HpARI (CCP1/2) (rec.) (His)
AG-40B-0201
Product group Proteins / Signaling Molecules
Overview
- SupplierAdipoGen Life Sciences
- Product NameHpARI (CCP1/2) (rec.) (His)
- Delivery Days Customer10
- CertificationResearch Use Only
- Concentration1 mg/ml
- Estimated Purity>90%
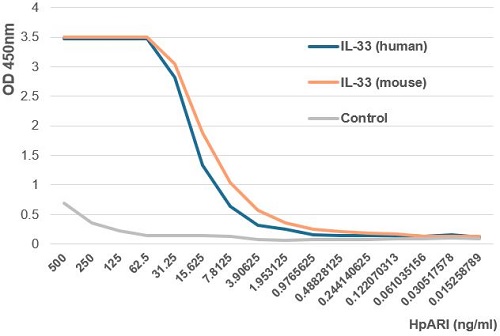
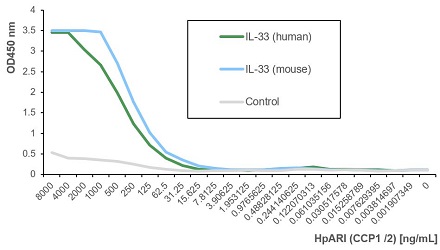
- Scientific DescriptionHpARI is a protein secreted by the mouse parasite Heligmosomoides polygyrus. The mature protein HpARI, containing three predicted Complement Control Protein (CCP)-like modules (also known as Short Consensus Repeats (SCRs) or sushi-domains), suppresses type 2 (allergic) immune responses through interference in the interleukin-33 (IL-33) pathway. During cell damage, HpARI gains access to the nucleus of necrotic cells, where it binds directly to IL-33 and nuclear DNA, preventing secretion and binding of IL-33 to its receptor. A non-natural truncation consisting of the first 2 domains of HpARI (CCP1/2) retains IL-33 and DNA binding capacity. HpARI (CCP1/2) is able to stabilize IL-33, increasing its half-life and amplifying its effects. HpARI (CCP1/2) increases IL-33 activity by protecting it from oxidation and proteolytic degradation. HpARI (CCP1/2) (rec.) (His) is a new type of reagent to study IL-33-mediated pathology in vivo. - Recombinant protein. Heligmosomoides polygyrus protein HpARI (aa 17-165) is fused at the C-terminus to a His-tag. Binds to human and mouse IL-33. Endotoxin: <0.01EU/microg purified protein (LAL test). Lyophilized. Contains PBS. HpARI is a protein secreted by the mouse parasite Heligmosomoides polygyrus. The mature protein HpARI, containing three predicted Complement Control Protein (CCP)-like modules (also known as Short Consensus Repeats (SCRs) or sushi-domains), suppresses type 2 (allergic) immune responses through interference in the interleukin-33 (IL-33) pathway. During cell damage, HpARI gains access to the nucleus of necrotic cells, where it binds directly to IL-33 and nuclear DNA, preventing secretion and binding of IL-33 to its receptor. A non-natural truncation consisting of the first 2 domains of HpARI (CCP1/2) retains IL-33 and DNA binding capacity. HpARI (CCP1/2) is able to stabilize IL-33, increasing its half-life and amplifying its effects. HpARI (CCP1/2) increases IL-33 activity by protecting it from oxidation and proteolytic degradation. HpARI (CCP1/2) (rec.) (His) is a new type of reagent to study IL-33-mediated pathology in vivo.
- Storage Instruction-20°C,2°C to 8°C
- UNSPSC41116120