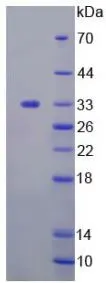
WB analysis of GTX00184-pro Human Tyrosine Aminotransferase protein.
Human Tyrosine Aminotransferase protein, His tag
GTX00184-PRO
Product group Molecular Biology
Overview
- SupplierGeneTex
- Product NameHuman Tyrosine Aminotransferase protein (active)
- Delivery Days Customer9
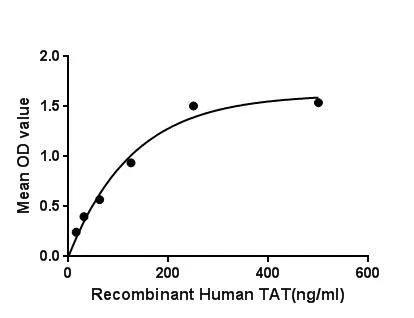
- Application Supplier NoteTyrosine aminotransferase (TAT) is an enzyme present in the liver and catalyzes the conversion of tyrosine to 4-hydroxyphenylpyruvate. In humans, the tyrosine aminotransferase protein is encoded by the TAT gene. A deficiency of the enzyme in humans can result in what is known as Type II Tyrosinemia, wherein there is an abundance of tyrosine as a result of tyrosine failing to undergo an aminotransferase reaction to form 4-hydroxyphenylpyruvate. Tyrosine Aminotransferase as a dimer has two identical active sights. Lys280 is attached to PLP, which is held in place via two nonpolar amino acid side chains; phenylalanine and isoleucine (see thumbnail on right). The PLP is also held in place by hydrogen bonding to surrounding molecules mainly by its phosphate group. Besides, Heat Shock 70kDa Protein 8 (HSPA8) has been identified as an interactor of TAT, thus a binding ELISA assay was conducted to detect the interaction of recombinant human TAT and recombinant human HSPA8. Briefly, TAT were diluted serially in PBS, with 0.01% BSA (pH 7.4). Duplicate samples of 100 microl were then transferred to HSPA8-coated microtiter wells and incubated for 2h at 37C. Wells were washed with PBST and incubated for 1h with anti-TAT pAb, then aspirated and washed 3 times. After incubation with HRP labelled secondary antibody, wells were aspirated and washed 3 times. With the addition of substrate solution , wells were incubated 15-25 minutes at 37C. Finally, add 50 microl stop solution to the wells and read at 450nm immediately. The binding activity of TAT and HSPA8 was in a dose dependent manner.
- ApplicationsFunctional Assay
- CertificationResearch Use Only
- ConjugateUnconjugated
- Scientific DescriptionThis nuclear gene encodes a mitochondrial protein tyrosine aminotransferase which is present in the liver and catalyzes the conversion of L-tyrosine into p-hydroxyphenylpyruvate. Mutations in this gene cause tyrosinemia (type II, Richner-Hanhart syndrome), a disorder accompanied by major skin and corneal lesions, with possible cognitive disability. A regulator gene for tyrosine aminotransferase is X-linked. [provided by RefSeq, Jul 2008]
- Storage Instruction-20°C or -80°C,2°C to 8°C
- UNSPSC12352204