Human C Peptide ELISA Kit
ARG80782
Product group Assays
Overview
- SupplierArigo Biolaboratories
- Product NameHuman C Peptide ELISA Kit
- Delivery Days Customer23
- ApplicationsELISA
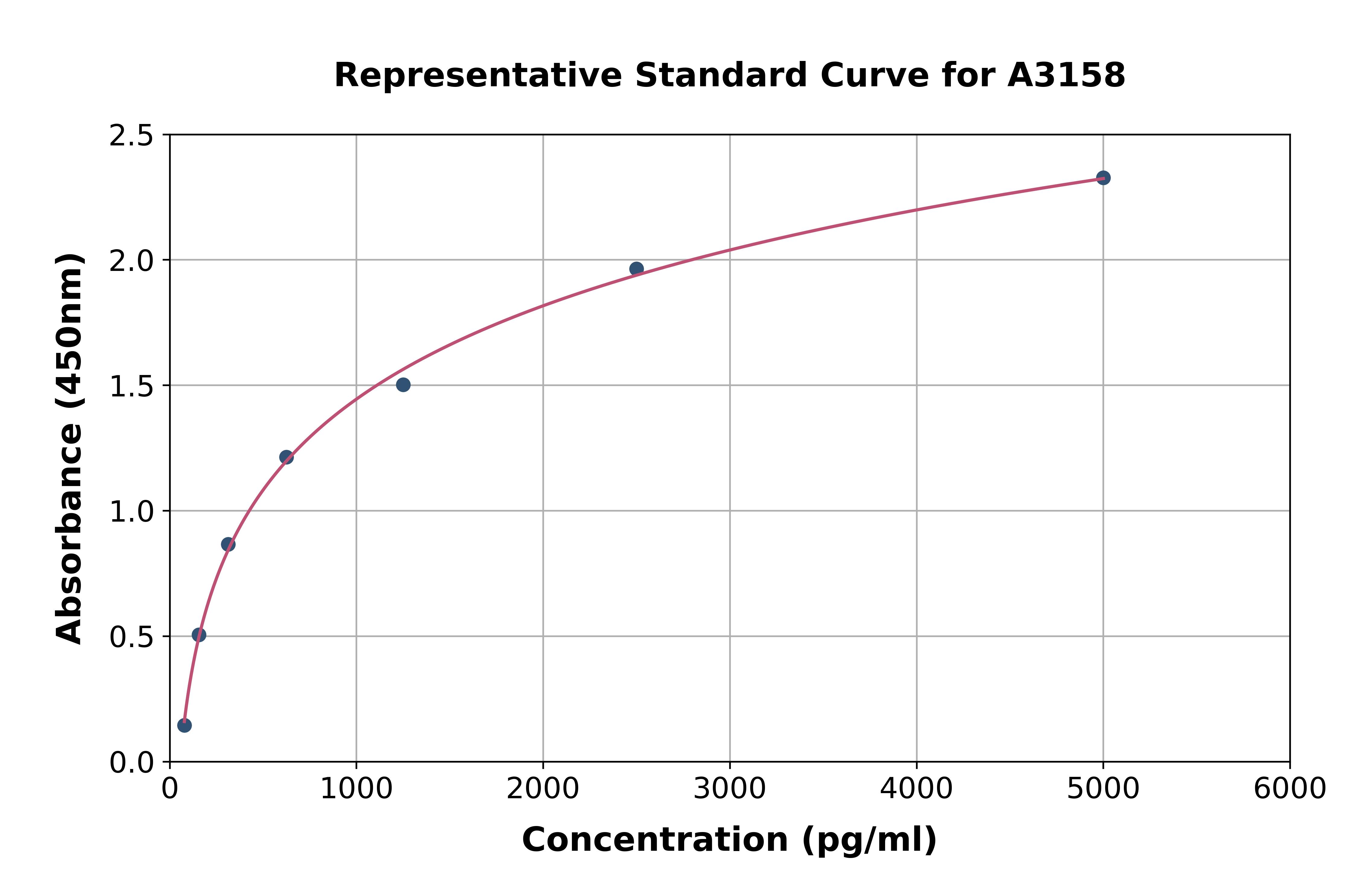
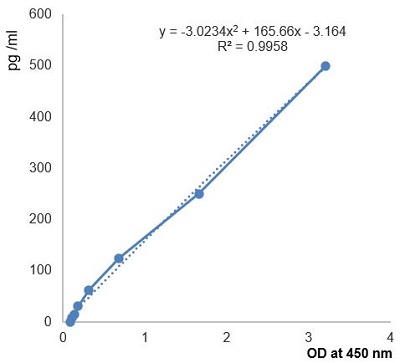
- Assay Sensitivity0.064 ng/ml
- Assay Time5 min, 3 h, 1 h, 30 min
- CertificationResearch Use Only
- ConjugateHRP
- Protein IDP01308
- Protein NameInsulin
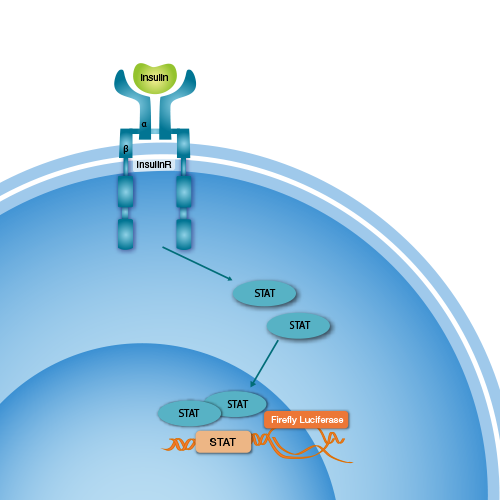
- Scientific DescriptionInsulin is synthesized in the pancreatic beta cells as a 6000 MW component of an 86 amino acid polypeptide called proinsulin. Proinsulin is subsequently cleaved enzymatically, releasing insulin into the circulation along with a residual 3000 MW fragment called connection (C) peptide, so-named because it connects A and B chains of insulin within the proinsulin molecule. Human C-Peptide, a 31 amino acid residue peptide, has a molecular mass of approximately 3000 daltons. C-Peptide has no metabolic function. However, since C-Peptide and insulin are secreted in equimolar amounts, the immunoassay of C-Peptide permits the quantitation of insulin secretion. This is the reason for the clinical interest of serum and urinary determinations of C-Peptide. Moreover, C-Peptide measurement has several advantages over immunoassays of insulin. The half-life of C-Peptide in the circulation is between two and five times longer than that of insulin. Therefore, C-Peptide levels are a more stable indicator of insulin secretion than the more rapidly changing levels of insulin. A very clear practical advantage of C-Peptide measurement arising from its relative metabolic inertness as compared to insulin is that C-Peptide levels in peripheral venous blood are about 5-6 times greater than insulin levels. Also, relative to