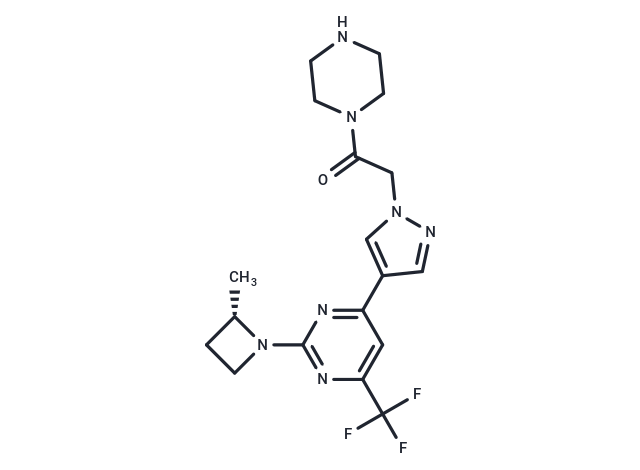
KHK-IN-3 (Example 1), a ketohexokinase (KHK) inhibitor, plays a crucial role in the study of various diseases including kidney disease, nonalcoholic steatohepatitis (NASH), diabetes, and heart failure. KHK, a pivotal rate-limiting enzyme and fructokinase, facilitates the metabolism of fructose by catalyzing the transformation of fructose into fructose-1-phosphate (FIP) utilizing ATP. This process lacks feedback inhibition, leading to the buildup of metabolites involved in lipogenesis, gluconeogenesis, and oxidative phosphorylation [1].