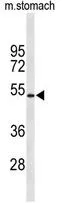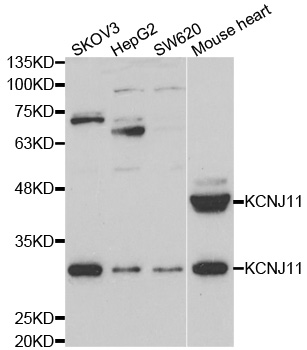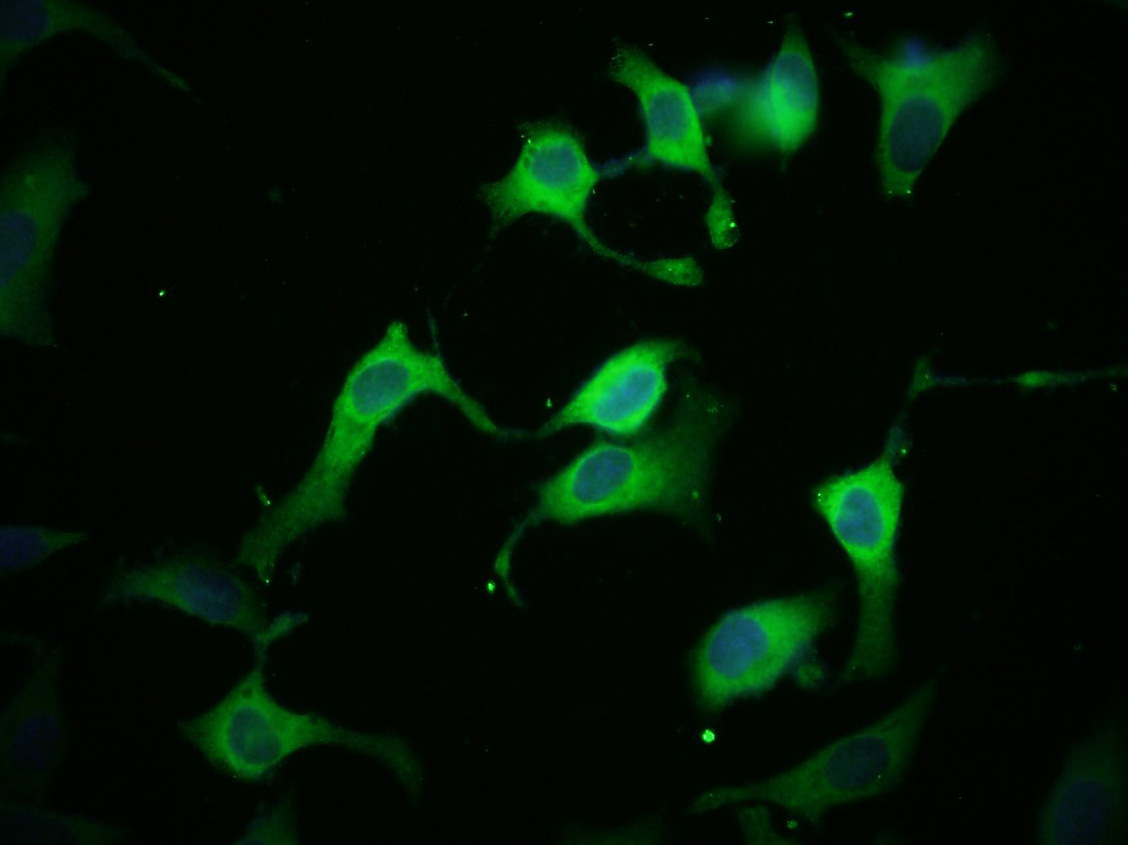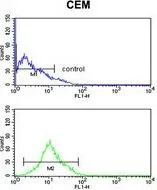
FACS analysis of CEM cells using GTX80493 Kir6.2 antibody, N-term. Top histogram : negative control Bottom histogram : CEM cells
Kir6.2 antibody, N-term
GTX80493
ApplicationsFlow Cytometry, Western Blot, ImmunoHistoChemistry, ImmunoHistoChemistry Frozen
Product group Antibodies
ReactivityHuman, Mouse
TargetKCNJ11
Overview
- SupplierGeneTex
- Product NameKir6.2 antibody, N-term
- Delivery Days Customer9
- Application Supplier NoteWB: 1:1000. FCM: 1:10-1:50. *Optimal dilutions/concentrations should be determined by the researcher.Not tested in other applications.
