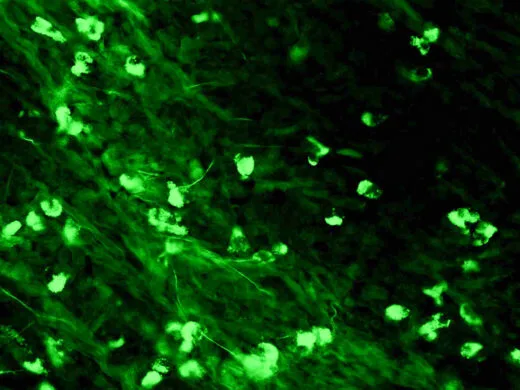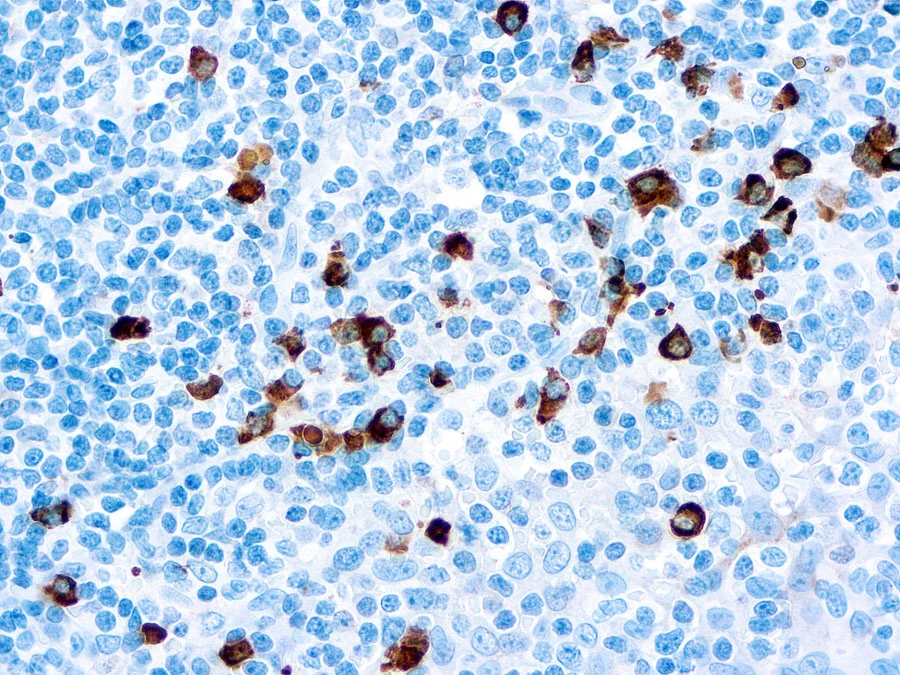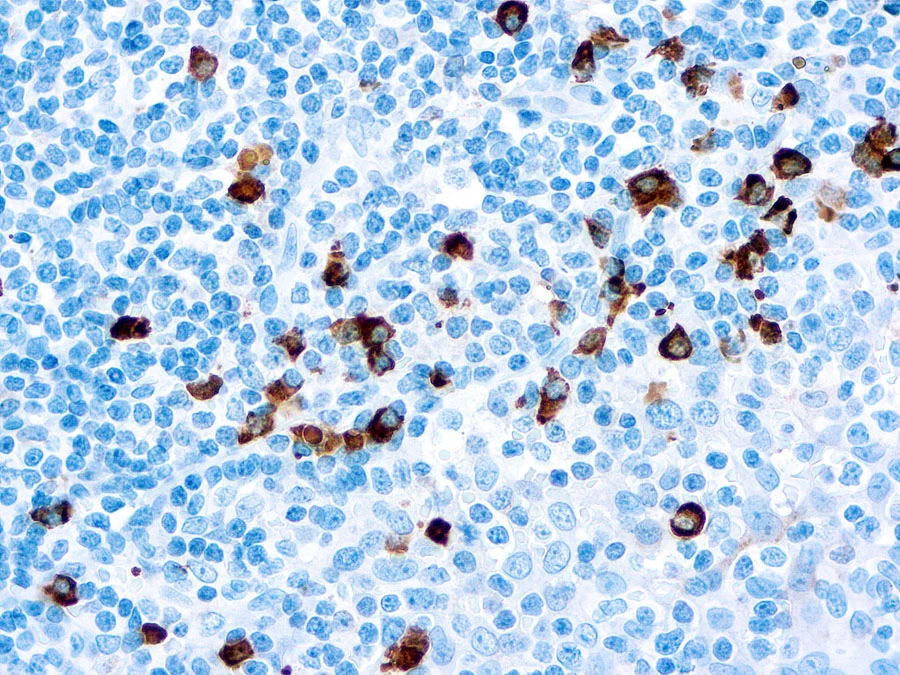
IHC-P analysis of human tonsil tissue using GTX22411 Human IgA antibody.
