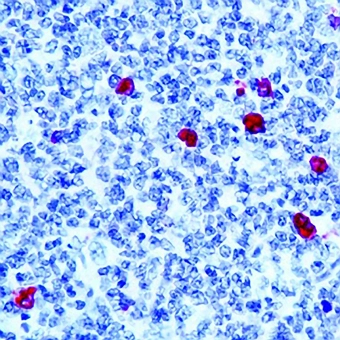
IHC-P analysis of human tonsil tissue using GTX17150 Human IgM antibody.
Rabbit Anti-Human IgM antibody
GTX17150
ApplicationsImmunoHistoChemistry, ImmunoHistoChemistry Paraffin
Product group Antibodies
ReactivityHuman
TargetIGHM
Overview
- SupplierGeneTex
- Product NameRabbit Anti-Human IgM antibody
- Delivery Days Customer9
- Application Supplier NoteIHC-P: 1:50-1:250. *Optimal dilutions/concentrations should be determined by the researcher.Not tested in other applications.
- ApplicationsImmunoHistoChemistry, ImmunoHistoChemistry Paraffin
- CertificationResearch Use Only
- ClonalityPolyclonal
- ConjugateUnconjugated
- Gene ID3507
- Target nameIGHM
- Target descriptionimmunoglobulin heavy constant mu
- Target synonymsAGM1, MU, VH, constant region of heavy chain of IgM, immunoglobulin mu chain
- HostRabbit
- IsotypeIgG
- Scientific DescriptionImmunoglobulins (Ig) are the antigen recognition molecules of B cells. An Ig molecule is made up of 2 identical heavy chains and 2 identical light chains (see MIM 147200) joined by disulfide bonds so that each heavy chain is linked to a light chain and the 2 heavy chains are linked together. Each Ig heavy chain has an N-terminal variable (V) region containing the antigen-binding site and a C-terminal constant (C) region, encoded by an individual C region gene, that determines the isotype of the antibody and provides effector or signaling functions. The heavy chain V region is encoded by 1 each of 3 types of genes: V genes (see MIM 147070), joining (J) genes (see MIM 147010), and diversity (D) genes (see MIM 146910). The C region genes are clustered downstream of the V region genes within the heavy chain locus on chromosome 14. The IGHM gene encodes the C region of the mu heavy chain, which defines the IgM isotype. Naive B cells express the transmembrane forms of IgM and IgD (see IGHD; MIM 1471770) on their surface. During an antibody response, activated B cells can switch to the expression of individual downstream heavy chain C region genes by a process of somatic recombination known as isotype switching. In addition, secreted Ig forms that act as antibodies can be produced by alternative RNA processing of the heavy chain C region sequences. Although the membrane forms of all Ig isotypes are monomeric, secreted IgM forms pentamers, and occasionally hexamers, in plasma (summary by Janeway et al., 2005).[supplied by OMIM, Aug 2010]
- ReactivityHuman
- Storage Instruction2°C to 8°C
- UNSPSC41116161