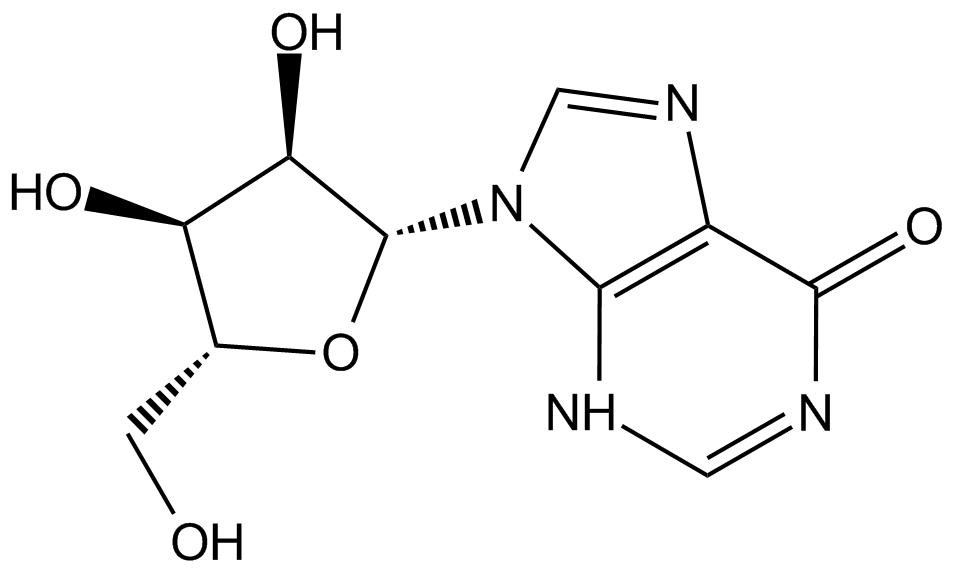
Chemical Structure
Inosine [58-63-9]
AG-CR1-3554
CAS Number58-63-9
Product group Chemicals
Estimated Purity>98%
Molecular Weight268.2
Overview
- SupplierAdipoGen Life Sciences
- Product NameInosine [58-63-9]
- Delivery Days Customer10
- CAS Number58-63-9
- CertificationResearch Use Only
- Estimated Purity>98%
- Molecular FormulaC10H12N4O5
- Molecular Weight268.2
- Scientific DescriptionChemical. CAS: 58-63-9. Formula: C10H12N4O5. MW: 268.2. Inosine, an intermediate in purine metabolism, consists of hypoxanthine and ribose. It is an inert purine nucleoside formed by breakdown of adenosine (deamination, known as A-to-I editing that occurs in tRNA and mRNA) or also is generated by the action of 5-nucleotidase on inosine monophosphate (IMP). Inosine has neuroprotective, cardioprotective, immunomodulatory, anti-tumor and anti-inflammatory effects in different experimental models. Inosine functions are mediated in receptor-dependent or-independent manners. The receptor-mediated function of inosine is thought to be related to adenosine receptor family members including A1, A2A, A2B, and A3 G-protein coupled receptors. It is an agonist for adenosine A1 (A1R) and A2A (A2AR) receptors. Inosine is released from brown adipocytes (BAs) upon stress. Inosine activates purinergic P1 receptors, triggering BA activation and white adipocyte browning. Consequently, inosine increases whole-body energy consumption and alleviates diet-induced obesity in mice. Inosine and other closely related purines might be a novel approach to tackle obesity and associated metabolic disorders by enhancing energy expenditure. Inosine is a potent activator of brown adipose tissue and energy homeostasis. - Inosine, an intermediate in purine metabolism, consists of hypoxanthine and ribose. It is an inert purine nucleoside formed by breakdown of adenosine (deamination, known as A-to-I editing that occurs in tRNA and mRNA) or also is generated by the action of 5-nucleotidase on inosine monophosphate (IMP). Inosine has neuroprotective, cardioprotective, immunomodulatory, anti-tumor and anti-inflammatory effects in different experimental models. Inosine functions are mediated in receptor-dependent or-independent manners. The receptor-mediated function of inosine is thought to be related to adenosine receptor family members including A1, A2A, A2B, and A3 G-protein coupled receptors. It is an agonist for adenosine A1 (A1R) and A2A (A2AR) receptors. Inosine is released from brown adipocytes (BAs) upon stress. Inosine activates purinergic P1 receptors, triggering BA activation and white adipocyte browning. Consequently, inosine increases whole-body energy consumption and alleviates diet-induced obesity in mice. Inosine and other closely related purines might be a novel approach to tackle obesity and associated metabolic disorders by enhancing energy expenditure. Inosine is a potent activator of brown adipose tissue and energy homeostasis.
- SMILESO[C@H]([C@@H](CO)O1)[C@@H](O)[C@@H]1N2C=NC3=C2NC=NC3=O
- Storage InstructionRT
- UNSPSC12352200


![Inosine [58-63-9]](https://www.targetmol.com/group3/M00/34/8C/CgoaEWarhc6EH1qgAAAAADiZKhU788.png)