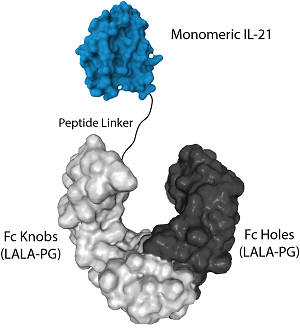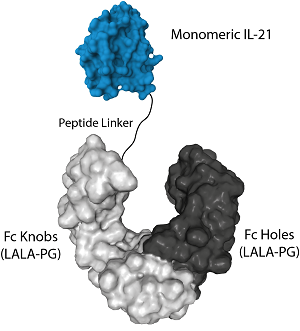
Protein structure of IL-21 (mouse) (monomeric):Fc (LALA-PG)-KIH (human) (rec.) (Prod. No. AG-40B-0250).
IL-21 (mouse) (monomer):Fc (silent) InVivoKine(tm)
AG-40B-0250
Protein IDQ9ES17
Product group Proteins / Signaling Molecules
Overview
- SupplierAdipoGen Life Sciences
- Product NameIL-21 (mouse) (monomer):Fc (silent) InVivoKine(tm)
- Delivery Days Customer10
- CertificationResearch Use Only
- Concentration1 mg/ml
- Estimated Purity>95%
- Gene ID60505
- Target nameIl21
- Target descriptioninterleukin 21
- Target synonymsIL-21, interleukin-21
- Protein IDQ9ES17
- Protein NameInterleukin-21
- Scientific DescriptionIL-21 is a monomeric 15 kDa cytokine, identified as a multifunctional cytokine principally produced by follicular helper T (Tfh), T helper 17 (Th17) and natural killer (NK) cells, but also by CD8+ T cells. As a receptor for IL-21, IL-21R, a class I cytokine heterodimeric receptor, shares a common cytokine receptor gamma chain with other cytokine families, including IL-2, IL-4, IL-7, IL-9 and IL-15. The IL-21 receptor (IL-21R) is heterodimeric (composed of an alpha and -chain) and physiologically expressed on immune cells (T and B cells, macrophages, DCs, thymocytes and splenocytes). Upon binding to its receptor, IL-21 induces strong and sustained activation of STAT3, which is critical for its effects on B cell and T cell differentiation. IL-21 produced by follicular helper CD4 T cells (TFH) acts directly on B cells to generate high-affinity, class-switched antibodies. IL-21 is important for the maturation of T and B cells in Germinal Centers (GCs) and supports the formation of antigen-specific memory B cells and long-lived plasma cells. The formation of Th17 cells is promoted by IL-21. IL-21 is an important key factor in chronic inflammatory and in autoantibody-mediated skin diseases, where Th17, Th1, Tfh or B cells are critically involved. IL-21 is a promising immunotherapeutic agent for cancer. CD8 T cells expressing IL-21R fight cancer and drive autoimmune disease. IL-21 promotes maturation, enhances cytotoxicity, and induces the production of IFN- gamma and perforin by NK cells. IL-21 is known to directly induce apoptosis in certain types of lymphoma. Finally, IL-21 is used in adoptive transfer of in vitro expanded tumor antigen-specific CD8 + T cells (TILs cells) and IL-21 induced a long-lived memory phenotype compared to the cells not treated with IL-21. The IL-21 (mouse) (monomer):Fc (silent) InVivoKine™ is produced by using two different vectors, one encoding for the IL-21 (mouse):Fc (LALA-PG) Knobs sequence (synthesizing a protein of 54kDa) and one encoding for the Fc (LALA-PG) Holes sequence (synthesizing a protein of 28kDa). Both vectors transfected into CHO cells produce both Fc (LALA-PG) molecules (Knobs-into-Holes technology; J.B. Ridgway, et al.; Protein Eng. 9, 617 (1996)) required for dimerization of the Fc moieties and for secretion of the final protein IL-21 (mouse) (monomer):Fc (silent) InVivoKine™. The LALA-PG mutations inhibit binding to FcgammaRs and C1q while FcRn binding and Fc stability remain unaffected. InVivoKines™ are a new generation of recombinant fusion proteins for immunotherapeutic, preclinical and translational in vivo research, developed and manufactured by AdipoGen Life Sciences. - InVivoKines™. Recombinant Protein. Mouse IL-21 (aa 18-146) is fused at the C-terminus to the Fc portion of human IgG1 (LALA-PG) (Knobs-into-Holes technology) (see reference: J.B. Ridgway, et al.; Protein Eng. 9, 617 (1996)). Endotoxin: <0.02EU/microg protein (LAL test).. Lyophilized. Contains PBS. IL-21 is a monomeric 15 kDa cytokine, identified as a multifunctional cytokine principally produced by follicular helper T (Tfh), T helper 17 (Th17) and natural killer (NK) cells, but also by CD8+ T cells. As a receptor for IL-21, IL-21R, a class I cytokine heterodimeric receptor, shares a common cytokine receptor gamma chain with other cytokine families, including IL-2, IL-4, IL-7, IL-9 and IL-15. The IL-21 receptor (IL-21R) is heterodimeric (composed of an alpha and -chain) and physiologically expressed on immune cells (T and B cells, macrophages, DCs, thymocytes and splenocytes). Upon binding to its receptor, IL-21 induces strong and sustained activation of STAT3, which is critical for its effects on B cell and T cell differentiation. IL-21 produced by follicular helper CD4 T cells (TFH) acts directly on B cells to generate high-affinity, class-switched antibodies. IL-21 is important for the maturation of T and B cells in Germinal Centers (GCs) and supports the formation of antigen-specific memory B cells and long-lived plasma cells. The formation of Th17 cells is promoted by IL-21. IL-21 is an important key factor in chronic inflammatory and in autoantibody-mediated skin diseases, where Th17, Th1, Tfh or B cells are critically involved. IL-21 is a promising immunotherapeutic agent for cancer. CD8 T cells expressing IL-21R fight cancer and drive autoimmune disease. IL-21 promotes maturation, enhances cytotoxicity, and induces the production of IFN- gamma and perforin by NK cells. IL-21 is known to directly induce apoptosis in certain types of lymphoma. Finally, IL-21 is used in adoptive transfer of in vitro expanded tumor antigen-specific CD8 + T cells (TILs cells) and IL-21 induced a long-lived memory phenotype compared to the cells not treated with IL-21. The protein IL-21 (mouse) (monomeric):Fc (LALA-PG)-KIH (human) (rec.) is produced by using two different vectors, one encoding for the IL-21 (mouse):Fc (LALA-PG) Knobs sequence (synthesizing a protein of 60kDa) and one encoding for the Fc (LALA-PG) Holes sequence (synthesizing a protein of 28kDa). Both vectors transfected into CHO cells produce both Fc (LALA-PG) molecules (Knobs-into-Holes technology; J.B. Ridgway, et al.; Protein Eng. 9, 617 (1996)) required for dimerization of the Fc moieties and for secretion of the final protein IL-21 (mouse) (monomeric):Fc (LALA-PG)-KIH (human). The LALA-PG mutations inhibit binding to FcgammaRs and C1q while FcRn binding and Fc stability remain unaffected.
- Storage Instruction-20°C,2°C to 8°C
- UNSPSC41116120
- SpeciesMouse