Chemical Structure
Kdo2-Lipid A (ready-to-use) [123621-04-5]

AG-CU1-0001
Overview
- SupplierAdipoGen Life Sciences
- Product NameKdo2-Lipid A (ready-to-use) [123621-04-5]
- Delivery Days Customer10
- CAS Number123621-04-5
- CertificationResearch Use Only
- Concentration0.5 mg/ml
- FormulationLiquid
- Hazard InformationWarning
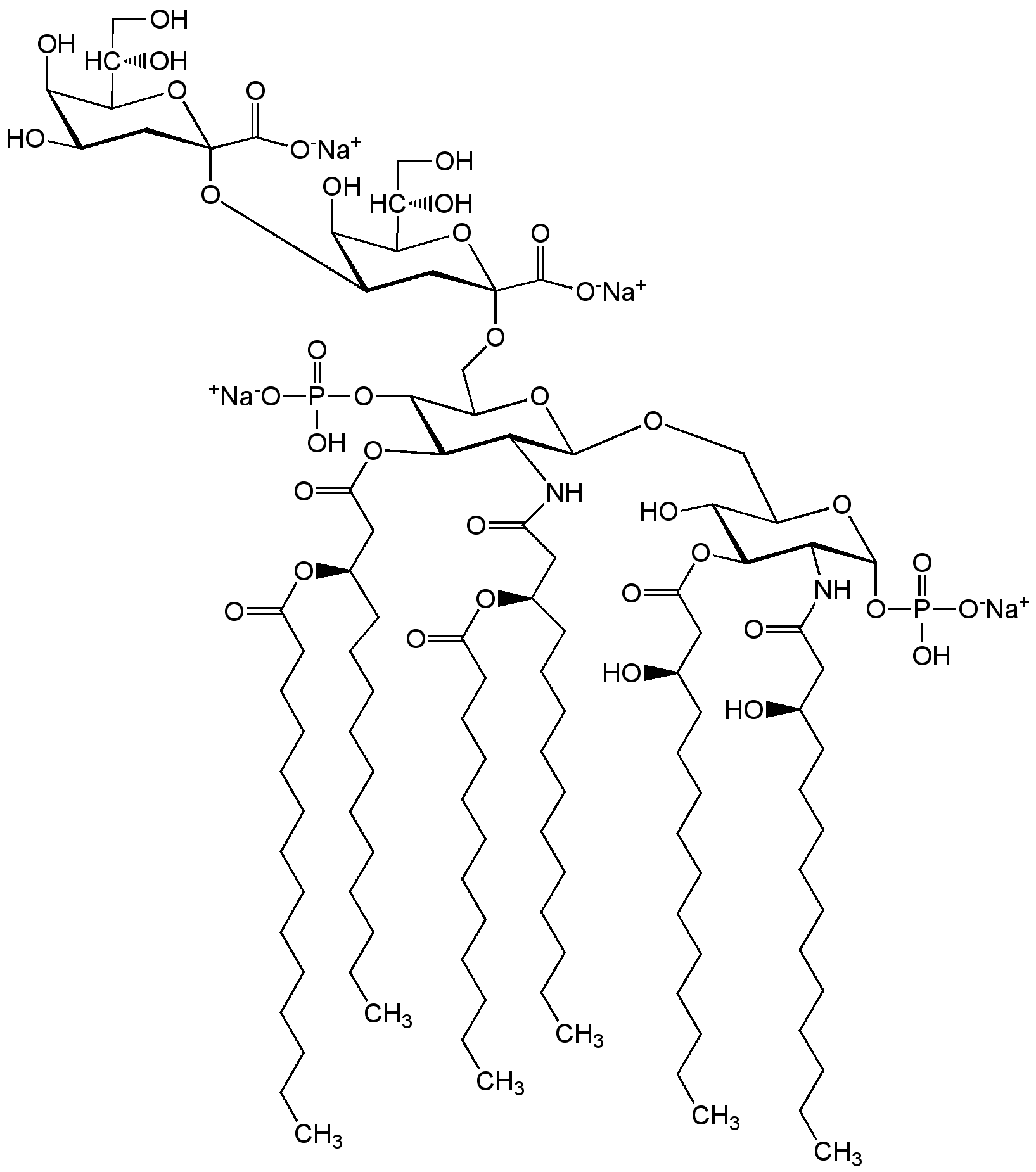
- Molecular FormulaC110H198N2Na4O39P2
- Molecular Weight2326.7
- Scientific DescriptionChemical. CAS: 123621-04-5 (free base). Formula: C110H198N2Na4O39P2. MW: 2326.7. Isolated and purified from E. coli K12 heptose-deficient strain WBB06 (Re mutant). Defined substructure of the Re mutant of lipopolysaccharide (LPS). Endotoxin activity equal to Re LPS. Strong activator (<10ng/ml) of macrophages via toll-like receptor 4 (TLR4). Does not activate TLR2 or other TLRs as determined with splenocytes and macrophages from TLR4 deficient mice by IL-6 ELISA. Facilitates the structural analysis of its complexes with signaling receptors, such as TLR4/MD2 and CD14. Kdo2-Lipid A was used in a recent animal atherosclerosis model. Induces sphingolipid biosynthesis, which is essential for induction of autophagy. - Defined substructure of the Re mutant of lipopolysaccharide (LPS) [1]. Endotoxin activity equal to Re LPS [1]. Strong activator (<10ng/ml) of macrophages via toll-like receptor 4 (TLR4) [1, 2, 3, 4, 9]. Does not activate TLR2 [5] or other TLRs as determined with splenocytes and macrophages from TLR4 deficient mice by IL-6 ELISA [1,4]. Facilitates the structural analysis of its complexes with signaling receptors, such as TLR4/MD2 [1,2] and CD14 [7]. Kdo2-Lipid A was used in a recent animal atherosclerosis model [6]. Induces sphingolipid biosynthesis, which is essential for induction of autophagy [8].
