HELLS antibody
GTX54157
ReactivityHuman
Product group Antibodies
TargetHELLS
Overview
- SupplierGeneTex
- Product NameHELLS antibody
- Delivery Days Customer7
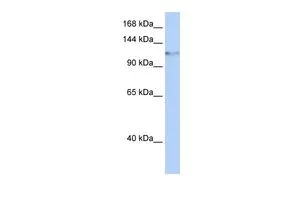
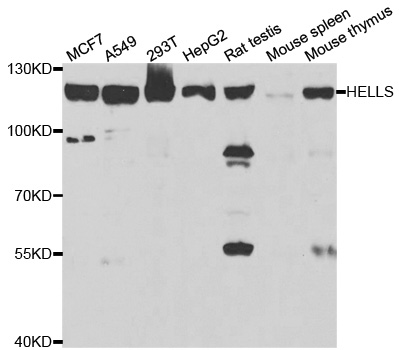
- Application Supplier NoteWB: 1:500 - 1:2000. IHC-P: 1:50 - 1:200. IP: 1:50 - 1:200. *Optimal dilutions/concentrations should be determined by the researcher.Not tested in other applications.
- CertificationResearch Use Only
- ClonalityPolyclonal
- Concentration1 mg/ml
- ConjugateUnconjugated
- Gene ID3070
- Target nameHELLS
- Target descriptionhelicase, lymphoid specific
- Target synonymsICF4, LSH, Nbla10143, PASG, SALNR, SMARCA6, lymphoid-specific helicase, SWI/SNF2-related, matrix-associated, actin-dependent regulator of chromatin, subfamily A, member 6, Senescence Associated Long Non-coding RNA, proliferation-associated SNF2-like protein
- HostRabbit
- IsotypeIgG
- Protein IDQ9NRZ9
- Protein NameLymphoid-specific helicase
- Scientific DescriptionThis gene encodes a lymphoid-specific helicase. Other helicases function in processes involving DNA strand separation, including replication, repair, recombination, and transcription. This protein is thought to be involved with cellular proliferation and may play a role in leukemogenesis. Alternatively spliced transcript variants encoding different isoforms have been identified. [provided by RefSeq, Jan 2014]
- ReactivityHuman
- Storage Instruction-20°C or -80°C,2°C to 8°C
- UNSPSC12352203
References
- Schuller S, Sieker J, Riemenschneider P, et al. HELLS Is Negatively Regulated by Wild-Type P53 in Liver Cancer by a Mechanism Involving P21 and FOXM1. Cancers (Basel). 2022,14(2). doi: 10.3390/cancers14020459Read this paper