Chemical Structure
Hyperforin . DCHA
AG-CN2-0008
CAS Number238074-03-8
Product group Chemicals
Estimated Purity>97%
Molecular Weight535.8 . 182.3
Overview
- SupplierAdipoGen Life Sciences
- Product NameHyperforin . DCHA
- Delivery Days Customer10
- CAS Number238074-03-8
- CertificationResearch Use Only
- Estimated Purity>97%
- Hazard InformationWarning
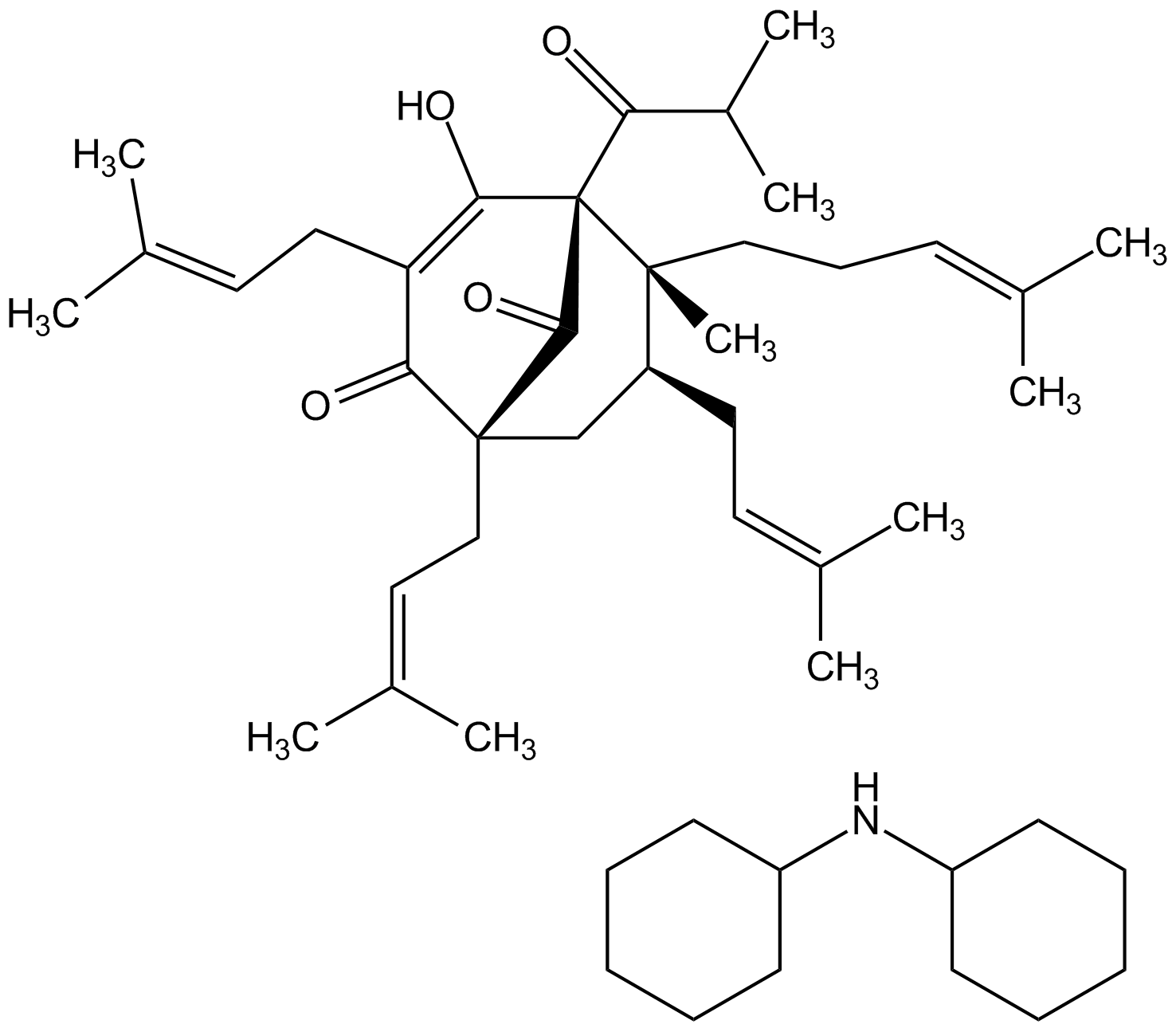
- Molecular FormulaC35H51O4 . C12H24N
- Molecular Weight535.8 . 182.3
- Scientific DescriptionChemical. CAS: 238074-03-8. Formula: C35H51O4 . C12H24N. MW: 535.8 . 182.3. Isolated from St. Johns wort (Hypericum perforatum). Key constituent of St. Johns wort. Shows properties of potential pharmacological interest, including antibacterial, anti-malarial, anti-inflammatory, anti-cancer and anti-angiogenic effects. Anti-depressant and anxiolytic compound. Specific activator of TRPC6 channels. Inhibits the re-uptake of neurotransmitters in synapses (serotonin, norepinephrine, dopamine, GABA, glutamate). Activator of the pregnane X receptor (PXR). Regulates expression of the cytochrome P450 CYP3A4 and CYP2C9 and hepatic drugs metabolism. Potential anti-Alzheimer compound. Potent SIRT1 (sirtuin 1) and SIRT2 (sirtuin 2) inhibitor. - Key constituent of St. Johns wort. Shows properties of potential pharmacological interest, including antibacterial [1], anti-malarial [13], anti-inflammatory [7, 14], anti-cancer and anti-angiogenic effects [5, 10]. Anti-depressant and anxiolytic compound [3]. Specific activator of TRPC6 channels [11]. Inhibits the re-uptake of neurotransmitters in synapses (serotonin, norepinephrine, dopamine, GABA, glutamate) [4]. Activator of the pregnane X receptor (PXR) [2]. Regulates expression of the cytochrome P450 CYP3A4 and CYP2C9 and hepatic drugs metabolism [8]. Potential anti-Alzheimer compound [6, 9, 15]. Potent SIRT1 (sirtuin 1) and SIRT2 (sirtuin 2) inhibitor [12]. Based on the anti-inflammatory activity of Hyperforin and its simultaneous blockade of multiple signaling pathways, such as IFN-gamma/IL-1beta/TNF-alpha, JAK/STAT, NF-kappaB and MAPK it has been suggested a valuable agent for cytokine storm treatment during COVID-19 [16].
- SMILESC1CCC(CC1)NC1CCCCC1.CC(C)C(=O)[C@@]12C(O)=C(CC=C(C)C)C(=O)[C@@](CC=C(C)C)(C[C@H](CC=C(C)C)[C@@]1(C)CCC=C(C)C)C2=O
- Storage Instruction-20°C,2°C to 8°C
- UNSPSC12352200

![Hyperforin dicyclohexylammonium salt [238074-03-8]](https://www.targetmol.com/group3/M00/36/1D/CgoaEGayOFKEYjTeAAAAAO2AdJ0920.png)
