.62. Glimepiride is a long-acting sulfonylurea antidiabetic agent inhibiting ATP-sensitive potassium (KATP) channels in pancreatic beta-cells, which leads to the release of insulin. In addition, Glimepiride increases the activity of intracellular insulin receptors. Studies conducted on adipocytes and skeletal muscle suggest that Glimepiride induces the PI3 kinase (PI3K) and Akt pathway, along with insulin receptor substrate-1/2 and endothelial nitric oxide synthase and stimulates glucose transporter 1 and 4 (GLUT1/4) expression. Glimepiride also increases osteoblast proliferation and differentiation, which is thought to be related to its ability to activate the PI3K and Akt pathway and exhibits neuroprotective benefit, decreasing expression and activity of BACE1 and amyloid-beta (Abeta) in neurons in a PPARgamma-dependent manner. - Glimepiride is a long-acting sulfonylurea antidiabetic agent inhibiting ATP-sensitive potassium (KATP) channels in pancreatic beta-cells, which leads to the release of insulin. In addition, Glimepiride increases the activity of intracellular insulin receptors. Studies conducted on adipocytes and skeletal muscle suggest that Glimepiride induces the PI3 kinase (PI3K) and Akt pathway, along with insulin receptor substrate-1/2 and endothelial nitric oxide synthase and stimulates glucose transporter 1 and 4 (GLUT1/4) expression. Glimepiride also increases osteoblast proliferation and differentiation, which is thought to be related to its ability to activate the PI3K and Akt pathway and exhibits neuroprotective benefit, decreasing expression and activity of BACE1 and amyloid-beta (Abeta) in neurons in a PPARgamma-dependent manner.
- SMILESO=C(N1C(C(CC)=C(C)C1)=O)NCCC2=CC=C(S(NC(N[C@H]3CC[C@H](C)CC3)=O)(=O)=O)C=C2
- Storage InstructionRT
- UNSPSC12352200


![Glimepiride [93479-97-1]](https://www.targetmol.com/group3/M00/02/79/CgoaEGY7NHaESzvCAAAAAJkQJt4535.png)