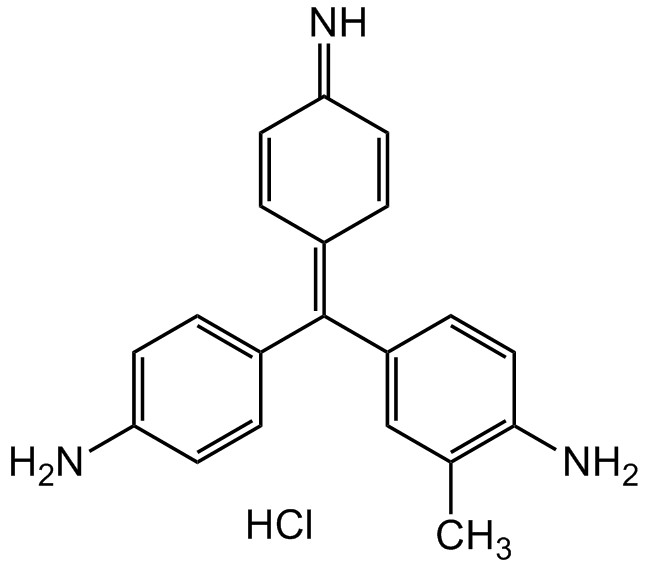
Chemical Structure
Grams fuchsin Solution [58969-01-0]

CDX-G0064
Overview
- SupplierChemodex
- Product NameGrams fuchsin Solution [632-99-5]
- Delivery Days Customer10
- CAS Number58969-01-0
- CertificationResearch Use Only
- FormulationLiquid
- Molecular FormulaC20H20ClN3
- Molecular Weight337.85
- Scientific DescriptionChemical. CAS: 632-99-5. Formula: C20H20ClN3. MW: 337.85. Grams Fuchsin Solution is a reagent that could be used in qualitative procedures to differentiate gram-negative from gram-positive organisms. The Gram staining allows a fast differentiation of bacteria in Gram-positive and Gram-negative. The mureine structure of the bacteria walls is the basis of the color affinity. Bacteria will be stained with Grams crystal violet solution - an aniline dye - in the first step. After the treatment with iod solution, a dye-iod complex will form. During the decolorizing step, this complex stays in the multilayer mureine structures of the Gram-positive bacteria and they will appear blue/violet. Gram-negative bacteria have a monolayer mureine structure only, the dye-iod complex does not stay bound to the cellwall, they will be decolorized. Gram-negative bacteria will be counterstained by Grams Fuchsin solution and appear red/pink. Both Gram-positive bacteria and Gram-negative bacteria pick up the counterstain. The counterstain, however, is unseen on Gram-positive bacteria because of the darker crystal violet stain. - Grams Fuchsin Solution is a reagent that could be used in qualitative procedures to differentiate gram-negative from gram-positive organisms. The Gram staining allows a fast differentiation of bacteria in Gram-positive and Gram-negative. The mureine structure of the bacteria walls is the basis of the color affinity. Bacteria will be stained with Grams crystal violet solution - an aniline dye - in the first step. After the treatment with iod solution, a dye-iod complex will form. During the decolorizing step, this complex stays in the multilayer mureine structures of the Gram-positive bacteria and they will appear blue/violet. Gram-negative bacteria have a monolayer mureine structure only, the dye-iod complex does not stay bound to the cellwall, they will be decolorized. Gram-negative bacteria will be counterstained by Grams Fuchsin solution and appear red/pink. Both Gram-positive bacteria and Gram-negative bacteria pick up the counterstain. The counterstain, however, is unseen on Gram-positive bacteria because of the darker crystal violet stain.
- SMILESNC1=CC=C(/C(C2=CC(C)=C(N)C=C2)=C3C=CC(C=C/3)=N)C=C1.Cl
- Storage Instruction2°C to 8°C,RT
- UNSPSC41116134
