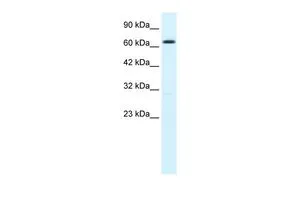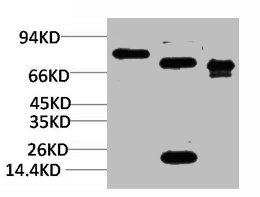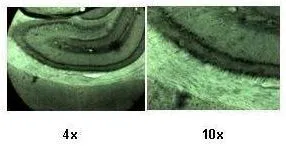
IHC-P analysis of rat brain tissue using GTX49068 KCa2.2 antibody at 1:500.
KCNN2 antibody, C-term
GTX49068
ApplicationsWestern Blot, ImmunoHistoChemistry, ImmunoHistoChemistry Paraffin
Product group Antibodies
ReactivityHuman, Monkey, Rat
TargetKCNN2
Overview
- SupplierGeneTex
- Product NameKCNN2 antibody, C-term
- Delivery Days Customer9
- Application Supplier NoteWB: 0.2-2.5 ug/ml. IHC-P: 2-10 ug/ml. *Optimal dilutions/concentrations should be determined by the researcher.Not tested in other applications.
- ApplicationsWestern Blot, ImmunoHistoChemistry, ImmunoHistoChemistry Paraffin
- CertificationResearch Use Only
- ClonalityPolyclonal
- Concentration0.5-1 mg/ml
- ConjugateUnconjugated
- Gene ID3781
- Target nameKCNN2
- Target descriptionpotassium calcium-activated channel subfamily N member 2
- Target synonymsDYT34, KCa2.2, NEDMAB, SK2, SKCA2, SKCa 2, hSK2, small conductance calcium-activated potassium channel protein 2, apamin-sensitive small-conductance Ca2+-activated potassium channel, potassium channel, calcium activated intermediate/small conductance subfamily N alpha, member 2, potassium intermediate/small conductance calcium-activated channel, subfamily N, member 2, small conductance calcium-activated potassium channel 2
- HostRabbit
- IsotypeIgG
- Protein IDQ9H2S1
- Protein NameSmall conductance calcium-activated potassium channel protein 2
- Scientific DescriptionAction potentials in vertebrate neurons are followed by an afterhyperpolarization (AHP) that may persist for several seconds and may have profound consequences for the firing pattern of the neuron. Each component of the AHP is kinetically distinct and is mediated by different calcium-activated potassium channels. The protein encoded by this gene is activated before membrane hyperpolarization and is thought to regulate neuronal excitability by contributing to the slow component of synaptic AHP. This gene is a member of the KCNN family of potassium channel genes. The encoded protein is an integral membrane protein that forms a voltage-independent calcium-activated channel with three other calmodulin-binding subunits. Alternate splicing of this gene results in multiple transcript variants. [provided by RefSeq, May 2013]
- ReactivityHuman, Monkey, Rat
- Storage Instruction-20°C or -80°C,2°C to 8°C
- UNSPSC41116161