Chemical Structure
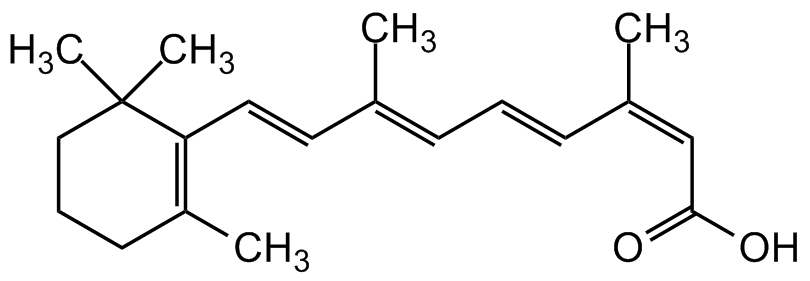
Isotretinoin [4759-48-2]

AG-CR1-3709
Overview
- SupplierAdipoGen Life Sciences
- Product NameIsotretinoin [4759-48-2]
- Delivery Days Customer10
- CAS Number4759-48-2
- CertificationResearch Use Only
- Estimated Purity>98%
- Hazard InformationDanger
- Molecular FormulaC20H28O2
- Molecular Weight300.4
- Scientific DescriptionChemical. CAS: 4759-48-2. Formula: C20H28O2. MW: 300.4. Vitamin A analog that inhibits cell proliferation and induces cell differentiation. It is converted in vivo into all-trans retinoic acid and has diverse biological activities. Anti-inflammatory agent used for severe acne treatment. Inhibits proliferation of primary human sebocytes by inducing cell-cycle arrest and inhibiting DNA synthesis. Amplifies production of neutrophil gelatinase-associated lipocalin (NGAL) in the skin, which has been shown to reduce sebum production by inducing apoptosis in sebaceous gland cells, while exhibiting an antimicrobial effect on Propionibacterium acnes. Decreases the size and sebum output of the sebaceous glands. It also decreases triglyceride, stearyl ester and free fatty acid synthesis and modulates keratin expression in primary human sebocyte. Isotretinoin produces significant anti-inflammatory effects by inhibition of monocyte and neutrophil chemotaxis across intact biological barriers in vivo. Shown to have anti-tumor activity, mediated through RAR-beta and RAR-alpha receptors (low affinity). Induces mitochondrial membrane permeability transition, observed as swelling and as a decrease in membrane potential and stimulates the release of cytochrome c implicating mechanisms through the apoptosis pathway. Induces apoptosis in various cells. Cell death may be induced in the meibomian glands, hypothalamic cells, hippocampus cells and in sebaceous gland cells (important for acne treatment). Downregulated telomerase and hTERT, inhibiting cellular immortalization and tumorigenesis. Inhibits the action of the metalloprotease MMP-9 (gelatinase) in sebum without any influence in the action of TIMP1 and TIMP2 (the tissue inhibitors of metalloproteases). Promotes neurite outgrowth, cell differentiation and inhibits proliferation in a neuroblastoma cell line. Shown to have neurological effects, by binding to dopaminergic receptors in the central nervous system that may affect dopaminergic neurotransmission by disrupting the structure of dopamine receptors and decreasing dopaminergic activity. Also affects the serotonergic system by increasing expression of 5-HT1A receptors in the pre-synaptic neuron, which inhibit serotonin secretion. Additional effects on CNS involve the modulation of the retinoic acid function in the hypothalamus, the hormone regulatory centre of the brain and part of the hypothalamus-pituitary-adrenal axis, a key part of the bodys stress response. Inducer of resistin-like molecule alpha (RELM-alpha) expression in epidermis, regulating skin immunity. The function of RELM-alpha is to kill bacteria of the skin via membrane disruption. - Vitamin A analog that inhibits cell proliferation and induces cell differentiation. It is converted in vivo into all-trans retinoic acid and has diverse biological activities. Anti-inflammatory agent used for severe acne treatment. Inhibits proliferation of primary human sebocytes by inducing cell-cycle arrest and inhibiting DNA synthesis. Amplifies production of neutrophil gelatinase-associated lipocalin (NGAL) in the skin, which has been shown to reduce sebum production by inducing apoptosis in sebaceous gland cells, while exhibiting an antimicrobial effect on Propionibacterium acnes. Decreases the size and sebum output of the sebaceous glands. It also decreases triglyceride, stearyl ester and free fatty acid synthesis and modulates keratin expression in primary human sebocyte. Isotretinoin produces significant anti-inflammatory effects by inhibition of monocyte and neutrophil chemotaxis across intact biological barriers in vivo. Shown to have anti-tumor activity, mediated through RAR-beta and RAR-alpha receptors (low affinity). Induces mitochondrial membrane permeability transition, observed as swelling and as a decrease in membrane potential and stimulates the release of cytochrome c implicating mechanisms through the apoptosis pathway. Induces apoptosis in various cells. Cell death may be induced in the meibomian glands, hypothalamic cells, hippocampus cells and in sebaceous gland cells (important for acne treatment). Downregulated telomerase and hTERT, inhibiting cellular immortalization and tumorigenesis. Inhibits the action of the metalloprotease MMP-9 (gelatinase) in sebum without any influence in the action of TIMP1 and TIMP2 (the tissue inhibitors of metalloproteases). Promotes neurite outgrowth, cell differentiation and inhibits proliferation in a neuroblastoma cell line. Shown to have neurological effects, by binding to dopaminergic receptors in the central nervous system that may affect dopaminergic neurotransmission by disrupting the structure of dopamine receptors and decreasing dopaminergic activity. Also affects the serotonergic system by increasing expression of 5-HT1A receptors in the pre-synaptic neuron, which inhibit serotonin secretion. Additional effects on CNS involve the modulation of the retinoic acid function in the hypothalamus, the hormone regulatory centre of the brain and part of the hypothalamus-pituitary-adrenal axis, a key part of the bodys stress response. Inducer of resistin-like molecule alpha (RELM-alpha) expression in epidermis, regulating skin immunity. The function of RELM-alpha is to kill bacteria of the skin via membrane disruption.
- SMILESCC1=C(/C=C/C(C)=C/C=C/C(C)=C\C(O)=O)C(C)(C)CCC1
- Storage Instruction-20°C,2°C to 8°C
- UNSPSC12352200