Rabbit Anti-Human IgA antibody
GTX22411
ApplicationsImmunoHistoChemistry, ImmunoHistoChemistry Paraffin
Product group Antibodies
ReactivityHuman
TargetIGH
Overview
- SupplierGeneTex
- Product NameRabbit Anti-Human IgA antibody
- Delivery Days Customer9
- Application Supplier NoteIHC-P: 1:25-1:100. *Optimal dilutions/concentrations should be determined by the researcher.Not tested in other applications.
- ApplicationsImmunoHistoChemistry, ImmunoHistoChemistry Paraffin
- CertificationResearch Use Only
- ClonalityPolyclonal
- ConjugateUnconjugated
- Gene ID3492
- Target nameIGH
- Target descriptionimmunoglobulin heavy locus
- Target synonymsIGD1, IGH.1@, IGH@, IGHD@, IGHDY1, IGHJ, IGHJ@, IGHV, IGHV@, D (diversity) region of heavy chains, J (joining) region of heavy chains, immunglobulin heavy chain variable region, immunoglobulin heavy diversity cluster, immunoglobulin heavy diversity group, immunoglobulin heavy diversity locus, immunoglobulin heavy joining cluster, immunoglobulin heavy joining group, immunoglobulin heavy polypeptide, joining region, immunoglobulin heavy variable cluster, immunoglobulin heavy variable group
- HostRabbit
- IsotypeIgG
- Scientific DescriptionImmunoglobulins recognize foreign antigens and initiate immune responses such as phagocytosis and the complement system. Each immunoglobulin molecule consists of two identical heavy chains and two identical light chains. This region represents the germline organization of the heavy chain locus. The locus includes V (variable), D (diversity), J (joining), and C (constant) segments. During B cell development, a recombination event at the DNA level joins a single D segment with a J segment; this partially rearranged D-J gene is then joined to a V segment. The rearranged V-D-J is then transcribed with the IGHM constant region; this transcript encodes a mu heavy chain. Later in development B cells generate V-D-J-Cmu-Cdelta pre-messenger RNA, which is alternatively spliced to encode either a mu or a delta heavy chain. Mature B cells in the lymph nodes undergo switch recombination, so that the V-D-J gene is brought in proximity to one of the IGHG, IGHA, or IGHE genes and each cell expresses either the gamma, alpha, or epsilon heavy chain. Recombination of many different V segments with several J segments provides a wide range of antigen recognition. Additional diversity is attained by junctional diversity, resulting from the random addition of nucleotides by terminal deoxynucleotidyltransferase, and by somatic hypermutation, which occurs during B cell maturation in the spleen and lymph nodes. Due to polymorphism, the numbers of functional V, J, and D genes differ among individuals and some V, D, J, and C segments may be pseudogenes. [provided by RefSeq, Dec 2017]
- ReactivityHuman
- Storage Instruction2°C to 8°C
- UNSPSC41116161
References
- Decreased humoral immune response in the bronchi of rapid decliners with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease.Read this paper