an insulin assay, the C-Peptide assays advantage is its ability to distinguish endogenous from injected insulin. Thus, low C-Peptide levels are to be expected when insulin is diminished (as in insulin-dependent diabetes) or suppressed (as a normal response to exogenous insulin), whereas elevated C-Peptide levels may result from the increased beta-cell activity observed in insulinomas. C-Peptide has also been measured as an additional means for evaluating glucose tolerance and glibenclamide glucose tests. C-Peptide levels are in many ways a better measurement of endogenous insulin secretion than peripheral insulin levels. C-Peptide may be measured in either blood or urine. With improved sensitive C-Peptide immunoassays, it is now possible to measure C-Peptide values at extremely low levels. The clinical indications for C-Peptide measurement include diagnosis of insulinoma and differentation from factitious hypoglycemia, follow-up of pancreatectomy, and evaluation of viability of islet cell transplants. Recently, these indications have been dramatically expanded to permit evaluation of insulin dependence in maturity onset diabetes mellitus. Clinical Indications for the C-Peptide ELISA - Assessment of residual beta-cell function in diabetics under insulin therapy - Detection and monitoring of the remission phase of type I diabetes - Adjunct in the differential diagnosis between type I (insulin dependent) and type II (non-insulin-dependent) diabetes - Diagnosis of insulin-induced factitious hypoglycemia. - Contribution to the diagnosis of insulinoma (insulin suppression test) - Prognostic index of fetal outcome in pregnant diabetic women - Evaluation of insulin secretion in liver disease - Monitoring of pancreasectomy
- Storage Instruction2°C to 8°C
- UNSPSC41116100
- SpeciesHuman