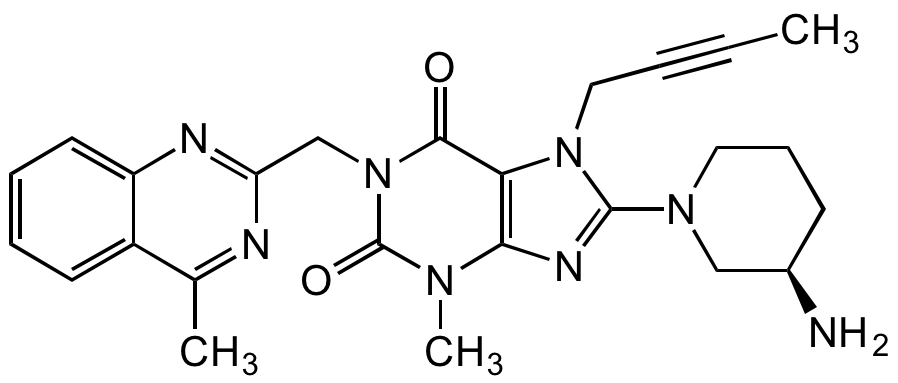
Chemical Structure
Linagliptin
AG-CR1-3618
CAS Number668270-12-0
Product group Chemicals
Estimated Purity>98%
Molecular Weight472.5
Overview
- SupplierAdipoGen Life Sciences
- Product NameLinagliptin
- Delivery Days Customer10
- CAS Number668270-12-0
- CertificationResearch Use Only
- Estimated Purity>98%
- Hazard InformationWarning
- Molecular FormulaC25H28N8O2
- Molecular Weight472.5
- Scientific DescriptionAntidiabetic agent. Highly potent and selective competitive inhibitor of dipeptidyl-peptidase 4 (DPP4; DPP IV; CD26), an enzyme that degrades, glucagon-like peptide-1 (GLP-1) and glucose-dependent insulinotropic polypeptide (GIP). Prevents the inactivation of endogenous GLP-1 and GIP. Shown to restore beta cell function and survival in human isolated islets through GLP-1 stabilization. Improves insulin sensitivity. Anti-inflammatory compound. DPP4 is a cell surface aminopeptidase that exerts diverse biological activities, such as protease activity, association with adenosine deaminase, interaction with the extracellular matrix, regulation of intracellular signal transduction coupled with the control of cell migration and proliferation, and in addition cell surface co-receptor activity mediating viral entry. DPP4 is a viral receptor of human coronaviruses and therefore is investigated as a potential target for SARS-CoV-2 infections. - Chemical. CAS: 668270-12-0. Formula: C25H28N8O2. MW: 472.5. Antidiabetic agent. Highly potent and selective competitive inhibitor of dipeptidyl-peptidase 4 (DPP4; DPP IV; CD26), an enzyme that degrades, glucagon-like peptide-1 (GLP-1) and glucose-dependent insulinotropic polypeptide (GIP). Prevents the inactivation of endogenous GLP-1 and GIP. Shown to restore beta cell function and survival in human isolated islets through GLP-1 stabilization. Improves insulin sensitivity. Anti-inflammatory compound.
- SMILESCC#CCN1C(=NC2=C1C(=O)N(CC1=NC3=CC=CC=C3C(C)=N1)C(=O)N2C)N1CCC[C@@H](N)C1
- Storage Instruction-20°C,2°C to 8°C
- UNSPSC12352200

![Linagliptin [668270-12-0]](https://www.targetmol.com/group3/M00/02/D1/CgoaEGY7Ps-ERjL1AAAAAMbFNTE785.png)
