Products
Are you looking for life science and diagnostic reagents? We offer one of the most extensive ranges in the Benelux. There are currently more than 8 million products in our webshop, which are manufactured by more than 130 suppliers. We hope to support your research with everything you need.
Product group Antibodies
anti-Adiponectin (human), mAb (HADI 773)AG-20A-0001
ApplicationsWestern Blot, ELISA, ImmunoHistoChemistry
ReactivityHuman
TargetADIPOQ
- SizePrice
Product group Antibodies
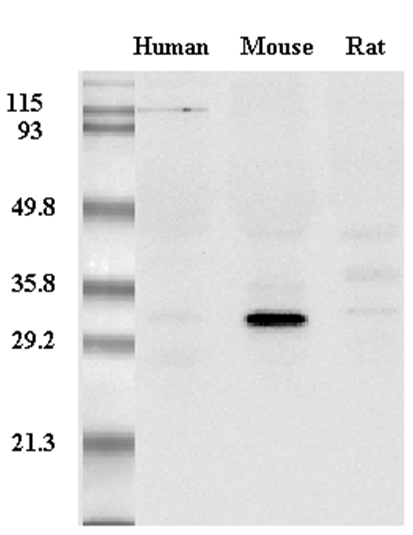
anti-Adiponectin (mouse), mAb (MADI 1147)AG-20A-0003
ApplicationsImmunoPrecipitation, Western Blot, ELISA
ReactivityMouse
TargetAdipoq
- SizePrice
Didn't find what you were looking for?
Search through our product groups to find the right product
Back to overview