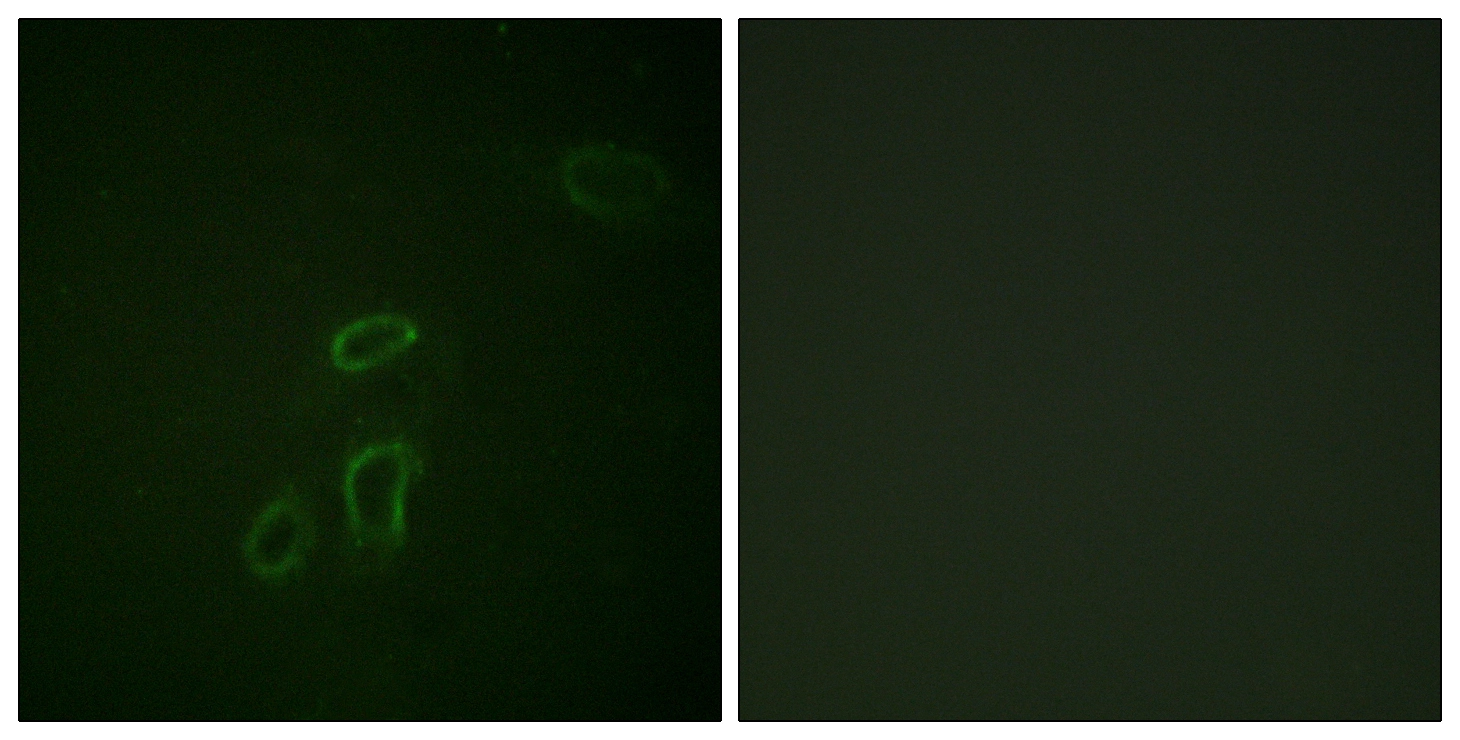
![GTX23200 at a dilution of 1/1000, staining L1CAM (green; Alexa 488 secondary at 1/2000) on 30m coronal rat brain tissue sections in free floating IHC. Images showing neuron body, cytoplasm and axon labeling: [A] neuron; 40x objective [B] neuron and axons; GTX23200 at a dilution of 1/1000, staining L1CAM (green; Alexa 488 secondary at 1/2000) on 30m coronal rat brain tissue sections in free floating IHC. Images showing neuron body, cytoplasm and axon labeling: [A] neuron; 40x objective [B] neuron and axons;](https://www.genetex.com/upload/website/prouct_img/normal/GTX23200/L1CAM-antibody-UJ127-GTX23200-IHC-1_w_23060620_589.webp)
GTX23200 at a dilution of 1/1000, staining L1CAM (green; Alexa 488 secondary at 1/2000) on 30m coronal rat brain tissue sections in free floating IHC. Images showing neuron body, cytoplasm and axon labeling: [A] neuron; 40x objective [B] neuron and axons;
L1CAM antibody [UJ127]
GTX23200
ApplicationsImmunoPrecipitation, Western Blot, ImmunoHistoChemistry, ImmunoHistoChemistry Paraffin
Product group Antibodies
TargetL1CAM
Overview
- SupplierGeneTex
- Product NameL1CAM antibody [UJ127]
- Delivery Days Customer9
- Application Supplier NoteImmunoprecipitation (natured and denatured): use at a concentration of 2microg / mg. Western Blotting: use at a concentration of 1 - 2microg / ml for 2hrs at RT. Immunohistochemistry (formalin fixed paraffin embedded): use at a concentration of 1 - 2microg / ml for 30 min at RT. Optimal dilutions/concentrations should be determined by the end user. By Western blot, this antibody detects a band of 220-240 kDa, which corresponds to the predicted molecular weight of L1CAM. Staining of formalin-fixed tissues requires boiling tissue sections in 10mM citrate buffer, pH 6.0, for 10-20 min followed by cooling at RT for 20 min.
