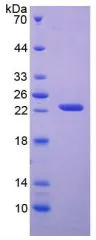
WB analysis of GTX00157-pro Human APRT protein.
Human APRT protein, His tag
GTX00157-PRO
Product group Molecular Biology
Overview
- SupplierGeneTex
- Product NameHuman APRT protein (active)
- Delivery Days Customer9
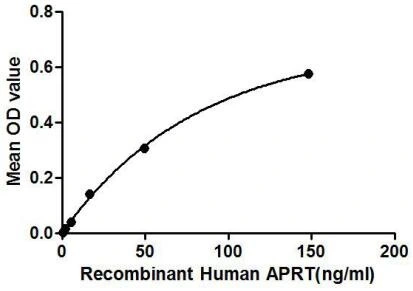
- Application Supplier NoteAdenine Phosphoribosyltransferase (APRT) is an enzyme involved in the purine nucleotide salvage pathway. It functions as a catalyst in the reaction between adenine and phosphoribosyl pyrophosphate (PRPP) to form AMP. Besides, Vascular Cell Adhesion Molecule 1 (VCAM1) has been identified as an interactor of APRT, thus a binding ELISA assay was conducted to detect the interaction of recombinant human APRT and recombinant human VCAM1. Briefly, APRT were diluted serially in PBS, with 0.01% BSA (pH 7.4). Duplicate samples of 100 microl were then transferred to VCAM1-coated microtiter wells and incubated for 2h at 37C. Wells were washed with PBST and incubated for 1h with anti-APRT pAb, then aspirated and washed 3 times. After incubation with HRP labelled secondary antibody, wells were aspirated and washed 3 times. With the addition of substrate solution, wells were incubated 15-25 minutes at 37C. Finally, add 50 microl stop solution to the wells and read at 450nm immediately. The binding activity of of APRT and VCAM1 was in a dose dependent manner.
- ApplicationsFunctional Assay
- CertificationResearch Use Only
- ConjugateUnconjugated
- Scientific DescriptionAdenine phosphoribosyltransferase belongs to the purine/pyrimidine phosphoribosyltransferase family. A conserved feature of this gene is the distribution of CpG dinucleotides. This enzyme catalyzes the formation of AMP and inorganic pyrophosphate from adenine and 5-phosphoribosyl-1-pyrophosphate (PRPP). It also produces adenine as a by-product of the polyamine biosynthesis pathway. A homozygous deficiency in this enzyme causes 2,8-dihydroxyadenine urolithiasis. Two transcript variants encoding different isoforms have been found for this gene. [provided by RefSeq, Jul 2008]
- Storage Instruction-20°C or -80°C,2°C to 8°C
- UNSPSC12352204