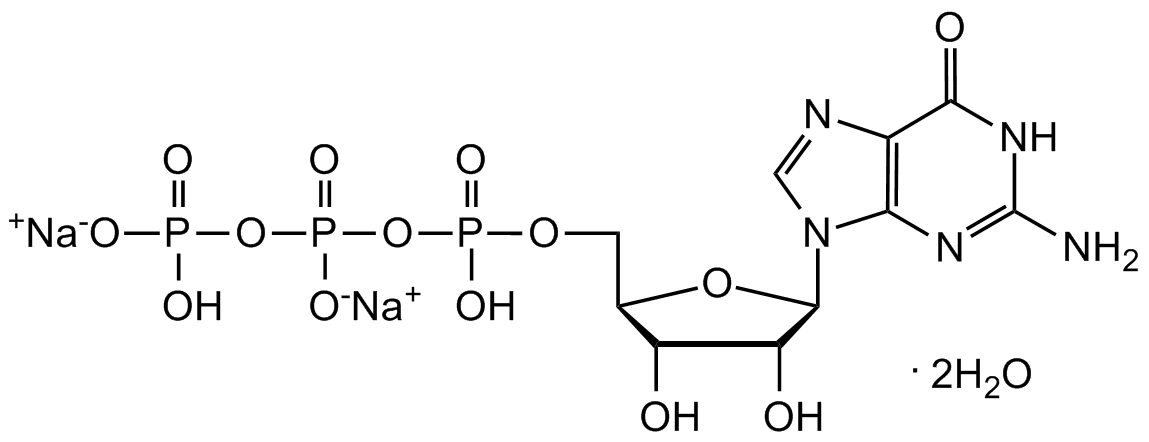
Chemical Structure
Guanosine 5-triphosphate sodium salt hydrate [36051-31-7]
CDX-G0069
CAS Number36051-31-7
Product group Chemicals
Estimated Purity>97%
Molecular Weight523.18 (free acid basis)
Overview
- SupplierChemodex
- Product NameGuanosine 5-triphosphate sodium salt hydrate [36051-31-7]
- Delivery Days Customer10
- CAS Number36051-31-7
- CertificationResearch Use Only
- Estimated Purity>97%
- Molecular FormulaC10H16N5O14P3 . xNa+
- Molecular Weight523.18 (free acid basis)
- Scientific DescriptionChemical. CAS: 36051-31-7. Formula: C10H16N5O14P3 . xNa+. Molecular Weight: 523.18 (free acid basis). Guanosine 5-triphosphate (GTP) trisodium salt activates the signal transducing G proteins which are involved in various cellular processes including proliferation, differentiation and activation of several intracellular kinase cascades. Proliferation and apoptosis are regulated in part by the hydrolysis of GTP by small GTPases Ras and Rho. Another type of small GTPase, Rab, plays a role in the docking and fusion of vesicles and may also be involved in vesicle GTP functions as a carrier of phosphates and pyrophosphates involved in channeling chemical energy into specific biosynthetic pathways. It also serves as an energy-rich precursor of mononucleotide units in the enzymatic biosynthesis of DNA and RNA. GTP is involved in the initiation of peptide synthesis during the binding of formylmethionyl-tRNA (F-met-tRNA) to the ribosome. It is also involved in polypeptide chain elongation. GTP is hydrolyzed by tubulin and its hydrolysis is accompanied by microtubule assembly. Guanosine 5-triphosphate trisodium salt up-regulates miRNA (specifically miR133a and miR133b) and myogenic regulator factor and induces human myogenic precursor cells to release exosomes stuffed with guanosine based molecules (mainly guanosine) in the extracellular milieu. - Guanosine 5-triphosphate (GTP) trisodium salt activates the signal transducing G proteins which are involved in various cellular processes including proliferation, differentiation and activation of several intracellular kinase cascades. Proliferation and apoptosis are regulated in part by the hydrolysis of GTP by small GTPases Ras and Rho. Another type of small GTPase, Rab, plays a role in the docking and fusion of vesicles and may also be involved in vesicle GTP functions as a carrier of phosphates and pyrophosphates involved in channeling chemical energy into specific biosynthetic pathways. It also serves as an energy-rich precursor of mononucleotide units in the enzymatic biosynthesis of DNA and RNA. GTP is involved in the initiation of peptide synthesis during the binding of formylmethionyl-tRNA (F-met-tRNA) to the ribosome. It is also involved in polypeptide chain elongation. GTP is hydrolyzed by tubulin and its hydrolysis is accompanied by microtubule assembly. Guanosine 5-triphosphate trisodium salt up-regulates miRNA (specifically miR133a and miR133b) and myogenic regulator factor and induces human myogenic precursor cells to release exosomes stuffed with guanosine based molecules (mainly guanosine) in the extracellular milieu.
- SMILESO[C@@H]1[C@H](O)[C@@H](COP(O)(OP(OP(O)([O-])=O)([O-])=O)=O)O[C@H]1N2C(N=C(N)NC3=O)=C3N=C2.[Na+].[Na+]
- Storage Instruction-20°C
- UNSPSC12352200


![Guanosine 5-triphosphate trisodium salt [36051-31-7]](https://www.targetmol.com/group3/M00/33/15/CgoaEWaPPR6EWW4eAAAAAAPwShE592.png)