- ApplicationsImmunoPrecipitation, Western Blot, ImmunoHistoChemistry, ImmunoHistoChemistry Paraffin
- CertificationResearch Use Only
- ClonalityMonoclonal
- Clone IDUJ127
- Concentration0.2 mg/ml
- ConjugateUnconjugated
- Gene ID3897
- Target nameL1CAM
- Target descriptionL1 cell adhesion molecule
- Target synonymsCAML1, CD171, HSAS, HSAS1, HYCX, MASA, MIC5, N-CAM-L1, N-CAML1, NCAM-L1, S10, SPG1, neural cell adhesion molecule L1, antigen identified by monoclonal antibody R1
- HostMouse
- IsotypeIgG1
- Protein IDP32004
- Protein NameNeural cell adhesion molecule L1
- Scientific DescriptionThe protein encoded by this gene is an axonal glycoprotein belonging to the immunoglobulin supergene family. The ectodomain, consisting of several immunoglobulin-like domains and fibronectin-like repeats (type III), is linked via a single transmembrane sequence to a conserved cytoplasmic domain. This cell adhesion molecule plays an important role in nervous system development, including neuronal migration and differentiation. Mutations in the gene cause X-linked neurological syndromes known as CRASH (corpus callosum hypoplasia, retardation, aphasia, spastic paraplegia and hydrocephalus). Alternative splicing of this gene results in multiple transcript variants, some of which include an alternate exon that is considered to be specific to neurons. [provided by RefSeq, May 2013]
- Storage Instruction2°C to 8°C
- UNSPSC12352203
References
- L1 stimulation of human glioma cell motility correlates with FAK activation. Yang M et al., 2011 Oct, J NeurooncolRead more
- Elevated invasive potential of glioblastoma stem cells. Cheng L et al., 2011 Mar 25, Biochem Biophys Res CommunRead more
- L1CAM regulates DNA damage checkpoint response of glioblastoma stem cells through NBS1. Cheng L et al., 2011 Mar 2, EMBO JRead more
- Soluble L1CAM promotes breast cancer cell adhesion and migration in vitro, but not invasion. Li Y et al., 2010 Sep 15, Cancer Cell IntRead more
- Stimulation of glioma cell motility by expression, proteolysis, and release of the L1 neural cell recognition molecule. Yang M et al., 2009 Oct 29, Cancer Cell IntRead more
- Targeting cancer stem cells through L1CAM suppresses glioma growth. Bao S et al., 2008 Aug 1, Cancer ResRead more


![FACS analysis of HEK293T cells transfected with either L1CAM plasmid(Red) or empty vector control plasmid(Blue) using GTX84232 L1CAM antibody [2G9].](https://www.genetex.com/upload/website/prouct_img/normal/GTX84232/GTX84232_330_FACS_w_23061420_550.webp)
![FACS analysis of Jurkat cells using GTX84236 L1CAM antibody [1A8]. Red : Primary antibody Blue : Negative control antibody](https://www.genetex.com/upload/website/prouct_img/normal/GTX84236/GTX84236_331_FACS_w_23061420_979.webp)
![IHC-P analysis of human liver tissue using GTX84241 L1CAM antibody [2C7]. Antigen retrieval : Heat-induced epitope retrieval by 10mM citrate buffer, pH6.0, 100oC for 10min.](https://www.genetex.com/upload/website/prouct_img/normal/GTX84241/GTX84241_2483_IHC-P_w_23061420_574.webp)
![FACS analysis of HEK293T cells transfected with either L1CAM plasmid(Red) or empty vector control plasmid(Blue) using GTX84244 L1CAM antibody [1H3].](https://www.genetex.com/upload/website/prouct_img/normal/GTX84244/GTX84244_335_FACS_w_23061420_966.webp)
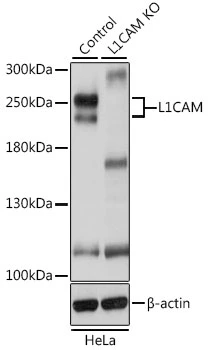
![WB analysis of G361 cells using GTX40148 L1CAM antibody [UJ127.11]. Dilution : 0.5 microg/mL(Lane 1) and 0.25 microg/mL(Lane 2)](https://www.genetex.com/upload/website/prouct_img/normal/GTX40148/GTX40148_WB_20210302_w_23060820_416.webp)