- SMILES[Na+].[Na+].[Na+].[Na+].CCCCCCCCCCCCCC(=O)O[C@H](CCCCCCCCCCC)CC(=O)OC1[C@H](NC(=O)C[C@@H](CCCCCCCCCCC)OC(=O)CCCCCCCCCCC)[C@H](OCC2O[C@H](OP(O)([O-])=O)[C@@H](NC(=O)C[C@H](O)CCCCCCCCCCC)C(OC(=O)C[C@H](O)CCCCCCCCCCC)[C@@H]2O)OC(CO[C@@]2(CC(O[C@@]3(CC(O)[C@@H](O)C(O3)[C@@H](O)CO)C([O-])=O)[C@@H](O)C(O2)[C@@H](O)CO)C([O-])=O)[C@H]1OP(O)([O-])=O
- Storage Instruction2°C to 8°C
- UNSPSC12352200
References
- Kdo2-Lipid A of Escherichia coli, a defined endotoxin that activates macrophages via TLR-4: C.R. Raetz, et al.; J. Lipid Res. 47, 1097 (2006)
- Aggregation behavior of an ultra-pure lipopolysaccharide that stimulates TLR-4 receptors: H. Sasaki & S.H. White; Biophys. J. 95, 986 (2008)
- TLR-4 mediated group IVA phospholipase A(2) activation is phosphatidic acid phosphohydrolase 1 and protein kinase C dependent: A. Grkovich, et al.; BBA 1791, 975 (2009)
- Subcellular organelle lipidomics in TLR 4-activated macrophages: A.Y. Andreyev, et al.; J. Lipid Res. 51, 2785(2010)
- Spinal glial TLR4-mediated nociception and production of prostaglandin E and TNF: O. Saito, et al.; Br. J. Pharmacol. 160, 1754 (2010)
- Low doses of lipopolysaccharide and minimally oxidized low-density lipoprotein cooperatively activate macrophages via nuclear factor kappab and activator protein-1- possible mechanism for acceleration of atherosclerosis by subclinical endotoxemia: P. Wiesner, et al.; Circ. Res. 107, 56 (2010)
- NMR spectral mapping of Lipid A molecular patterns affected by interaction with the innate immune receptor CD14: S. Albright, et al.; BBRC 378, 721 (2009)
- Kdo2-lipid A, a TLR4-specific agonist, induces de novo sphingolipid biosynthesis in RAW264.7 macrophages, which is essential for induction of autophagy: K. Sims, et al.; J. Biol. Chem. 285, 28568 (2010)
- ATF3 plays a key role in Kdo2-lipid A-induced TLR4-dependent gene expression via NF-?B activation: E.Y. Kim, et al.; PLoS One 5, e14181 (2010)