- ApplicationsFlow Cytometry, Western Blot, ImmunoHistoChemistry, ImmunoHistoChemistry Frozen
- CertificationResearch Use Only
- ClonalityPolyclonal
- ConjugateUnconjugated
- Gene ID3767
- Target nameKCNJ11
- Target descriptionpotassium inwardly rectifying channel subfamily J member 11
- Target synonymsBIR, HHF2, IKATP, KIR6.2, MODY13, PHHI, PNDM2, TNDM3, ATP-sensitive inward rectifier potassium channel 11, beta-cell inward rectifier subunit, inward rectifier K(+) channel Kir6.2, inwardly rectifing potassium channel subfamily J member 11, inwardly rectifying potassium channel KIR6.2, inwardly-rectifying potassium channel subfamily J member 11, potassium channel inwardly rectifing subfamily J member 11, potassium channel, inwardly rectifying subfamily J member 11, potassium voltage-gated channel subfamily J member 11
- HostRabbit
- IsotypeIgG
- Protein IDQ14654
- Protein NameATP-sensitive inward rectifier potassium channel 11
- Scientific DescriptionPotassium channels are present in most mammalian cells, where they participate in a wide range of physiologic responses. The protein encoded by this gene is an integral membrane protein and inward-rectifier type potassium channel. The encoded protein, which has a greater tendency to allow potassium to flow into a cell rather than out of a cell, is controlled by G-proteins and is found associated with the sulfonylurea receptor SUR. Mutations in this gene are a cause of familial persistent hyperinsulinemic hypoglycemia of infancy (PHHI), an autosomal recessive disorder characterized by unregulated insulin secretion. Defects in this gene may also contribute to autosomal dominant non-insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus type II (NIDDM), transient neonatal diabetes mellitus type 3 (TNDM3), and permanent neonatal diabetes mellitus (PNDM). Multiple alternatively spliced transcript variants that encode different protein isoforms have been described for this gene. [provided by RefSeq, Oct 2009]
- ReactivityHuman, Mouse
- Storage Instruction-20°C or -80°C,2°C to 8°C
- UNSPSC41116161
References
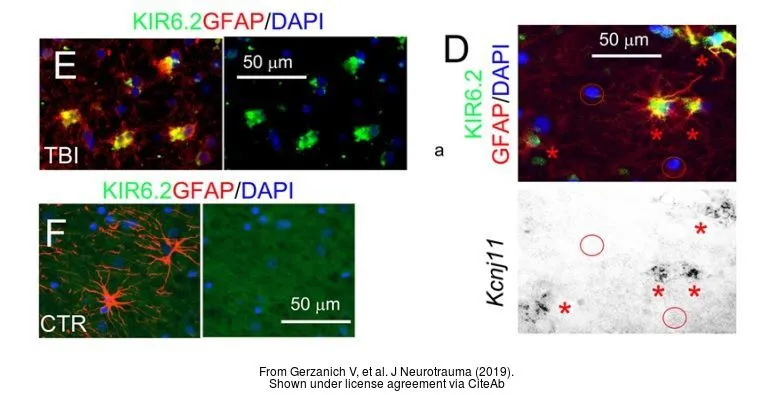
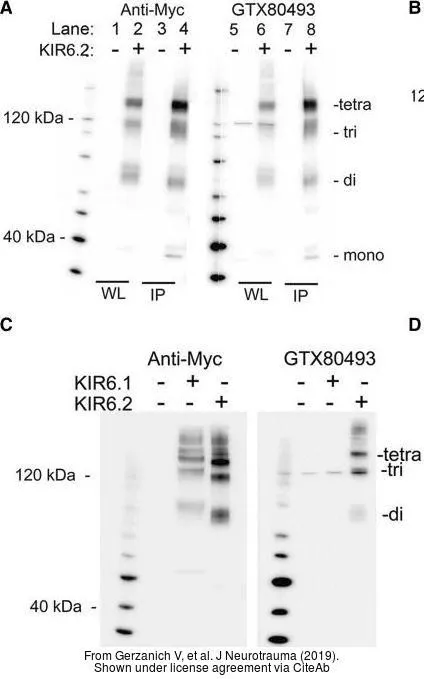
- Sulfonylurea Receptor 1, Transient Receptor Potential Cation Channel Subfamily M Member 4, and KIR6.2:Role in Hemorrhagic Progression of Contusion. Gerzanich V et al., 2019 Apr 1, J NeurotraumaRead this paper
- Kir6.2, the Pore-Forming Subunit of ATP-Sensitive K+ Channels, Is Overexpressed in Human Posttraumatic Brain Contusions. Castro L et al., 2018 Jul 24, J NeurotraumaRead this paper