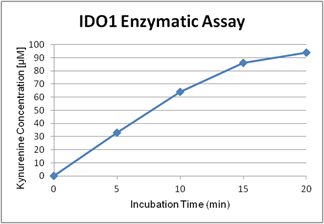
Activity assay figure of IDO (human) (rec.) (His) (highly active) (AG-40B-0161). IDO (human) has been tested with a protocol using catalase (see our website). The specific activity has been calculated to be >100000U/mg protein with L-tryptophan as substr
IDO1 (human) (rec.) (His) (highly active)
AG-40B-0161
Overview
- SupplierAdipoGen Life Sciences
- Product NameIDO1 (human) (rec.) (His) (highly active)
- Delivery Days Customer10
- CertificationResearch Use Only
- Estimated Purity>90%
- Protein IDP14902
- Protein NameIndoleamine 2,3-dioxygenase 1
- Scientific DescriptionIDO1 is a heme enzyme that catalyzes the first and rate-limiting step in the main pathway of human tryptophan catabolism, the kynurenine pathway, causing depletion of tryptophan which can lead to halted growth of microbes as well as T cells. IDO1 is an immune checkpoint protein, thought to play a role in a variety of pathophysiological processes such as antimicrobial and antitumor defense, neuropathology, immunoregulation and antioxidant activity. Cancer cells are able to evade the immune system is by hijacking the checkpoint proteins. Increased IDO1 protein levels drive growth arrest and apoptosis of the effector T cells, a group of immune cells that mediate the immune systems ability to destroy pathogens. By reducing the number of effector T cells, IDO1 overexpression prevents the immune system from effectively destroying cancer cells. IDO1 overexpression has been observed in a wide range of human cancers such as prostatic, colorectal, pancreatic, cervical, gastric, ovarian, head or lung cancer. Physiological IDO1 activity has been implicated in T cell tolerance to tumors, dysfunctional selftolerance in non-obese diabetic (NOD) mice, and as a protective negative regulator in autoimmune disorders. Biological active IDO1 enzyme can be used for screening of IDO1 inhibitors, which have shown promising antitumor activity and appear to be synergistic in combination with chemotherapy and other forms of immunotherapy. - Protein. Human IDO (aa 1-403) is fused at the N-terminus to a His-tag. Source: E. coli. Endotoxin content: 90% (SDS-PAGE). IDO is a heme enzyme that catalyzes the first and rate-limiting step in the main pathway of human tryptophan catabolism, the kynurenine pathway, causing depletion of tryptophan which can lead to halted growth of microbes as well as T cells. IDO is an immune checkpoint protein, thought to play a role in a variety of pathophysiological processes such as antimicrobial and antitumor defense, neuropathology, immunoregulation and antioxidant activity. Cancer cells are able to evade the immune system is by hijacking the checkpoint proteins. Increased IDO protein levels drive growth arrest and apoptosis of the effector T cells, a group of immune cells that mediate the immune systems ability to destroy pathogens. By reducing the number of effector T cells, IDO overexpression prevents the immune system from effectively destroying cancer cells. IDO overexpression has been observed in a wide range of human cancers such as prostatic, colorectal, pancreatic, cervical, gastric, ovarian, head or lung cancer. Physiological IDO activity has been implicated in T cell tolerance to tumors, dysfunctional selftolerance in non-obese diabetic (NOD) mice, and as a protective negative regulator in autoimmune disorders. Biological active IDO enzyme can be used for screening of IDO inhibitors, which have shown promising antitumor activity and appear to be synergistic in combination with chemotherapy and other forms of immunotherapy.
- Storage Instruction-20°C,-80°C
- UNSPSC12352202